init
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
name: Issue template
|
||||
about: Issue template for code error.
|
||||
title: ''
|
||||
labels: ''
|
||||
assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
请提供下述完整信息以便快速定位问题/Please provide the following information to quickly locate the problem
|
||||
|
||||
- 系统环境/System Environment:
|
||||
- 版本号/Version:Paddle: PaddleOCR: 问题相关组件/Related components:
|
||||
- 运行指令/Command Code:
|
||||
- 完整报错/Complete Error Message:
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
name: New Feature Issue template
|
||||
about: Issue template for new features.
|
||||
title: ''
|
||||
labels: 'Code PR is needed'
|
||||
assignees: 'shiyutang'
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 背景
|
||||
|
||||
经过需求征集https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/10334 和每周技术研讨会 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/10223 讨论,我们确定了XXXX任务。
|
||||
|
||||
## 解决步骤
|
||||
1. 根据开源代码进行网络结构、评估指标转换。代码链接:XXXX
|
||||
2. 结合[论文复现指南](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models/blob/release%2F2.2/tutorials/article-implementation/ArticleReproduction_CV.md),进行前反向对齐等操作,达到论文Table.1中的指标。
|
||||
3. 参考[PR提交规范](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6/doc/doc_ch/code_and_doc.md)提交代码PR到ppocr中。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
|||
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
.ipynb_checkpoints/
|
||||
*.py[cod]
|
||||
*$py.class
|
||||
|
||||
# C extensions
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
|
||||
inference/
|
||||
inference_results/
|
||||
output/
|
||||
train_data/
|
||||
log/
|
||||
*.DS_Store
|
||||
*.vs
|
||||
*.user
|
||||
*~
|
||||
*.vscode
|
||||
*.idea
|
||||
|
||||
*.log
|
||||
.clang-format
|
||||
.clang_format.hook
|
||||
|
||||
build/
|
||||
dist/
|
||||
paddleocr.egg-info/
|
||||
/deploy/android_demo/app/OpenCV/
|
||||
/deploy/android_demo/app/PaddleLite/
|
||||
/deploy/android_demo/app/.cxx/
|
||||
/deploy/android_demo/app/cache/
|
||||
test_tipc/web/models/
|
||||
test_tipc/web/node_modules/
|
||||
/PPOCRLabel/
|
||||
/doc/
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|||
- repo: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/mirrors-yapf.git
|
||||
sha: 0d79c0c469bab64f7229c9aca2b1186ef47f0e37
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: yapf
|
||||
files: \.py$
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
|
||||
sha: a11d9314b22d8f8c7556443875b731ef05965464
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: check-merge-conflict
|
||||
- id: check-symlinks
|
||||
- id: detect-private-key
|
||||
files: (?!.*paddle)^.*$
|
||||
- id: end-of-file-fixer
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- id: trailing-whitespace
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/Lucas-C/pre-commit-hooks
|
||||
sha: v1.0.1
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: forbid-crlf
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- id: remove-crlf
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- id: forbid-tabs
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- id: remove-tabs
|
||||
files: \.md$
|
||||
- repo: local
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: clang-format
|
||||
name: clang-format
|
||||
description: Format files with ClangFormat
|
||||
entry: bash .clang_format.hook -i
|
||||
language: system
|
||||
files: \.(c|cc|cxx|cpp|cu|h|hpp|hxx|cuh|proto)$
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
|||
[style]
|
||||
based_on_style = pep8
|
||||
column_limit = 80
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
|
||||
|
||||
Apache License
|
||||
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
||||
|
||||
1. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
||||
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
||||
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
||||
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
||||
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
||||
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
||||
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
||||
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
||||
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
||||
|
||||
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
||||
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
||||
source, and configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
||||
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
||||
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
||||
and conversions to other media types.
|
||||
|
||||
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
||||
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
||||
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
||||
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
||||
|
||||
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
||||
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
||||
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
||||
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
||||
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
||||
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
||||
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
||||
|
||||
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
||||
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
||||
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
||||
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
||||
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
||||
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
||||
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
||||
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
||||
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
||||
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
||||
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
||||
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
||||
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
||||
|
||||
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
||||
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
||||
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
||||
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
||||
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
||||
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
||||
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
||||
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
||||
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
||||
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
||||
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
||||
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
||||
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
||||
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
||||
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
||||
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
||||
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
||||
meet the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
||||
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
||||
|
||||
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
||||
stating that You changed the files; and
|
||||
|
||||
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
||||
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
||||
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
||||
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
||||
the Derivative Works; and
|
||||
|
||||
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
||||
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
||||
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
||||
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
||||
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
||||
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
||||
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
||||
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
||||
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
||||
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
||||
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
||||
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
||||
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
||||
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
||||
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
||||
as modifying the License.
|
||||
|
||||
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
||||
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
||||
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
||||
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
||||
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
||||
the conditions stated in this License.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
||||
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
||||
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
||||
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
||||
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
||||
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
||||
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
||||
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
||||
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
||||
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
||||
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
||||
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
||||
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
||||
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
||||
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
||||
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
||||
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
||||
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
||||
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
||||
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
||||
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
||||
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
||||
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
||||
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
||||
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
||||
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
||||
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
||||
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
||||
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
||||
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
||||
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
||||
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
||||
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
||||
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
||||
|
||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
||||
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
|
||||
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
||||
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
||||
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
||||
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
||||
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
||||
identification within third-party archives.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2016 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
include LICENSE
|
||||
include README.md
|
||||
|
||||
recursive-include ppocr/utils *.*
|
||||
recursive-include ppocr/data *.py
|
||||
recursive-include ppocr/postprocess *.py
|
||||
recursive-include tools/infer *.py
|
||||
recursive-include tools __init__.py
|
||||
recursive-include ppocr/utils/e2e_utils *.py
|
||||
recursive-include ppstructure *.py
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,260 @@
|
|||
[English](README_en.md) | 简体中文 | [हिन्दी](./doc/doc_i18n/README_हिन्द.md) | [日本語](./doc/doc_i18n/README_日本語.md) | [한국인](./doc/doc_i18n/README_한국어.md) | [Pу́сский язы́к](./doc/doc_i18n/README_Ру́сский_язы́к.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/PaddleOCR_log.png" align="middle" width = "600"/>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<p align="left">
|
||||
<a href="./LICENSE"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/license-Apache%202-dfd.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ffa"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/python-3.7+-aff.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/os-linux%2C%20win%2C%20mac-pink.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/format/PaddleOCR?color=c77"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/PaddleOCR/"><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/PaddleOCR?color=9cf"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/stargazers"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ccf"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR旨在打造一套丰富、领先、且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型,并应用落地。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0/test_add_91.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0/00006737.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📣 近期更新
|
||||
- **🔥2023.8.7 发布 PaddleOCR [release/2.7](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.7)**
|
||||
- 发布[PP-OCRv4](./doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv4_introduction.md),提供mobile和server两种模型
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4-mobile:速度可比情况下,中文场景效果相比于PP-OCRv3再提升4.5%,英文场景提升10%,80语种多语言模型平均识别准确率提升8%以上
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4-server:发布了目前精度最高的OCR模型,中英文场景上检测模型精度提升4.9%, 识别模型精度提升2%
|
||||
可参考[快速开始](./doc/doc_ch/quickstart.md) 一行命令快速使用,同时也可在飞桨AI套件(PaddleX)中的[通用OCR产业方案](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=286)中低代码完成模型训练、推理、高性能部署全流程
|
||||
- 发布[PP-ChatOCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=332) ,使用融合PP-OCR模型和文心大模型的通用场景关键信息抽取全新方案
|
||||
- 🔨**2022.11 新增实现[4种前沿算法](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)**:文本检测 [DRRG](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_det_drrg.md), 文本识别 [RFL](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_rfl.md), 文本超分[Text Telescope](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_sr_telescope.md),公式识别[CAN](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_can.md)
|
||||
- **2022.10 优化[JS版PP-OCRv3模型](./deploy/paddlejs/README_ch.md)**:模型大小仅4.3M,预测速度提升8倍,配套web demo开箱即用
|
||||
- **💥 直播回放:PaddleOCR研发团队详解PP-StructureV2优化策略**。微信扫描[下方二维码](#开源社区),关注公众号并填写问卷后进入官方交流群,获取直播回放链接与20G重磅OCR学习大礼包(内含PDF转Word应用程序、10种垂类模型、《动手学OCR》电子书等)
|
||||
- **🔥2022.8.24 发布 PaddleOCR [release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.6)**
|
||||
- 发布[PP-StructureV2](./ppstructure/README_ch.md),系统功能性能全面升级,适配中文场景,新增支持[版面复原](./ppstructure/recovery/README_ch.md),支持**一行命令完成PDF转Word**;
|
||||
- [版面分析](./ppstructure/layout/README_ch.md)模型优化:模型存储减少95%,速度提升11倍,平均CPU耗时仅需41ms;
|
||||
- [表格识别](./ppstructure/table/README_ch.md)模型优化:设计3大优化策略,预测耗时不变情况下,模型精度提升6%;
|
||||
- [关键信息抽取](./ppstructure/kie/README_ch.md)模型优化:设计视觉无关模型结构,语义实体识别精度提升2.8%,关系抽取精度提升9.1%。
|
||||
- 🔥**2022.8 发布 [OCR场景应用集合](./applications)**:包含数码管、液晶屏、车牌、高精度SVTR模型、手写体识别等**9个垂类模型**,覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用。
|
||||
|
||||
> [更多](./doc/doc_ch/update.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🌟 特性
|
||||
|
||||
支持多种OCR相关前沿算法,在此基础上打造产业级特色模型[PP-OCR](./doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md)、[PP-Structure](./ppstructure/README_ch.md)和[PP-ChatOCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6488689),并打通数据生产、模型训练、压缩、预测部署全流程。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tink2123/test/master/ppocrv4.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
> 上述内容的使用方法建议从文档教程中的快速开始体验
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ⚡ 快速开始
|
||||
|
||||
- 在线网站体验:
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4 在线体验地址:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6611435
|
||||
- PP-ChatOCR 在线体验地址:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6488689
|
||||
- 一行命令快速使用:[快速开始(中英文/多语言/文档分析)](./doc/doc_ch/quickstart.md)
|
||||
- 飞桨AI套件(PaddleX)中训练、推理、高性能部署全流程体验:
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=286
|
||||
- PP-ChatOCR:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=332
|
||||
- 移动端demo体验:[安装包DEMO下载地址](https://ai.baidu.com/easyedge/app/openSource?from=paddlelite)(基于EasyEdge和Paddle-Lite, 支持iOS和Android系统)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="技术交流合作"></a>
|
||||
## 📖 技术交流合作
|
||||
- 飞桨AI套件([PaddleX](http://10.136.157.23:8080/paddle/paddleX))提供了飞桨模型训压推一站式全流程高效率开发平台,其使命是助力AI技术快速落地,愿景是使人人成为AI Developer!
|
||||
- PaddleX 目前覆盖图像分类、目标检测、图像分割、3D、OCR和时序预测等领域方向,已内置了36种基础单模型,例如RT-DETR、PP-YOLOE、PP-HGNet、PP-LCNet、PP-LiteSeg等;集成了12种实用的产业方案,例如PP-OCRv4、PP-ChatOCR、PP-ShiTu、PP-TS、车载路面垃圾检测、野生动物违禁制品识别等。
|
||||
- PaddleX 提供了“工具箱”和“开发者”两种AI开发模式。工具箱模式可以无代码调优关键超参,开发者模式可以低代码进行单模型训压推和多模型串联推理,同时支持云端和本地端。
|
||||
- PaddleX 还支持联创开发,利润分成!目前 PaddleX 正在快速迭代,欢迎广大的个人开发者和企业开发者参与进来,共创繁荣的 AI 技术生态!
|
||||
|
||||
微信扫描下面二维码添加运营同学,并回复【paddlex】,运营同学会邀请您加入官方交流群,获得更高效的问题答疑。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/dygraph/doc/joinus_paddlex.jpg" width = "150" height = "150",caption='' />
|
||||
<p>飞桨AI套件【PaddleX】技术交流群二维码</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="电子书"></a>
|
||||
## 📚《动手学OCR》电子书
|
||||
- [《动手学OCR》电子书](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="开源共建"></a>
|
||||
## 🚀 开源共建
|
||||
- **👫 加入社区**:感谢大家长久以来对 PaddleOCR 的支持和关注,与广大开发者共同构建一个专业、和谐、相互帮助的开源社区是 PaddleOCR 的目标。我们非常欢迎各位开发者参与到飞桨社区的开源建设中,加入开源、共建飞桨。**为感谢社区开发者在 PaddleOCR release2.7 中做出的代码贡献,我们将为贡献者制作与邮寄[开源贡献证书](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/community/blob/master/contributors/certificate-inspection.md),烦请[填写问卷](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vm/wFNr6w7.aspx)提供必要的邮寄信息。**
|
||||
- **🤩 社区活动**:飞桨开源社区长期运营与发布各类丰富的活动与开发任务,在 PaddleOCR 社区,你可以关注以下社区活动,并选择自己感兴趣的内容参与开源共建:
|
||||
- **🎁 飞桨套件快乐开源常规赛 | [传送门](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/10223)**:OCR 社区常规赛升级版,以建设更好用的 OCR 套件为目标,包括但不限于学术前沿模型训练与推理、打磨优化 OCR 工具与应用项目开发等,任何有利于社区意见流动和问题解决的行为都热切希望大家的参与。让我们共同成长为飞桨套件的重要 Contributor 🎉🎉🎉。
|
||||
- **💡 新需求征集 | [传送门](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/10334)**:你在日常研究和实践深度学习过程中,有哪些你期望的 feature 亟待实现?请按照格式描述你想实现的 feature 和你提出的初步实现思路,我们会定期沟通与讨论这些需求,并将其纳入未来的版本规划中。
|
||||
- **💬 PP-SIG 技术研讨会 | [传送门](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/community/tree/master/ppsigs)**:PP-SIG 是飞桨社区开发者由于相同的兴趣汇聚在一起形成的虚拟组织,通过定期召开技术研讨会的方式,分享行业前沿动态、探讨社区需求与技术开发细节、发起社区联合贡献任务。PaddleOCR 希望可以通过 AI 的力量助力任何一位有梦想的开发者实现自己的想法,享受创造价值带来的愉悦。
|
||||
- **📑 项目合作**:如果你有企业中明确的 OCR 垂类应用需求,我们推荐你使用训压推一站式全流程高效率开发平台 PaddleX,助力 AI 技术快速落地。PaddleX 还支持联创开发,利润分成!欢迎广大的个人开发者和企业开发者参与进来,共创繁荣的 AI 技术生态!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="模型下载"></a>
|
||||
## 🛠️ PP-OCR系列模型列表(更新中)
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型简介 | 模型名称 | 推荐场景 | 检测模型 | 方向分类器 | 识别模型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv4模型(15.8M) | ch_PP-OCRv4_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(13.4M) | en_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
- 超轻量OCR系列更多模型下载(包括多语言),可以参考[PP-OCR系列模型下载](./doc/doc_ch/models_list.md),文档分析相关模型参考[PP-Structure系列模型下载](./ppstructure/docs/models_list.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### PaddleOCR场景应用模型
|
||||
|
||||
| 行业 | 类别 | 亮点 | 文档说明 | 模型下载 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------ | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 制造 | 数码管识别 | 数码管数据合成、漏识别调优 | [光功率计数码管字符识别](./applications/光功率计数码管字符识别/光功率计数码管字符识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
| 金融 | 通用表单识别 | 多模态通用表单结构化提取 | [多模态表单识别](./applications/多模态表单识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
| 交通 | 车牌识别 | 多角度图像处理、轻量模型、端侧部署 | [轻量级车牌识别](./applications/轻量级车牌识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用模型(如电表、液晶屏、高精度SVTR模型等),可参考[场景应用模型下载](./applications)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="文档教程"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📖 文档教程
|
||||
|
||||
- [运行环境准备](./doc/doc_ch/environment.md)
|
||||
- [PP-OCR文本检测识别🔥](./doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md)
|
||||
- [快速开始](./doc/doc_ch/quickstart.md)
|
||||
- [模型库](./doc/doc_ch/models_list.md)
|
||||
- [模型训练](./doc/doc_ch/training.md)
|
||||
- [文本检测](./doc/doc_ch/detection.md)
|
||||
- [文本识别](./doc/doc_ch/recognition.md)
|
||||
- [文本方向分类器](./doc/doc_ch/angle_class.md)
|
||||
- 模型压缩
|
||||
- [模型量化](./deploy/slim/quantization/README.md)
|
||||
- [模型裁剪](./deploy/slim/prune/README.md)
|
||||
- [知识蒸馏](./doc/doc_ch/knowledge_distillation.md)
|
||||
- [推理部署](./deploy/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [基于Python预测引擎推理](./doc/doc_ch/inference_ppocr.md)
|
||||
- [基于C++预测引擎推理](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
- [服务化部署](./deploy/pdserving/README_CN.md)
|
||||
- [端侧部署](./deploy/lite/readme.md)
|
||||
- [Paddle2ONNX模型转化与预测](./deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md)
|
||||
- [云上飞桨部署工具](./deploy/paddlecloud/README.md)
|
||||
- [Benchmark](./doc/doc_ch/benchmark.md)
|
||||
- [PP-Structure文档分析🔥](./ppstructure/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [快速开始](./ppstructure/docs/quickstart.md)
|
||||
- [模型库](./ppstructure/docs/models_list.md)
|
||||
- [模型训练](./doc/doc_ch/training.md)
|
||||
- [版面分析](./ppstructure/layout/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别](./ppstructure/table/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息提取](./ppstructure/kie/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [推理部署](./deploy/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [基于Python预测引擎推理](./ppstructure/docs/inference.md)
|
||||
- [基于C++预测引擎推理](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
- [服务化部署](./deploy/hubserving/readme.md)
|
||||
- [前沿算法与模型🚀](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [文本检测算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [文本识别算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [端到端OCR算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息抽取算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [使用PaddleOCR架构添加新算法](./doc/doc_ch/add_new_algorithm.md)
|
||||
- [场景应用](./applications)
|
||||
- 数据标注与合成
|
||||
- [半自动标注工具PPOCRLabel](./PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [数据合成工具Style-Text](./StyleText/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [其它数据标注工具](./doc/doc_ch/data_annotation.md)
|
||||
- [其它数据合成工具](./doc/doc_ch/data_synthesis.md)
|
||||
- 数据集
|
||||
- [通用中英文OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/datasets.md)
|
||||
- [手写中文OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/handwritten_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [垂类多语言OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/vertical_and_multilingual_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [版面分析数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/layout_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/table_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息提取数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/kie_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [代码组织结构](./doc/doc_ch/tree.md)
|
||||
- [效果展示](#效果展示)
|
||||
- [《动手学OCR》电子书📚](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md)
|
||||
- [开源社区](#开源社区)
|
||||
- FAQ
|
||||
- [通用问题](./doc/doc_ch/FAQ.md)
|
||||
- [PaddleOCR实战问题](./doc/doc_ch/FAQ.md)
|
||||
- [参考文献](./doc/doc_ch/reference.md)
|
||||
- [许可证书](#许可证书)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="效果展示"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 👀 效果展示 [more](./doc/doc_ch/visualization.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 中文模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic001.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic002.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic003.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 英文模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_1.png" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_2.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 多语言模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/japan_2.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/korean_1.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-Structure 文档分析</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
- 版面分析+表格识别
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./ppstructure/docs/table/ppstructure.GIF" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- SER(语义实体识别)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185310636-6ce02f7c-790d-479f-b163-ea97a5a04808.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185539517-ccf2372a-f026-4a7c-ad28-c741c770f60a.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/197464552-69de557f-edff-4c7f-acbf-069df1ba097f.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- RE(关系提取)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185540080-0431e006-9235-4b6d-b63d-0b3c6e1de48f.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25809855/186094813-3a8e16cc-42e5-4982-b9f4-0134dfb5688d.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="许可证书"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 许可证书
|
||||
本项目的发布受<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/master/LICENSE">Apache 2.0 license</a>许可认证。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,254 @@
|
|||
[English](README.md) | 简体中文 | [हिन्दी](./doc/doc_i18n/README_हिन्द.md) | [日本語](./doc/doc_i18n/README_日本語.md) | [한국인](./doc/doc_i18n/README_한국어.md) | [Pу́сский язы́к](./doc/doc_i18n/README_Ру́сский_язы́к.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/PaddleOCR_log.png" align="middle" width = "600"/>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<p align="left">
|
||||
<a href="./LICENSE"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/license-Apache%202-dfd.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ffa"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/python-3.7+-aff.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/os-linux%2C%20win%2C%20mac-pink.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/format/PaddleOCR?color=c77"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/PaddleOCR/"><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/PaddleOCR?color=9cf"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/stargazers"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ccf"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR旨在打造一套丰富、领先、且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型,并应用落地。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0/test_add_91.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0/00006737.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📣 近期更新
|
||||
|
||||
- **🔥2023.3.10 PaddleOCR集成了高性能、全场景模型部署方案FastDeploy,欢迎参考[指南](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/dygraph/deploy/fastdeploy)试用(注意使用dygraph分支)。**
|
||||
- 📚**2022.12 发布[《OCR产业范例20讲》电子书](./applications/README.md)**,新增蒙古文、身份证、液晶屏缺陷等**7个场景应用范例**
|
||||
- 🔨**2022.11 新增实现[4种前沿算法](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)**:文本检测 [DRRG](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_det_drrg.md), 文本识别 [RFL](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_rfl.md), 文本超分[Text Telescope](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_sr_telescope.md),公式识别[CAN](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_can.md)
|
||||
- **2022.10 优化[JS版PP-OCRv3模型](./deploy/paddlejs/README_ch.md)**:模型大小仅4.3M,预测速度提升8倍,配套web demo开箱即用
|
||||
- **💥 直播回放:PaddleOCR研发团队详解PP-StructureV2优化策略**。微信扫描[下方二维码](#开源社区),关注公众号并填写问卷后进入官方交流群,获取直播回放链接与20G重磅OCR学习大礼包(内含PDF转Word应用程序、10种垂类模型、《动手学OCR》电子书等)
|
||||
|
||||
- **🔥2022.8.24 发布 PaddleOCR [release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.6)**
|
||||
- 发布[PP-StructureV2](./ppstructure/README_ch.md),系统功能性能全面升级,适配中文场景,新增支持[版面复原](./ppstructure/recovery/README_ch.md),支持**一行命令完成PDF转Word**;
|
||||
- [版面分析](./ppstructure/layout/README_ch.md)模型优化:模型存储减少95%,速度提升11倍,平均CPU耗时仅需41ms;
|
||||
- [表格识别](./ppstructure/table/README_ch.md)模型优化:设计3大优化策略,预测耗时不变情况下,模型精度提升6%;
|
||||
- [关键信息抽取](./ppstructure/kie/README_ch.md)模型优化:设计视觉无关模型结构,语义实体识别精度提升2.8%,关系抽取精度提升9.1%。
|
||||
- **2022.8 发布 [OCR场景应用集合](./applications)**:包含数码管、液晶屏、车牌、高精度SVTR模型、手写体识别等**9个垂类模型**,覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用。
|
||||
- **2022.8 新增实现[8种前沿算法](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)**
|
||||
- 文本检测:[FCENet](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_det_fcenet.md), [DB++](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_det_db.md)
|
||||
- 文本识别:[ViTSTR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_vitstr.md), [ABINet](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_abinet.md), [VisionLAN](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_visionlan.md), [SPIN](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_spin.md), [RobustScanner](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_robustscanner.md)
|
||||
- 表格识别:[TableMaster](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.6rc/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_table_master.md)
|
||||
|
||||
- **2022.5.9 发布 PaddleOCR [release/2.5](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.5)**
|
||||
- 发布[PP-OCRv3](./doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md#pp-ocrv3),速度可比情况下,中文场景效果相比于PP-OCRv2再提升5%,英文场景提升11%,80语种多语言模型平均识别准确率提升5%以上;
|
||||
- 发布半自动标注工具[PPOCRLabelv2](./PPOCRLabel):新增表格文字图像、图像关键信息抽取任务和不规则文字图像的标注功能;
|
||||
- 发布OCR产业落地工具集:打通22种训练部署软硬件环境与方式,覆盖企业90%的训练部署环境需求;
|
||||
- 发布交互式OCR开源电子书[《动手学OCR》](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md),覆盖OCR全栈技术的前沿理论与代码实践,并配套教学视频。
|
||||
|
||||
> [更多](./doc/doc_ch/update.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🌟 特性
|
||||
|
||||
支持多种OCR相关前沿算法,在此基础上打造产业级特色模型[PP-OCR](./doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md)和[PP-Structure](./ppstructure/README_ch.md),并打通数据生产、模型训练、压缩、预测部署全流程。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25809855/186170862-b8f80f6c-fee7-4b26-badc-de9c327c76ce.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
> 上述内容的使用方法建议从文档教程中的快速开始体验
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ⚡ 快速开始
|
||||
|
||||
- 在线网站体验:超轻量PP-OCR mobile模型体验地址:https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/hub/scene/ocr
|
||||
- 移动端demo体验:[安装包DEMO下载地址](https://ai.baidu.com/easyedge/app/openSource?from=paddlelite)(基于EasyEdge和Paddle-Lite, 支持iOS和Android系统)
|
||||
- 一行命令快速使用:[快速开始(中英文/多语言/文档分析)](./doc/doc_ch/quickstart.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="电子书"></a>
|
||||
## 📚《动手学OCR》电子书
|
||||
- [《动手学OCR》电子书](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="开源社区"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 👫 开源社区
|
||||
- **📑项目合作:** 如果您是企业开发者且有明确的OCR垂类应用需求,填写[问卷](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vj/QwF7GKw.aspx)后可免费与官方团队展开不同层次的合作。
|
||||
- **👫加入社区:** **微信扫描二维码并填写问卷之后,加入交流群领取20G重磅OCR学习大礼包**
|
||||
- **包括《动手学OCR》电子书** ,配套讲解视频和notebook项目;**PaddleOCR历次发版直播课回放链接**;
|
||||
- **OCR场景应用模型集合:** 包含数码管、液晶屏、车牌、高精度SVTR模型、手写体识别等垂类模型,覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用。
|
||||
- PDF2Word应用程序;OCR社区优秀开发者项目分享视频。
|
||||
- **🏅️社区项目**:[社区项目](./doc/doc_ch/thirdparty.md)文档中包含了社区用户**使用PaddleOCR开发的各种工具、应用**以及**为PaddleOCR贡献的功能、优化的文档与代码**等,是官方为社区开发者打造的荣誉墙,也是帮助优质项目宣传的广播站。
|
||||
- **🎁社区常规赛**:社区常规赛是面向OCR开发者的积分赛事,覆盖文档、代码、模型和应用四大类型,以季度为单位评选并发放奖励,赛题详情与报名方法可参考[链接](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/4982)。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/dygraph/doc/joinus.PNG" width = "150" height = "150",caption='' />
|
||||
<p>PaddleOCR官方交流群二维码</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="模型下载"></a>
|
||||
## 🛠️ PP-OCR系列模型列表(更新中)
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型简介 | 模型名称 | 推荐场景 | 检测模型 | 方向分类器 | 识别模型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(13.4M) | en_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
- 超轻量OCR系列更多模型下载(包括多语言),可以参考[PP-OCR系列模型下载](./doc/doc_ch/models_list.md),文档分析相关模型参考[PP-Structure系列模型下载](./ppstructure/docs/models_list.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### PaddleOCR场景应用模型
|
||||
|
||||
| 行业 | 类别 | 亮点 | 文档说明 | 模型下载 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------ | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 制造 | 数码管识别 | 数码管数据合成、漏识别调优 | [光功率计数码管字符识别](./applications/光功率计数码管字符识别/光功率计数码管字符识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
| 金融 | 通用表单识别 | 多模态通用表单结构化提取 | [多模态表单识别](./applications/多模态表单识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
| 交通 | 车牌识别 | 多角度图像处理、轻量模型、端侧部署 | [轻量级车牌识别](./applications/轻量级车牌识别.md) | [下载链接](./applications/README.md#模型下载) |
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用模型(如电表、液晶屏、高精度SVTR模型等),可参考[场景应用模型下载](./applications)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="文档教程"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📖 文档教程
|
||||
|
||||
- [运行环境准备](./doc/doc_ch/environment.md)
|
||||
- [PP-OCR文本检测识别🔥](./doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md)
|
||||
- [快速开始](./doc/doc_ch/quickstart.md)
|
||||
- [模型库](./doc/doc_ch/models_list.md)
|
||||
- [模型训练](./doc/doc_ch/training.md)
|
||||
- [文本检测](./doc/doc_ch/detection.md)
|
||||
- [文本识别](./doc/doc_ch/recognition.md)
|
||||
- [文本方向分类器](./doc/doc_ch/angle_class.md)
|
||||
- 模型压缩
|
||||
- [模型量化](./deploy/slim/quantization/README.md)
|
||||
- [模型裁剪](./deploy/slim/prune/README.md)
|
||||
- [知识蒸馏](./doc/doc_ch/knowledge_distillation.md)
|
||||
- [推理部署](./deploy/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [基于Python预测引擎推理](./doc/doc_ch/inference_ppocr.md)
|
||||
- [基于C++预测引擎推理](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
- [服务化部署](./deploy/pdserving/README_CN.md)
|
||||
- [端侧部署](./deploy/lite/readme.md)
|
||||
- [Paddle2ONNX模型转化与预测](./deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md)
|
||||
- [云上飞桨部署工具](./deploy/paddlecloud/README.md)
|
||||
- [Benchmark](./doc/doc_ch/benchmark.md)
|
||||
- [PP-Structure文档分析🔥](./ppstructure/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [快速开始](./ppstructure/docs/quickstart.md)
|
||||
- [模型库](./ppstructure/docs/models_list.md)
|
||||
- [模型训练](./doc/doc_ch/training.md)
|
||||
- [版面分析](./ppstructure/layout/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别](./ppstructure/table/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息提取](./ppstructure/kie/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [推理部署](./deploy/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [基于Python预测引擎推理](./ppstructure/docs/inference.md)
|
||||
- [基于C++预测引擎推理](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
- [服务化部署](./deploy/hubserving/readme.md)
|
||||
- [前沿算法与模型🚀](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [文本检测算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [文本识别算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [端到端OCR算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息抽取算法](./doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview.md)
|
||||
- [使用PaddleOCR架构添加新算法](./doc/doc_ch/add_new_algorithm.md)
|
||||
- [场景应用](./applications)
|
||||
- 数据标注与合成
|
||||
- [半自动标注工具PPOCRLabel](./PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [数据合成工具Style-Text](./StyleText/README_ch.md)
|
||||
- [其它数据标注工具](./doc/doc_ch/data_annotation.md)
|
||||
- [其它数据合成工具](./doc/doc_ch/data_synthesis.md)
|
||||
- 数据集
|
||||
- [通用中英文OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/datasets.md)
|
||||
- [手写中文OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/handwritten_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [垂类多语言OCR数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/vertical_and_multilingual_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [版面分析数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/layout_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [表格识别数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/table_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [关键信息提取数据集](doc/doc_ch/dataset/kie_datasets.md)
|
||||
- [代码组织结构](./doc/doc_ch/tree.md)
|
||||
- [效果展示](#效果展示)
|
||||
- [《动手学OCR》电子书📚](./doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md)
|
||||
- [开源社区](#开源社区)
|
||||
- FAQ
|
||||
- [通用问题](./doc/doc_ch/FAQ.md)
|
||||
- [PaddleOCR实战问题](./doc/doc_ch/FAQ.md)
|
||||
- [参考文献](./doc/doc_ch/reference.md)
|
||||
- [许可证书](#许可证书)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="效果展示"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 👀 效果展示 [more](./doc/doc_ch/visualization.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 中文模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic001.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic002.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic003.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 英文模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_1.png" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_2.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 多语言模型</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/japan_2.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/korean_1.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-Structure 文档分析</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
- 版面分析+表格识别
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./ppstructure/docs/table/ppstructure.GIF" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- SER(语义实体识别)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185310636-6ce02f7c-790d-479f-b163-ea97a5a04808.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185539517-ccf2372a-f026-4a7c-ad28-c741c770f60a.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/197464552-69de557f-edff-4c7f-acbf-069df1ba097f.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- RE(关系提取)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185540080-0431e006-9235-4b6d-b63d-0b3c6e1de48f.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25809855/186094813-3a8e16cc-42e5-4982-b9f4-0134dfb5688d.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="许可证书"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 许可证书
|
||||
本项目的发布受<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/master/LICENSE">Apache 2.0 license</a>许可认证。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,265 @@
|
|||
English | [简体中文](README_ch.md) | [हिन्दी](./doc/doc_i18n/README_हिन्द.md) | [日本語](./doc/doc_i18n/README_日本語.md) | [한국인](./doc/doc_i18n/README_한국어.md) | [Pу́сский язы́к](./doc/doc_i18n/README_Ру́сский_язы́к.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/PaddleOCR_log.png" align="middle" width = "600"/>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<p align="left">
|
||||
<a href="./LICENSE"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/license-Apache%202-dfd.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/v/release/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ffa"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/python-3.7+-aff.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/os-linux%2C%20win%2C%20mac-pink.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href=""><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/format/PaddleOCR?color=c77"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/PaddleOCR/"><img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/PaddleOCR?color=9cf"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/stargazers"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR?color=ccf"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR aims to create multilingual, awesome, leading, and practical OCR tools that help users train better models and apply them into practice.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_4.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./doc/imgs_results/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0/00006737.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📣 Recent updates
|
||||
- **🔥2023.8.7 Release PaddleOCR[release/2.7](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.7)**
|
||||
- Release [PP-OCRv4](./doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv4_introduction.md), support mobile version and server version
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4-mobile:When the speed is comparable, the effect of the Chinese scene is improved by 4.5% compared with PP-OCRv3, the English scene is improved by 10%, and the average recognition accuracy of the 80-language multilingual model is increased by more than 8%.
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4-server:Release the OCR model with the highest accuracy at present, the detection model accuracy increased by 4.9% in the Chinese and English scenes, and the recognition model accuracy increased by 2%
|
||||
refer [quickstart](./doc/doc_en/quickstart_en.md) quick use by one line command, At the same time, the whole process of model training, reasoning, and high-performance deployment can also be completed with few code in the [General OCR Industry Solution](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=286) in PaddleX.
|
||||
- Release[PP-ChatOCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=332), a new scheme for extracting key information of general scenes using PP-OCR model and ERNIE LLM.
|
||||
- 🔨**2022.11 Add implementation of [4 cutting-edge algorithms](doc/doc_ch/algorithm_overview_en.md)**:Text Detection [DRRG](doc/doc_en/algorithm_det_drrg_en.md), Text Recognition [RFL](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_rfl_en.md), Image Super-Resolution [Text Telescope](doc/doc_en/algorithm_sr_telescope_en.md),Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition [CAN](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_can_en.md)
|
||||
- **2022.10 release [optimized JS version PP-OCRv3 model](./deploy/paddlejs/README.md)** with 4.3M model size, 8x faster inference time, and a ready-to-use web demo
|
||||
- 💥 **Live Playback: Introduction to PP-StructureV2 optimization strategy**. Scan [the QR code below](#Community) using WeChat, follow the PaddlePaddle official account and fill out the questionnaire to join the WeChat group, get the live link and 20G OCR learning materials (including PDF2Word application, 10 models in vertical scenarios, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **🔥2022.8.24 Release PaddleOCR [release/2.6](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.6)**
|
||||
- Release [PP-StructureV2](./ppstructure/),with functions and performance fully upgraded, adapted to Chinese scenes, and new support for [Layout Recovery](./ppstructure/recovery) and **one line command to convert PDF to Word**;
|
||||
- [Layout Analysis](./ppstructure/layout) optimization: model storage reduced by 95%, while speed increased by 11 times, and the average CPU time-cost is only 41ms;
|
||||
- [Table Recognition](./ppstructure/table) optimization: 3 optimization strategies are designed, and the model accuracy is improved by 6% under comparable time consumption;
|
||||
- [Key Information Extraction](./ppstructure/kie) optimization:a visual-independent model structure is designed, the accuracy of semantic entity recognition is increased by 2.8%, and the accuracy of relation extraction is increased by 9.1%.
|
||||
- **🔥2022.8 Release [OCR scene application collection](./applications/README_en.md)**
|
||||
- Release **9 vertical models** such as digital tube, LCD screen, license plate, handwriting recognition model, high-precision SVTR model, etc, covering the main OCR vertical applications in general, manufacturing, finance, and transportation industries.
|
||||
- **2022.8 Add implementation of [8 cutting-edge algorithms](doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)**
|
||||
- Text Detection: [FCENet](doc/doc_en/algorithm_det_fcenet_en.md), [DB++](doc/doc_en/algorithm_det_db_en.md)
|
||||
- Text Recognition: [ViTSTR](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_vitstr_en.md), [ABINet](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_abinet_en.md), [VisionLAN](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_visionlan_en.md), [SPIN](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_spin_en.md), [RobustScanner](doc/doc_en/algorithm_rec_robustscanner_en.md)
|
||||
- Table Recognition: [TableMaster](doc/doc_en/algorithm_table_master_en.md)
|
||||
- **2022.5.9 Release PaddleOCR [release/2.5](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.5)**
|
||||
- Release [PP-OCRv3](./doc/doc_en/ppocr_introduction_en.md#pp-ocrv3): With comparable speed, the effect of Chinese scene is further improved by 5% compared with PP-OCRv2, the effect of English scene is improved by 11%, and the average recognition accuracy of 80 language multilingual models is improved by more than 5%.
|
||||
- Release [PPOCRLabelv2](./PPOCRLabel): Add the annotation function for table recognition task, key information extraction task and irregular text image.
|
||||
- Release interactive e-book [*"Dive into OCR"*](./doc/doc_en/ocr_book_en.md), covers the cutting-edge theory and code practice of OCR full stack technology.
|
||||
- [more](./doc/doc_en/update_en.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 🌟 Features
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR support a variety of cutting-edge algorithms related to OCR, and developed industrial featured models/solution [PP-OCR](./doc/doc_en/ppocr_introduction_en.md)、 [PP-Structure](./ppstructure/README.md) and [PP-ChatOCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6488689) on this basis, and get through the whole process of data production, model training, compression, inference and deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25809855/186171245-40abc4d7-904f-4949-ade1-250f86ed3a90.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
> It is recommended to start with the “quick experience” in the document tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ⚡ Quick Experience
|
||||
|
||||
- Web online experience
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4 online experience:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6611435
|
||||
- PP-ChatOCR online experience:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/6488689
|
||||
- One line of code quick use: [Quick Start(Chinese/English/Multilingual/Document Analysis](./doc/doc_en/quickstart_en.md)
|
||||
- Full-process experience of training, inference, and high-performance deployment in the Paddle AI suite (PaddleX):
|
||||
- PP-OCRv4:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=286
|
||||
- PP-ChatOCR:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/modelsdetail?modelId=332
|
||||
- Mobile demo experience:[Installation DEMO](https://ai.baidu.com/easyedge/app/openSource?from=paddlelite)(Based on EasyEdge and Paddle-Lite, support iOS and Android systems)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Technical exchange and cooperation"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 📖 Technical exchange and cooperation
|
||||
- ([PaddleX](http://10.136.157.23:8080/paddle/paddleX))provides a one-stop full-process high-efficiency development platform for flying paddle ecological model training, pressure, and push. Its mission is to help AI technology quickly land, and its vision is to make everyone an AI Developer!
|
||||
- PaddleX currently covers areas such as image classification, object detection, image segmentation, 3D, OCR, and time series prediction, and has built-in 36 basic single models, such as RP-DETR, PP-YOLOE, PP-HGNet, PP-LCNet, PP- LiteSeg, etc.; integrated 12 practical industrial solutions, such as PP-OCRv4, PP-ChatOCR, PP-ShiTu, PP-TS, vehicle-mounted road waste detection, identification of prohibited wildlife products, etc.
|
||||
- PaddleX provides two AI development modes: "Toolbox" and "Developer". The toolbox mode can tune key hyperparameters without code, and the developer mode can perform single-model training, push and multi-model serial inference with low code, and supports both cloud and local terminals.
|
||||
- PaddleX also supports joint innovation and development, profit sharing! At present, PaddleX is rapidly iterating, and welcomes the participation of individual developers and enterprise developers to create a prosperous AI technology ecosystem!
|
||||
|
||||
Scan the QR code below on WeChat to add operation students, and reply [paddlex], operation students will invite you to join the official communication group for more efficient questions and answers.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/dygraph/doc/joinus_paddlex.jpg" width = "150" height = "150",caption='' />
|
||||
<p>[PaddleX] technology exchange group QR code</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="book"></a>
|
||||
## 📚 E-book: *Dive Into OCR*
|
||||
- [Dive Into OCR ](./doc/doc_en/ocr_book_en.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Community"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 👫 Community
|
||||
|
||||
- For international developers, we regard [PaddleOCR Discussions](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/discussions) as our international community platform. All ideas and questions can be discussed here in English.
|
||||
|
||||
- For Chinese develops, Scan the QR code below with your Wechat, you can join the official technical discussion group. For richer community content, please refer to [中文README](README_ch.md), looking forward to your participation.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/dygraph/doc/joinus.PNG" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Supported-Chinese-model-list"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 🛠️ PP-OCR Series Model List(Update on September 8th)
|
||||
|
||||
| Model introduction | Model name | Recommended scene | Detection model | Direction classifier | Recognition model |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Chinese and English ultra-lightweight PP-OCRv4 model(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv4_xx | Mobile & Server | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_det_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_det_distill_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_rec_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv4/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv4_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| Chinese and English ultra-lightweight PP-OCRv3 model(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv3_xx | Mobile & Server | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| English ultra-lightweight PP-OCRv3 model(13.4M) | en_PP-OCRv3_xx | Mobile & Server | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [inference model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [trained model](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
- For more model downloads (including multiple languages), please refer to [PP-OCR series model downloads](./doc/doc_en/models_list_en.md).
|
||||
- For a new language request, please refer to [Guideline for new language_requests](#language_requests).
|
||||
- For structural document analysis models, please refer to [PP-Structure models](./ppstructure/docs/models_list_en.md).
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="tutorials"></a>
|
||||
## 📖 Tutorials
|
||||
- [Environment Preparation](./doc/doc_en/environment_en.md)
|
||||
- [PP-OCR 🔥](./doc/doc_en/ppocr_introduction_en.md)
|
||||
- [Quick Start](./doc/doc_en/quickstart_en.md)
|
||||
- [Model Zoo](./doc/doc_en/models_en.md)
|
||||
- [Model training](./doc/doc_en/training_en.md)
|
||||
- [Text Detection](./doc/doc_en/detection_en.md)
|
||||
- [Text Recognition](./doc/doc_en/recognition_en.md)
|
||||
- [Text Direction Classification](./doc/doc_en/angle_class_en.md)
|
||||
- Model Compression
|
||||
- [Model Quantization](./deploy/slim/quantization/README_en.md)
|
||||
- [Model Pruning](./deploy/slim/prune/README_en.md)
|
||||
- [Knowledge Distillation](./doc/doc_en/knowledge_distillation_en.md)
|
||||
- [Inference and Deployment](./deploy/README.md)
|
||||
- [Python Inference](./doc/doc_en/inference_ppocr_en.md)
|
||||
- [C++ Inference](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme.md)
|
||||
- [Serving](./deploy/pdserving/README.md)
|
||||
- [Mobile](./deploy/lite/readme.md)
|
||||
- [Paddle2ONNX](./deploy/paddle2onnx/readme.md)
|
||||
- [PaddleCloud](./deploy/paddlecloud/README.md)
|
||||
- [Benchmark](./doc/doc_en/benchmark_en.md)
|
||||
- [PP-Structure 🔥](./ppstructure/README.md)
|
||||
- [Quick Start](./ppstructure/docs/quickstart_en.md)
|
||||
- [Model Zoo](./ppstructure/docs/models_list_en.md)
|
||||
- [Model training](./doc/doc_en/training_en.md)
|
||||
- [Layout Analysis](./ppstructure/layout/README.md)
|
||||
- [Table Recognition](./ppstructure/table/README.md)
|
||||
- [Key Information Extraction](./ppstructure/kie/README.md)
|
||||
- [Inference and Deployment](./deploy/README.md)
|
||||
- [Python Inference](./ppstructure/docs/inference_en.md)
|
||||
- [C++ Inference](./deploy/cpp_infer/readme.md)
|
||||
- [Serving](./deploy/hubserving/readme_en.md)
|
||||
- [Academic Algorithms](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [Text detection](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [Text recognition](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [End-to-end OCR](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [Table Recognition](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [Key Information Extraction](./doc/doc_en/algorithm_overview_en.md)
|
||||
- [Add New Algorithms to PaddleOCR](./doc/doc_en/add_new_algorithm_en.md)
|
||||
- Data Annotation and Synthesis
|
||||
- [Semi-automatic Annotation Tool: PPOCRLabel](./PPOCRLabel/README.md)
|
||||
- [Data Synthesis Tool: Style-Text](./StyleText/README.md)
|
||||
- [Other Data Annotation Tools](./doc/doc_en/data_annotation_en.md)
|
||||
- [Other Data Synthesis Tools](./doc/doc_en/data_synthesis_en.md)
|
||||
- Datasets
|
||||
- [General OCR Datasets(Chinese/English)](doc/doc_en/dataset/datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [HandWritten_OCR_Datasets(Chinese)](doc/doc_en/dataset/handwritten_datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [Various OCR Datasets(multilingual)](doc/doc_en/dataset/vertical_and_multilingual_datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [Layout Analysis](doc/doc_en/dataset/layout_datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [Table Recognition](doc/doc_en/dataset/table_datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [Key Information Extraction](doc/doc_en/dataset/kie_datasets_en.md)
|
||||
- [Code Structure](./doc/doc_en/tree_en.md)
|
||||
- [Visualization](#Visualization)
|
||||
- [Community](#Community)
|
||||
- [New language requests](#language_requests)
|
||||
- [FAQ](./doc/doc_en/FAQ_en.md)
|
||||
- [References](./doc/doc_en/reference_en.md)
|
||||
- [License](#LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Visualization"></a>
|
||||
## 👀 Visualization [more](./doc/doc_en/visualization_en.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 Chinese model</summary>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic001.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic002.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/ch/PP-OCRv3-pic003.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 English model</summary>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_1.png" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/en/en_2.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-OCRv3 Multilingual model</summary>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/japan_2.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="doc/imgs_results/PP-OCRv3/multi_lang/korean_1.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>PP-StructureV2</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
- layout analysis + table recognition
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="./ppstructure/docs/table/ppstructure.GIF" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- SER (Semantic entity recognition)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/197464552-69de557f-edff-4c7f-acbf-069df1ba097f.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185310636-6ce02f7c-790d-479f-b163-ea97a5a04808.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185539517-ccf2372a-f026-4a7c-ad28-c741c770f60a.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
- RE (Relation Extraction)
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25809855/186094813-3a8e16cc-42e5-4982-b9f4-0134dfb5688d.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185540080-0431e006-9235-4b6d-b63d-0b3c6e1de48f.jpg" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="language_requests"></a>
|
||||
## 🇺🇳 Guideline for New Language Requests
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to request a new language support, a PR with 1 following files are needed:
|
||||
|
||||
1. In folder [ppocr/utils/dict](./ppocr/utils/dict),
|
||||
it is necessary to submit the dict text to this path and name it with `{language}_dict.txt` that contains a list of all characters. Please see the format example from other files in that folder.
|
||||
|
||||
If your language has unique elements, please tell me in advance within any way, such as useful links, wikipedia and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
More details, please refer to [Multilingual OCR Development Plan](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/issues/1048).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="LICENSE"></a>
|
||||
## 📄 License
|
||||
This project is released under <a href="https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/master/LICENSE">Apache 2.0 license</a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
|
|||
English | [简体中文](README_ch.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Style Text
|
||||
|
||||
### Contents
|
||||
- [1. Introduction](#Introduction)
|
||||
- [2. Preparation](#Preparation)
|
||||
- [3. Quick Start](#Quick_Start)
|
||||
- [4. Applications](#Applications)
|
||||
- [5. Code Structure](#Code_structure)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Introduction"></a>
|
||||
### Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/3.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/9.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The Style-Text data synthesis tool is a tool based on Baidu and HUST cooperation research work, "Editing Text in the Wild" [https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03047](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03047).
|
||||
|
||||
Different from the commonly used GAN-based data synthesis tools, the main framework of Style-Text includes:
|
||||
* (1) Text foreground style transfer module.
|
||||
* (2) Background extraction module.
|
||||
* (3) Fusion module.
|
||||
|
||||
After these three steps, you can quickly realize the image text style transfer. The following figure is some results of the data synthesis tool.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/10.png" width="1000">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Preparation"></a>
|
||||
#### Preparation
|
||||
|
||||
1. Please refer the [QUICK INSTALLATION](../doc/doc_en/installation_en.md) to install PaddlePaddle. Python3 environment is strongly recommended.
|
||||
2. Download the pretrained models and unzip:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd StyleText
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/style_text/style_text_models.zip
|
||||
unzip style_text_models.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you save the model in another location, please modify the address of the model file in `configs/config.yml`, and you need to modify these three configurations at the same time:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bg_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/bg_generator
|
||||
...
|
||||
text_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/text_generator
|
||||
...
|
||||
fusion_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/fusion_generator
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Quick_Start"></a>
|
||||
### Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
#### Synthesis single image
|
||||
|
||||
1. You can run `tools/synth_image` and generate the demo image, which is saved in the current folder.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python3 tools/synth_image.py -c configs/config.yml --style_image examples/style_images/2.jpg --text_corpus PaddleOCR --language en
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Note 1: The language options is correspond to the corpus. Currently, the tool only supports English(en), Simplified Chinese(ch) and Korean(ko).
|
||||
* Note 2: Synth-Text is mainly used to generate images for OCR recognition models.
|
||||
So the height of style images should be around 32 pixels. Images in other sizes may behave poorly.
|
||||
* Note 3: You can modify `use_gpu` in `configs/config.yml` to determine whether to use GPU for prediction.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For example, enter the following image and corpus `PaddleOCR`.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/2.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The result `fake_fusion.jpg` will be generated.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/4.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
What's more, the medium result `fake_bg.jpg` will also be saved, which is the background output.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/7.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`fake_text.jpg` * `fake_text.jpg` is the generated image with the same font style as `Style Input`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/8.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Batch synthesis
|
||||
|
||||
In actual application scenarios, it is often necessary to synthesize pictures in batches and add them to the training set. StyleText can use a batch of style pictures and corpus to synthesize data in batches. The synthesis process is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The referenced dataset can be specifed in `configs/dataset_config.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Global`:
|
||||
* `output_dir:`:Output synthesis data path.
|
||||
* `StyleSampler`:
|
||||
* `image_home`:style images' folder.
|
||||
* `label_file`:Style images' file list. If label is provided, then it is the label file path.
|
||||
* `with_label`:Whether the `label_file` is label file list.
|
||||
* `CorpusGenerator`:
|
||||
* `method`:Method of CorpusGenerator,supports `FileCorpus` and `EnNumCorpus`. If `EnNumCorpus` is used,No other configuration is needed,otherwise you need to set `corpus_file` and `language`.
|
||||
* `language`:Language of the corpus. Currently, the tool only supports English(en), Simplified Chinese(ch) and Korean(ko).
|
||||
* `corpus_file`: Filepath of the corpus. Corpus file should be a text file which will be split by line-endings('\n'). Corpus generator samples one line each time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Example of corpus file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
飞桨文字识别
|
||||
StyleText
|
||||
风格文本图像数据合成
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a general dataset containing Chinese, English and Korean (50,000 images in all) for your trial ([download link](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/style_text/chkoen_5w.tar)), some examples are given below :
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/5.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
2. You can run the following command to start synthesis task:
|
||||
|
||||
``` bash
|
||||
python3 tools/synth_dataset.py -c configs/dataset_config.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We also provide example corpus and images in `examples` folder.
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/1.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/2.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
If you run the code above directly, you will get example output data in `output_data` folder.
|
||||
You will get synthesis images and labels as below:
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/12.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
There will be some cache under the `label` folder. If the program exit unexpectedly, you can find cached labels there.
|
||||
When the program finish normally, you will find all the labels in `label.txt` which give the final results.
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Applications"></a>
|
||||
### Applications
|
||||
We take two scenes as examples, which are metal surface English number recognition and general Korean recognition, to illustrate practical cases of using StyleText to synthesize data to improve text recognition. The following figure shows some examples of real scene images and composite images:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/11.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
After adding the above synthetic data for training, the accuracy of the recognition model is improved, which is shown in the following table:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Scenario | Characters | Raw Data | Test Data | Only Use Raw Data</br>Recognition Accuracy | New Synthetic Data | Simultaneous Use of Synthetic Data</br>Recognition Accuracy | Index Improvement |
|
||||
| -------- | ---------- | -------- | -------- | -------------------------- | ------------ | ---------------------- | -------- |
|
||||
| Metal surface | English and numbers | 2203 | 650 | 59.38% | 20000 | 75.46% | 16.08% |
|
||||
| Random background | Korean | 5631 | 1230 | 30.12% | 100000 | 50.57% | 20.45% |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="Code_structure"></a>
|
||||
### Code Structure
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
StyleText
|
||||
|-- arch // Network module files.
|
||||
| |-- base_module.py
|
||||
| |-- decoder.py
|
||||
| |-- encoder.py
|
||||
| |-- spectral_norm.py
|
||||
| `-- style_text_rec.py
|
||||
|-- configs // Config files.
|
||||
| |-- config.yml
|
||||
| `-- dataset_config.yml
|
||||
|-- engine // Synthesis engines.
|
||||
| |-- corpus_generators.py // Sample corpus from file or generate random corpus.
|
||||
| |-- predictors.py // Predict using network.
|
||||
| |-- style_samplers.py // Sample style images.
|
||||
| |-- synthesisers.py // Manage other engines to synthesis images.
|
||||
| |-- text_drawers.py // Generate standard input text images.
|
||||
| `-- writers.py // Write synthesis images and labels into files.
|
||||
|-- examples // Example files.
|
||||
| |-- corpus
|
||||
| | `-- example.txt
|
||||
| |-- image_list.txt
|
||||
| `-- style_images
|
||||
| |-- 1.jpg
|
||||
| `-- 2.jpg
|
||||
|-- fonts // Font files.
|
||||
| |-- ch_standard.ttf
|
||||
| |-- en_standard.ttf
|
||||
| `-- ko_standard.ttf
|
||||
|-- tools // Program entrance.
|
||||
| |-- __init__.py
|
||||
| |-- synth_dataset.py // Synthesis dataset.
|
||||
| `-- synth_image.py // Synthesis image.
|
||||
`-- utils // Module of basic functions.
|
||||
|-- config.py
|
||||
|-- load_params.py
|
||||
|-- logging.py
|
||||
|-- math_functions.py
|
||||
`-- sys_funcs.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
|
|||
简体中文 | [English](README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Style Text
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 目录
|
||||
- [一、工具简介](#工具简介)
|
||||
- [二、环境配置](#环境配置)
|
||||
- [三、快速上手](#快速上手)
|
||||
- [四、应用案例](#应用案例)
|
||||
- [五、代码结构](#代码结构)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="工具简介"></a>
|
||||
### 一、工具简介
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/3.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/1.png" width="600">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Style-Text数据合成工具是基于百度和华科合作研发的文本编辑算法《Editing Text in the Wild》https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03047
|
||||
|
||||
不同于常用的基于GAN的数据合成工具,Style-Text主要框架包括:1.文本前景风格迁移模块 2.背景抽取模块 3.融合模块。经过这样三步,就可以迅速实现图像文本风格迁移。下图是一些该数据合成工具效果图。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/2.png" width="1000">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="环境配置"></a>
|
||||
### 二、环境配置
|
||||
|
||||
1. 参考[快速安装](../doc/doc_ch/installation.md),安装PaddleOCR。
|
||||
2. 进入`StyleText`目录,下载模型,并解压:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd StyleText
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/style_text/style_text_models.zip
|
||||
unzip style_text_models.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果您将模型保存再其他位置,请在`configs/config.yml`中修改模型文件的地址,修改时需要同时修改这三个配置:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bg_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/bg_generator
|
||||
...
|
||||
text_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/text_generator
|
||||
...
|
||||
fusion_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/fusion_generator
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="快速上手"></a>
|
||||
### 三、快速上手
|
||||
|
||||
#### 合成单张图
|
||||
输入一张风格图和一段文字语料,运行tools/synth_image,合成单张图片,结果图像保存在当前目录下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python3 tools/synth_image.py -c configs/config.yml --style_image examples/style_images/2.jpg --text_corpus PaddleOCR --language en
|
||||
```
|
||||
* 注1:语言选项和语料相对应,目前支持英文(en)、简体中文(ch)和韩语(ko)。
|
||||
* 注2:Style-Text生成的数据主要应用于OCR识别场景。基于当前PaddleOCR识别模型的设计,我们主要支持高度在32左右的风格图像。
|
||||
如果输入图像尺寸相差过多,效果可能不佳。
|
||||
* 注3:可以通过修改配置文件`configs/config.yml`中的`use_gpu`(true或者false)参数来决定是否使用GPU进行预测。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
例如,输入如下图片和语料"PaddleOCR":
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/2.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
生成合成数据`fake_fusion.jpg`:
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/4.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,程序还会生成并保存中间结果`fake_bg.jpg`:为风格参考图去掉文字后的背景;
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/7.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
`fake_text.jpg`:是用提供的字符串,仿照风格参考图中文字的风格,生成在灰色背景上的文字图片。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/8.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 批量合成
|
||||
在实际应用场景中,经常需要批量合成图片,补充到训练集中。Style-Text可以使用一批风格图片和语料,批量合成数据。合成过程如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在`configs/dataset_config.yml`中配置目标场景风格图像和语料的路径,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Global`:
|
||||
* `output_dir:`:保存合成数据的目录。
|
||||
* `StyleSampler`:
|
||||
* `image_home`:风格图片目录;
|
||||
* `label_file`:风格图片路径列表文件,如果所用数据集有label,则label_file为label文件路径;
|
||||
* `with_label`:标志`label_file`是否为label文件。
|
||||
* `CorpusGenerator`:
|
||||
* `method`:语料生成方法,目前有`FileCorpus`和`EnNumCorpus`可选。如果使用`EnNumCorpus`,则不需要填写其他配置,否则需要修改`corpus_file`和`language`;
|
||||
* `language`:语料的语种,目前支持英文(en)、简体中文(ch)和韩语(ko);
|
||||
* `corpus_file`: 语料文件路径。语料文件应使用文本文件。语料生成器首先会将语料按行切分,之后每次随机选取一行。
|
||||
|
||||
语料文件格式示例:
|
||||
```
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
飞桨文字识别
|
||||
StyleText
|
||||
风格文本图像数据合成
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Style-Text也提供了一批中英韩5万张通用场景数据用作文本风格图像,便于合成场景丰富的文本图像,下图给出了一些示例。
|
||||
|
||||
中英韩5万张通用场景数据: [下载地址](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/style_text/chkoen_5w.tar)
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/5.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
2. 运行`tools/synth_dataset`合成数据:
|
||||
|
||||
``` bash
|
||||
python3 tools/synth_dataset.py -c configs/dataset_config.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
我们在examples目录下提供了样例图片和语料。
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/1.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
<img src="examples/style_images/2.jpg" width="300">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
直接运行上述命令,可以在output_data中产生样例输出,包括图片和用于训练识别模型的标注文件:
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/12.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
其中label目录下的标注文件为程序运行过程中产生的缓存,如果程序在中途异常终止,可以使用缓存的标注文件。
|
||||
如果程序正常运行完毕,则会在output_data下生成label.txt,为最终的标注结果。
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="应用案例"></a>
|
||||
### 四、应用案例
|
||||
下面以金属表面英文数字识别和通用韩语识别两个场景为例,说明使用Style-Text合成数据,来提升文本识别效果的实际案例。下图给出了一些真实场景图像和合成图像的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="doc/images/6.png" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
在添加上述合成数据进行训练后,识别模型的效果提升,如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 场景 | 字符 | 原始数据 | 测试数据 | 只使用原始数据</br>识别准确率 | 新增合成数据 | 同时使用合成数据</br>识别准确率 | 指标提升 |
|
||||
| -------- | ---------- | -------- | -------- | -------------------------- | ------------ | ---------------------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 金属表面 | 英文和数字 | 2203 | 650 | 59.38% | 20000 | 75.46% | 16.08% |
|
||||
| 随机背景 | 韩语 | 5631 | 1230 | 30.12% | 100000 | 50.57% | 20.45% |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="代码结构"></a>
|
||||
### 五、代码结构
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
StyleText
|
||||
|-- arch // 网络结构定义文件
|
||||
| |-- base_module.py
|
||||
| |-- decoder.py
|
||||
| |-- encoder.py
|
||||
| |-- spectral_norm.py
|
||||
| `-- style_text_rec.py
|
||||
|-- configs // 配置文件
|
||||
| |-- config.yml
|
||||
| `-- dataset_config.yml
|
||||
|-- engine // 数据合成引擎
|
||||
| |-- corpus_generators.py // 从文本采样或随机生成语料
|
||||
| |-- predictors.py // 调用网络生成数据
|
||||
| |-- style_samplers.py // 采样风格图片
|
||||
| |-- synthesisers.py // 调度各个模块,合成数据
|
||||
| |-- text_drawers.py // 生成标准文字图片,用作输入
|
||||
| `-- writers.py // 将合成的图片和标签写入本地目录
|
||||
|-- examples // 示例文件
|
||||
| |-- corpus
|
||||
| | `-- example.txt
|
||||
| |-- image_list.txt
|
||||
| `-- style_images
|
||||
| |-- 1.jpg
|
||||
| `-- 2.jpg
|
||||
|-- fonts // 字体文件
|
||||
| |-- ch_standard.ttf
|
||||
| |-- en_standard.ttf
|
||||
| `-- ko_standard.ttf
|
||||
|-- tools // 程序入口
|
||||
| |-- __init__.py
|
||||
| |-- synth_dataset.py // 批量合成数据
|
||||
| `-- synth_image.py // 合成单张图片
|
||||
`-- utils // 其他基础功能模块
|
||||
|-- config.py
|
||||
|-- load_params.py
|
||||
|-- logging.py
|
||||
|-- math_functions.py
|
||||
`-- sys_funcs.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import paddle.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from arch.spectral_norm import spectral_norm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CBN(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
name,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0,
|
||||
dilation=1,
|
||||
groups=1,
|
||||
use_bias=False,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=None,
|
||||
act_attr=None):
|
||||
super(CBN, self).__init__()
|
||||
if use_bias:
|
||||
bias_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_bias")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bias_attr = None
|
||||
self._conv = paddle.nn.Conv2D(
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=stride,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
dilation=dilation,
|
||||
groups=groups,
|
||||
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_weights"),
|
||||
bias_attr=bias_attr)
|
||||
if norm_layer:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = getattr(paddle.nn, norm_layer)(
|
||||
num_features=out_channels, name=name + "_bn")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = None
|
||||
if act:
|
||||
if act_attr:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(**act_attr,
|
||||
name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = None
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
out = self._conv(x)
|
||||
if self._norm_layer:
|
||||
out = self._norm_layer(out)
|
||||
if self._act:
|
||||
out = self._act(out)
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SNConv(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
name,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0,
|
||||
dilation=1,
|
||||
groups=1,
|
||||
use_bias=False,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=None,
|
||||
act_attr=None):
|
||||
super(SNConv, self).__init__()
|
||||
if use_bias:
|
||||
bias_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_bias")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bias_attr = None
|
||||
self._sn_conv = spectral_norm(
|
||||
paddle.nn.Conv2D(
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=stride,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
dilation=dilation,
|
||||
groups=groups,
|
||||
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_weights"),
|
||||
bias_attr=bias_attr))
|
||||
if norm_layer:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = getattr(paddle.nn, norm_layer)(
|
||||
num_features=out_channels, name=name + "_bn")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = None
|
||||
if act:
|
||||
if act_attr:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(**act_attr,
|
||||
name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = None
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
out = self._sn_conv(x)
|
||||
if self._norm_layer:
|
||||
out = self._norm_layer(out)
|
||||
if self._act:
|
||||
out = self._act(out)
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SNConvTranspose(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
name,
|
||||
in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=0,
|
||||
output_padding=0,
|
||||
dilation=1,
|
||||
groups=1,
|
||||
use_bias=False,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=None,
|
||||
act_attr=None):
|
||||
super(SNConvTranspose, self).__init__()
|
||||
if use_bias:
|
||||
bias_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_bias")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bias_attr = None
|
||||
self._sn_conv_transpose = spectral_norm(
|
||||
paddle.nn.Conv2DTranspose(
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=kernel_size,
|
||||
stride=stride,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
output_padding=output_padding,
|
||||
dilation=dilation,
|
||||
groups=groups,
|
||||
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_weights"),
|
||||
bias_attr=bias_attr))
|
||||
if norm_layer:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = getattr(paddle.nn, norm_layer)(
|
||||
num_features=out_channels, name=name + "_bn")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._norm_layer = None
|
||||
if act:
|
||||
if act_attr:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(**act_attr,
|
||||
name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = getattr(paddle.nn, act)(name=name + "_" + act)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._act = None
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
out = self._sn_conv_transpose(x)
|
||||
if self._norm_layer:
|
||||
out = self._norm_layer(out)
|
||||
if self._act:
|
||||
out = self._act(out)
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MiddleNet(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, in_channels, mid_channels, out_channels,
|
||||
use_bias):
|
||||
super(MiddleNet, self).__init__()
|
||||
self._sn_conv1 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_sn_conv1",
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=mid_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=None)
|
||||
self._pad2d = nn.Pad2D(padding=[1, 1, 1, 1], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._sn_conv2 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_sn_conv2",
|
||||
in_channels=mid_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=mid_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias)
|
||||
self._sn_conv3 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_sn_conv3",
|
||||
in_channels=mid_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
|
||||
sn_conv1 = self._sn_conv1.forward(x)
|
||||
pad_2d = self._pad2d.forward(sn_conv1)
|
||||
sn_conv2 = self._sn_conv2.forward(pad_2d)
|
||||
sn_conv3 = self._sn_conv3.forward(sn_conv2)
|
||||
return sn_conv3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResBlock(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, channels, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias):
|
||||
super(ResBlock, self).__init__()
|
||||
if use_dilation:
|
||||
padding_mat = [1, 1, 1, 1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
padding_mat = [0, 0, 0, 0]
|
||||
self._pad1 = nn.Pad2D(padding_mat, mode="replicate")
|
||||
|
||||
self._sn_conv1 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_sn_conv1",
|
||||
in_channels=channels,
|
||||
out_channels=channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
padding=0,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None)
|
||||
if use_dropout:
|
||||
self._dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._dropout = None
|
||||
self._pad2 = nn.Pad2D([1, 1, 1, 1], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._sn_conv2 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_sn_conv2",
|
||||
in_channels=channels,
|
||||
out_channels=channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
pad1 = self._pad1.forward(x)
|
||||
sn_conv1 = self._sn_conv1.forward(pad1)
|
||||
pad2 = self._pad2.forward(sn_conv1)
|
||||
sn_conv2 = self._sn_conv2.forward(pad2)
|
||||
return sn_conv2 + x
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import paddle.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from arch.base_module import SNConv, SNConvTranspose, ResBlock
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Decoder(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, encode_dim, out_channels, use_bias, norm_layer,
|
||||
act, act_attr, conv_block_dropout, conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation, out_conv_act, out_conv_act_attr):
|
||||
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
|
||||
conv_blocks = []
|
||||
for i in range(conv_block_num):
|
||||
conv_blocks.append(
|
||||
ResBlock(
|
||||
name="{}_conv_block_{}".format(name, i),
|
||||
channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
use_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias))
|
||||
self.conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(*conv_blocks)
|
||||
self._up1 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up2 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up3 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up3",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._pad2d = paddle.nn.Pad2D([1, 1, 1, 1], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._out_conv = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_out_conv",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=out_conv_act,
|
||||
act_attr=out_conv_act_attr)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
if isinstance(x, (list, tuple)):
|
||||
x = paddle.concat(x, axis=1)
|
||||
output_dict = dict()
|
||||
output_dict["conv_blocks"] = self.conv_blocks.forward(x)
|
||||
output_dict["up1"] = self._up1.forward(output_dict["conv_blocks"])
|
||||
output_dict["up2"] = self._up2.forward(output_dict["up1"])
|
||||
output_dict["up3"] = self._up3.forward(output_dict["up2"])
|
||||
output_dict["pad2d"] = self._pad2d.forward(output_dict["up3"])
|
||||
output_dict["out_conv"] = self._out_conv.forward(output_dict["pad2d"])
|
||||
return output_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DecoderUnet(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, encode_dim, out_channels, use_bias, norm_layer,
|
||||
act, act_attr, conv_block_dropout, conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation, out_conv_act, out_conv_act_attr):
|
||||
super(DecoderUnet, self).__init__()
|
||||
conv_blocks = []
|
||||
for i in range(conv_block_num):
|
||||
conv_blocks.append(
|
||||
ResBlock(
|
||||
name="{}_conv_block_{}".format(name, i),
|
||||
channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
use_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias))
|
||||
self._conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(*conv_blocks)
|
||||
self._up1 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up2 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up3 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up3",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._pad2d = paddle.nn.Pad2D([1, 1, 1, 1], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._out_conv = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_out_conv",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=out_conv_act,
|
||||
act_attr=out_conv_act_attr)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x, y, feature2, feature1):
|
||||
output_dict = dict()
|
||||
output_dict["conv_blocks"] = self._conv_blocks(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(x, y), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict["up1"] = self._up1.forward(output_dict["conv_blocks"])
|
||||
output_dict["up2"] = self._up2.forward(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict["up1"], feature2), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict["up3"] = self._up3.forward(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict["up2"], feature1), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict["pad2d"] = self._pad2d.forward(output_dict["up3"])
|
||||
output_dict["out_conv"] = self._out_conv.forward(output_dict["pad2d"])
|
||||
return output_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SingleDecoder(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, encode_dim, out_channels, use_bias, norm_layer,
|
||||
act, act_attr, conv_block_dropout, conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation, out_conv_act, out_conv_act_attr):
|
||||
super(SingleDecoder, self).__init__()
|
||||
conv_blocks = []
|
||||
for i in range(conv_block_num):
|
||||
conv_blocks.append(
|
||||
ResBlock(
|
||||
name="{}_conv_block_{}".format(name, i),
|
||||
channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
use_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias))
|
||||
self._conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(*conv_blocks)
|
||||
self._up1 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up2 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 8,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up3 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up3",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
output_padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._pad2d = paddle.nn.Pad2D([1, 1, 1, 1], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._out_conv = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_out_conv",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=out_channels,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=None,
|
||||
act=out_conv_act,
|
||||
act_attr=out_conv_act_attr)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x, feature2, feature1):
|
||||
output_dict = dict()
|
||||
output_dict["conv_blocks"] = self._conv_blocks.forward(x)
|
||||
output_dict["up1"] = self._up1.forward(output_dict["conv_blocks"])
|
||||
output_dict["up2"] = self._up2.forward(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict["up1"], feature2), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict["up3"] = self._up3.forward(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict["up2"], feature1), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict["pad2d"] = self._pad2d.forward(output_dict["up3"])
|
||||
output_dict["out_conv"] = self._out_conv.forward(output_dict["pad2d"])
|
||||
return output_dict
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import paddle.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from arch.base_module import SNConv, SNConvTranspose, ResBlock
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Encoder(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, in_channels, encode_dim, use_bias, norm_layer,
|
||||
act, act_attr, conv_block_dropout, conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation):
|
||||
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
|
||||
self._pad2d = paddle.nn.Pad2D([3, 3, 3, 3], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._in_conv = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_in_conv",
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=7,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down1 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down2 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down3 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down3",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
conv_blocks = []
|
||||
for i in range(conv_block_num):
|
||||
conv_blocks.append(
|
||||
ResBlock(
|
||||
name="{}_conv_block_{}".format(name, i),
|
||||
channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
use_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias))
|
||||
self._conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(*conv_blocks)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
out_dict = dict()
|
||||
x = self._pad2d(x)
|
||||
out_dict["in_conv"] = self._in_conv.forward(x)
|
||||
out_dict["down1"] = self._down1.forward(out_dict["in_conv"])
|
||||
out_dict["down2"] = self._down2.forward(out_dict["down1"])
|
||||
out_dict["down3"] = self._down3.forward(out_dict["down2"])
|
||||
out_dict["res_blocks"] = self._conv_blocks.forward(out_dict["down3"])
|
||||
return out_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EncoderUnet(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, in_channels, encode_dim, use_bias, norm_layer,
|
||||
act, act_attr):
|
||||
super(EncoderUnet, self).__init__()
|
||||
self._pad2d = paddle.nn.Pad2D([3, 3, 3, 3], mode="replicate")
|
||||
self._in_conv = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_in_conv",
|
||||
in_channels=in_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=7,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down1 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down2 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down3 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down3",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._down4 = SNConv(
|
||||
name=name + "_down4",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up1 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up1",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 2,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
self._up2 = SNConvTranspose(
|
||||
name=name + "_up2",
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim * 4,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=2,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act=act,
|
||||
act_attr=act_attr)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
output_dict = dict()
|
||||
x = self._pad2d(x)
|
||||
output_dict['in_conv'] = self._in_conv.forward(x)
|
||||
output_dict['down1'] = self._down1.forward(output_dict['in_conv'])
|
||||
output_dict['down2'] = self._down2.forward(output_dict['down1'])
|
||||
output_dict['down3'] = self._down3.forward(output_dict['down2'])
|
||||
output_dict['down4'] = self._down4.forward(output_dict['down3'])
|
||||
output_dict['up1'] = self._up1.forward(output_dict['down4'])
|
||||
output_dict['up2'] = self._up2.forward(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict['down3'], output_dict['up1']), axis=1))
|
||||
output_dict['concat'] = paddle.concat(
|
||||
(output_dict['down2'], output_dict['up2']), axis=1)
|
||||
return output_dict
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import paddle.nn as nn
|
||||
import paddle.nn.functional as F
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def normal_(x, mean=0., std=1.):
|
||||
temp_value = paddle.normal(mean, std, shape=x.shape)
|
||||
x.set_value(temp_value)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SpectralNorm(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, name='weight', n_power_iterations=1, dim=0, eps=1e-12):
|
||||
self.name = name
|
||||
self.dim = dim
|
||||
if n_power_iterations <= 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError('Expected n_power_iterations to be positive, but '
|
||||
'got n_power_iterations={}'.format(
|
||||
n_power_iterations))
|
||||
self.n_power_iterations = n_power_iterations
|
||||
self.eps = eps
|
||||
|
||||
def reshape_weight_to_matrix(self, weight):
|
||||
weight_mat = weight
|
||||
if self.dim != 0:
|
||||
# transpose dim to front
|
||||
weight_mat = weight_mat.transpose([
|
||||
self.dim,
|
||||
* [d for d in range(weight_mat.dim()) if d != self.dim]
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
height = weight_mat.shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
return weight_mat.reshape([height, -1])
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_weight(self, module, do_power_iteration):
|
||||
weight = getattr(module, self.name + '_orig')
|
||||
u = getattr(module, self.name + '_u')
|
||||
v = getattr(module, self.name + '_v')
|
||||
weight_mat = self.reshape_weight_to_matrix(weight)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_power_iteration:
|
||||
with paddle.no_grad():
|
||||
for _ in range(self.n_power_iterations):
|
||||
v.set_value(
|
||||
F.normalize(
|
||||
paddle.matmul(
|
||||
weight_mat,
|
||||
u,
|
||||
transpose_x=True,
|
||||
transpose_y=False),
|
||||
axis=0,
|
||||
epsilon=self.eps, ))
|
||||
|
||||
u.set_value(
|
||||
F.normalize(
|
||||
paddle.matmul(weight_mat, v),
|
||||
axis=0,
|
||||
epsilon=self.eps, ))
|
||||
if self.n_power_iterations > 0:
|
||||
u = u.clone()
|
||||
v = v.clone()
|
||||
|
||||
sigma = paddle.dot(u, paddle.mv(weight_mat, v))
|
||||
weight = weight / sigma
|
||||
return weight
|
||||
|
||||
def remove(self, module):
|
||||
with paddle.no_grad():
|
||||
weight = self.compute_weight(module, do_power_iteration=False)
|
||||
delattr(module, self.name)
|
||||
delattr(module, self.name + '_u')
|
||||
delattr(module, self.name + '_v')
|
||||
delattr(module, self.name + '_orig')
|
||||
|
||||
module.add_parameter(self.name, weight.detach())
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, module, inputs):
|
||||
setattr(
|
||||
module,
|
||||
self.name,
|
||||
self.compute_weight(
|
||||
module, do_power_iteration=module.training))
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def apply(module, name, n_power_iterations, dim, eps):
|
||||
for k, hook in module._forward_pre_hooks.items():
|
||||
if isinstance(hook, SpectralNorm) and hook.name == name:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(
|
||||
"Cannot register two spectral_norm hooks on "
|
||||
"the same parameter {}".format(name))
|
||||
|
||||
fn = SpectralNorm(name, n_power_iterations, dim, eps)
|
||||
weight = module._parameters[name]
|
||||
|
||||
with paddle.no_grad():
|
||||
weight_mat = fn.reshape_weight_to_matrix(weight)
|
||||
h, w = weight_mat.shape
|
||||
|
||||
# randomly initialize u and v
|
||||
u = module.create_parameter([h])
|
||||
u = normal_(u, 0., 1.)
|
||||
v = module.create_parameter([w])
|
||||
v = normal_(v, 0., 1.)
|
||||
u = F.normalize(u, axis=0, epsilon=fn.eps)
|
||||
v = F.normalize(v, axis=0, epsilon=fn.eps)
|
||||
|
||||
# delete fn.name form parameters, otherwise you can not set attribute
|
||||
del module._parameters[fn.name]
|
||||
module.add_parameter(fn.name + "_orig", weight)
|
||||
# still need to assign weight back as fn.name because all sorts of
|
||||
# things may assume that it exists, e.g., when initializing weights.
|
||||
# However, we can't directly assign as it could be an Parameter and
|
||||
# gets added as a parameter. Instead, we register weight * 1.0 as a plain
|
||||
# attribute.
|
||||
setattr(module, fn.name, weight * 1.0)
|
||||
module.register_buffer(fn.name + "_u", u)
|
||||
module.register_buffer(fn.name + "_v", v)
|
||||
|
||||
module.register_forward_pre_hook(fn)
|
||||
return fn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def spectral_norm(module,
|
||||
name='weight',
|
||||
n_power_iterations=1,
|
||||
eps=1e-12,
|
||||
dim=None):
|
||||
|
||||
if dim is None:
|
||||
if isinstance(module, (nn.Conv1DTranspose, nn.Conv2DTranspose,
|
||||
nn.Conv3DTranspose, nn.Linear)):
|
||||
dim = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dim = 0
|
||||
SpectralNorm.apply(module, name, n_power_iterations, dim, eps)
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,285 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import paddle.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from arch.base_module import MiddleNet, ResBlock
|
||||
from arch.encoder import Encoder
|
||||
from arch.decoder import Decoder, DecoderUnet, SingleDecoder
|
||||
from utils.load_params import load_dygraph_pretrain
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class StyleTextRec(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super(StyleTextRec, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.text_generator = TextGenerator(config["Predictor"][
|
||||
"text_generator"])
|
||||
self.bg_generator = BgGeneratorWithMask(config["Predictor"][
|
||||
"bg_generator"])
|
||||
self.fusion_generator = FusionGeneratorSimple(config["Predictor"][
|
||||
"fusion_generator"])
|
||||
bg_generator_pretrain = config["Predictor"]["bg_generator"]["pretrain"]
|
||||
text_generator_pretrain = config["Predictor"]["text_generator"][
|
||||
"pretrain"]
|
||||
fusion_generator_pretrain = config["Predictor"]["fusion_generator"][
|
||||
"pretrain"]
|
||||
load_dygraph_pretrain(
|
||||
self.bg_generator,
|
||||
self.logger,
|
||||
path=bg_generator_pretrain,
|
||||
load_static_weights=False)
|
||||
load_dygraph_pretrain(
|
||||
self.text_generator,
|
||||
self.logger,
|
||||
path=text_generator_pretrain,
|
||||
load_static_weights=False)
|
||||
load_dygraph_pretrain(
|
||||
self.fusion_generator,
|
||||
self.logger,
|
||||
path=fusion_generator_pretrain,
|
||||
load_static_weights=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, style_input, text_input):
|
||||
text_gen_output = self.text_generator.forward(style_input, text_input)
|
||||
fake_text = text_gen_output["fake_text"]
|
||||
fake_sk = text_gen_output["fake_sk"]
|
||||
bg_gen_output = self.bg_generator.forward(style_input)
|
||||
bg_encode_feature = bg_gen_output["bg_encode_feature"]
|
||||
bg_decode_feature1 = bg_gen_output["bg_decode_feature1"]
|
||||
bg_decode_feature2 = bg_gen_output["bg_decode_feature2"]
|
||||
fake_bg = bg_gen_output["fake_bg"]
|
||||
|
||||
fusion_gen_output = self.fusion_generator.forward(fake_text, fake_bg)
|
||||
fake_fusion = fusion_gen_output["fake_fusion"]
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"fake_fusion": fake_fusion,
|
||||
"fake_text": fake_text,
|
||||
"fake_sk": fake_sk,
|
||||
"fake_bg": fake_bg,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TextGenerator(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super(TextGenerator, self).__init__()
|
||||
name = config["module_name"]
|
||||
encode_dim = config["encode_dim"]
|
||||
norm_layer = config["norm_layer"]
|
||||
conv_block_dropout = config["conv_block_dropout"]
|
||||
conv_block_num = config["conv_block_num"]
|
||||
conv_block_dilation = config["conv_block_dilation"]
|
||||
if norm_layer == "InstanceNorm2D":
|
||||
use_bias = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
use_bias = False
|
||||
self.encoder_text = Encoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_encoder_text",
|
||||
in_channels=3,
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation)
|
||||
self.encoder_style = Encoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_encoder_style",
|
||||
in_channels=3,
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation)
|
||||
self.decoder_text = Decoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_decoder_text",
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=int(encode_dim / 2),
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
out_conv_act="Tanh",
|
||||
out_conv_act_attr=None)
|
||||
self.decoder_sk = Decoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_decoder_sk",
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
out_conv_act="Sigmoid",
|
||||
out_conv_act_attr=None)
|
||||
|
||||
self.middle = MiddleNet(
|
||||
name=name + "_middle_net",
|
||||
in_channels=int(encode_dim / 2) + 1,
|
||||
mid_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, style_input, text_input):
|
||||
style_feature = self.encoder_style.forward(style_input)["res_blocks"]
|
||||
text_feature = self.encoder_text.forward(text_input)["res_blocks"]
|
||||
fake_c_temp = self.decoder_text.forward([text_feature,
|
||||
style_feature])["out_conv"]
|
||||
fake_sk = self.decoder_sk.forward([text_feature,
|
||||
style_feature])["out_conv"]
|
||||
fake_text = self.middle(paddle.concat((fake_c_temp, fake_sk), axis=1))
|
||||
return {"fake_sk": fake_sk, "fake_text": fake_text}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BgGeneratorWithMask(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super(BgGeneratorWithMask, self).__init__()
|
||||
name = config["module_name"]
|
||||
encode_dim = config["encode_dim"]
|
||||
norm_layer = config["norm_layer"]
|
||||
conv_block_dropout = config["conv_block_dropout"]
|
||||
conv_block_num = config["conv_block_num"]
|
||||
conv_block_dilation = config["conv_block_dilation"]
|
||||
self.output_factor = config.get("output_factor", 1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
if norm_layer == "InstanceNorm2D":
|
||||
use_bias = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
use_bias = False
|
||||
|
||||
self.encoder_bg = Encoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_encoder_bg",
|
||||
in_channels=3,
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation)
|
||||
|
||||
self.decoder_bg = SingleDecoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_decoder_bg",
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
out_conv_act="Tanh",
|
||||
out_conv_act_attr=None)
|
||||
|
||||
self.decoder_mask = Decoder(
|
||||
name=name + "_decoder_mask",
|
||||
encode_dim=encode_dim // 2,
|
||||
out_channels=1,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
act="ReLU",
|
||||
act_attr=None,
|
||||
conv_block_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
conv_block_num=conv_block_num,
|
||||
conv_block_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
out_conv_act="Sigmoid",
|
||||
out_conv_act_attr=None)
|
||||
|
||||
self.middle = MiddleNet(
|
||||
name=name + "_middle_net",
|
||||
in_channels=3 + 1,
|
||||
mid_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=3,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, style_input):
|
||||
encode_bg_output = self.encoder_bg(style_input)
|
||||
decode_bg_output = self.decoder_bg(encode_bg_output["res_blocks"],
|
||||
encode_bg_output["down2"],
|
||||
encode_bg_output["down1"])
|
||||
|
||||
fake_c_temp = decode_bg_output["out_conv"]
|
||||
fake_bg_mask = self.decoder_mask.forward(encode_bg_output[
|
||||
"res_blocks"])["out_conv"]
|
||||
fake_bg = self.middle(
|
||||
paddle.concat(
|
||||
(fake_c_temp, fake_bg_mask), axis=1))
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"bg_encode_feature": encode_bg_output["res_blocks"],
|
||||
"bg_decode_feature1": decode_bg_output["up1"],
|
||||
"bg_decode_feature2": decode_bg_output["up2"],
|
||||
"fake_bg": fake_bg,
|
||||
"fake_bg_mask": fake_bg_mask,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FusionGeneratorSimple(nn.Layer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super(FusionGeneratorSimple, self).__init__()
|
||||
name = config["module_name"]
|
||||
encode_dim = config["encode_dim"]
|
||||
norm_layer = config["norm_layer"]
|
||||
conv_block_dropout = config["conv_block_dropout"]
|
||||
conv_block_dilation = config["conv_block_dilation"]
|
||||
if norm_layer == "InstanceNorm2D":
|
||||
use_bias = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
use_bias = False
|
||||
|
||||
self._conv = nn.Conv2D(
|
||||
in_channels=6,
|
||||
out_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
groups=1,
|
||||
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_conv_weights"),
|
||||
bias_attr=False)
|
||||
|
||||
self._res_block = ResBlock(
|
||||
name="{}_conv_block".format(name),
|
||||
channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
norm_layer=norm_layer,
|
||||
use_dropout=conv_block_dropout,
|
||||
use_dilation=conv_block_dilation,
|
||||
use_bias=use_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
self._reduce_conv = nn.Conv2D(
|
||||
in_channels=encode_dim,
|
||||
out_channels=3,
|
||||
kernel_size=3,
|
||||
stride=1,
|
||||
padding=1,
|
||||
groups=1,
|
||||
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(name=name + "_reduce_conv_weights"),
|
||||
bias_attr=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, fake_text, fake_bg):
|
||||
fake_concat = paddle.concat((fake_text, fake_bg), axis=1)
|
||||
fake_concat_tmp = self._conv(fake_concat)
|
||||
output_res = self._res_block(fake_concat_tmp)
|
||||
fake_fusion = self._reduce_conv(output_res)
|
||||
return {"fake_fusion": fake_fusion}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
output_num: 10
|
||||
output_dir: output_data
|
||||
use_gpu: false
|
||||
image_height: 32
|
||||
image_width: 320
|
||||
TextDrawer:
|
||||
fonts:
|
||||
en: fonts/en_standard.ttf
|
||||
ch: fonts/ch_standard.ttf
|
||||
ko: fonts/ko_standard.ttf
|
||||
Predictor:
|
||||
method: StyleTextRecPredictor
|
||||
algorithm: StyleTextRec
|
||||
scale: 0.00392156862745098
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
expand_result: false
|
||||
bg_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/bg_generator
|
||||
module_name: bg_generator
|
||||
generator_type: BgGeneratorWithMask
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: null
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
output_factor: 1.05
|
||||
text_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/text_generator
|
||||
module_name: text_generator
|
||||
generator_type: TextGenerator
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: InstanceNorm2D
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
fusion_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/fusion_generator
|
||||
module_name: fusion_generator
|
||||
generator_type: FusionGeneratorSimple
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: null
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
Writer:
|
||||
method: SimpleWriter
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
|||
Global:
|
||||
output_num: 10
|
||||
output_dir: output_data
|
||||
use_gpu: false
|
||||
image_height: 32
|
||||
image_width: 320
|
||||
standard_font: fonts/en_standard.ttf
|
||||
TextDrawer:
|
||||
fonts:
|
||||
en: fonts/en_standard.ttf
|
||||
ch: fonts/ch_standard.ttf
|
||||
ko: fonts/ko_standard.ttf
|
||||
StyleSampler:
|
||||
method: DatasetSampler
|
||||
image_home: examples
|
||||
label_file: examples/image_list.txt
|
||||
with_label: true
|
||||
CorpusGenerator:
|
||||
method: FileCorpus
|
||||
language: ch
|
||||
corpus_file: examples/corpus/example.txt
|
||||
Predictor:
|
||||
method: StyleTextRecPredictor
|
||||
algorithm: StyleTextRec
|
||||
scale: 0.00392156862745098
|
||||
mean:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
std:
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
- 0.5
|
||||
expand_result: false
|
||||
bg_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/bg_generator
|
||||
module_name: bg_generator
|
||||
generator_type: BgGeneratorWithMask
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: null
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
output_factor: 1.05
|
||||
text_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/text_generator
|
||||
module_name: text_generator
|
||||
generator_type: TextGenerator
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: InstanceNorm2D
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
fusion_generator:
|
||||
pretrain: style_text_models/fusion_generator
|
||||
module_name: fusion_generator
|
||||
generator_type: FusionGeneratorSimple
|
||||
encode_dim: 64
|
||||
norm_layer: null
|
||||
conv_block_num: 4
|
||||
conv_block_dropout: false
|
||||
conv_block_dilation: true
|
||||
Writer:
|
||||
method: SimpleWriter
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 168 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 192 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 126 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 148 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 201 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 68 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.6 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 118 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 125 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.5 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.4 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 154 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FileCorpus(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.logger.info("using FileCorpus")
|
||||
|
||||
self.char_list = " 0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
|
||||
|
||||
corpus_file = config["CorpusGenerator"]["corpus_file"]
|
||||
self.language = config["CorpusGenerator"]["language"]
|
||||
with open(corpus_file, 'r') as f:
|
||||
corpus_raw = f.read()
|
||||
self.corpus_list = corpus_raw.split("\n")[:-1]
|
||||
assert len(self.corpus_list) > 0
|
||||
random.shuffle(self.corpus_list)
|
||||
self.index = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(self, corpus_length=0):
|
||||
if self.index >= len(self.corpus_list):
|
||||
self.index = 0
|
||||
random.shuffle(self.corpus_list)
|
||||
corpus = self.corpus_list[self.index]
|
||||
if corpus_length != 0:
|
||||
corpus = corpus[0:corpus_length]
|
||||
if corpus_length > len(corpus):
|
||||
self.logger.warning("generated corpus is shorter than expected.")
|
||||
self.index += 1
|
||||
return self.language, corpus
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EnNumCorpus(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.logger.info("using NumberCorpus")
|
||||
self.num_list = "0123456789"
|
||||
self.en_char_list = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
|
||||
self.height = config["Global"]["image_height"]
|
||||
self.max_width = config["Global"]["image_width"]
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(self, corpus_length=0):
|
||||
corpus = ""
|
||||
if corpus_length == 0:
|
||||
corpus_length = random.randint(5, 15)
|
||||
for i in range(corpus_length):
|
||||
if random.random() < 0.2:
|
||||
corpus += "{}".format(random.choice(self.en_char_list))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
corpus += "{}".format(random.choice(self.num_list))
|
||||
return "en", corpus
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
from arch import style_text_rec
|
||||
from utils.sys_funcs import check_gpu
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class StyleTextRecPredictor(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
algorithm = config['Predictor']['algorithm']
|
||||
assert algorithm in ["StyleTextRec"
|
||||
], "Generator {} not supported.".format(algorithm)
|
||||
use_gpu = config["Global"]['use_gpu']
|
||||
check_gpu(use_gpu)
|
||||
paddle.set_device('gpu' if use_gpu else 'cpu')
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.generator = getattr(style_text_rec, algorithm)(config)
|
||||
self.height = config["Global"]["image_height"]
|
||||
self.width = config["Global"]["image_width"]
|
||||
self.scale = config["Predictor"]["scale"]
|
||||
self.mean = config["Predictor"]["mean"]
|
||||
self.std = config["Predictor"]["std"]
|
||||
self.expand_result = config["Predictor"]["expand_result"]
|
||||
|
||||
def reshape_to_same_height(self, img_list):
|
||||
h = img_list[0].shape[0]
|
||||
for idx in range(1, len(img_list)):
|
||||
new_w = round(1.0 * img_list[idx].shape[1] /
|
||||
img_list[idx].shape[0] * h)
|
||||
img_list[idx] = cv2.resize(img_list[idx], (new_w, h))
|
||||
return img_list
|
||||
|
||||
def predict_single_image(self, style_input, text_input):
|
||||
style_input = self.rep_style_input(style_input, text_input)
|
||||
tensor_style_input = self.preprocess(style_input)
|
||||
tensor_text_input = self.preprocess(text_input)
|
||||
style_text_result = self.generator.forward(tensor_style_input,
|
||||
tensor_text_input)
|
||||
fake_fusion = self.postprocess(style_text_result["fake_fusion"])
|
||||
fake_text = self.postprocess(style_text_result["fake_text"])
|
||||
fake_sk = self.postprocess(style_text_result["fake_sk"])
|
||||
fake_bg = self.postprocess(style_text_result["fake_bg"])
|
||||
bbox = self.get_text_boundary(fake_text)
|
||||
if bbox:
|
||||
left, right, top, bottom = bbox
|
||||
fake_fusion = fake_fusion[top:bottom, left:right, :]
|
||||
fake_text = fake_text[top:bottom, left:right, :]
|
||||
fake_sk = fake_sk[top:bottom, left:right, :]
|
||||
fake_bg = fake_bg[top:bottom, left:right, :]
|
||||
|
||||
# fake_fusion = self.crop_by_text(img_fake_fusion, img_fake_text)
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"fake_fusion": fake_fusion,
|
||||
"fake_text": fake_text,
|
||||
"fake_sk": fake_sk,
|
||||
"fake_bg": fake_bg,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def predict(self, style_input, text_input_list):
|
||||
if not isinstance(text_input_list, (tuple, list)):
|
||||
return self.predict_single_image(style_input, text_input_list)
|
||||
|
||||
synth_result_list = []
|
||||
for text_input in text_input_list:
|
||||
synth_result = self.predict_single_image(style_input, text_input)
|
||||
synth_result_list.append(synth_result)
|
||||
|
||||
for key in synth_result:
|
||||
res = [r[key] for r in synth_result_list]
|
||||
res = self.reshape_to_same_height(res)
|
||||
synth_result[key] = np.concatenate(res, axis=1)
|
||||
return synth_result
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, img):
|
||||
img = (img.astype('float32') * self.scale - self.mean) / self.std
|
||||
img_height, img_width, channel = img.shape
|
||||
assert channel == 3, "Please use an rgb image."
|
||||
ratio = img_width / float(img_height)
|
||||
if math.ceil(self.height * ratio) > self.width:
|
||||
resized_w = self.width
|
||||
else:
|
||||
resized_w = int(math.ceil(self.height * ratio))
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(img, (resized_w, self.height))
|
||||
|
||||
new_img = np.zeros([self.height, self.width, 3]).astype('float32')
|
||||
new_img[:, 0:resized_w, :] = img
|
||||
img = new_img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
|
||||
img = img[np.newaxis, :, :, :]
|
||||
return paddle.to_tensor(img)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, tensor):
|
||||
img = tensor.numpy()[0]
|
||||
img = img.transpose((1, 2, 0))
|
||||
img = (img * self.std + self.mean) / self.scale
|
||||
img = np.maximum(img, 0.0)
|
||||
img = np.minimum(img, 255.0)
|
||||
img = img.astype('uint8')
|
||||
return img
|
||||
|
||||
def rep_style_input(self, style_input, text_input):
|
||||
rep_num = int(1.2 * (text_input.shape[1] / text_input.shape[0]) /
|
||||
(style_input.shape[1] / style_input.shape[0])) + 1
|
||||
style_input = np.tile(style_input, reps=[1, rep_num, 1])
|
||||
max_width = int(self.width / self.height * style_input.shape[0])
|
||||
style_input = style_input[:, :max_width, :]
|
||||
return style_input
|
||||
|
||||
def get_text_boundary(self, text_img):
|
||||
img_height = text_img.shape[0]
|
||||
img_width = text_img.shape[1]
|
||||
bounder = 3
|
||||
text_canny_img = cv2.Canny(text_img, 10, 20)
|
||||
edge_num_h = text_canny_img.sum(axis=0)
|
||||
no_zero_list_h = np.where(edge_num_h > 0)[0]
|
||||
edge_num_w = text_canny_img.sum(axis=1)
|
||||
no_zero_list_w = np.where(edge_num_w > 0)[0]
|
||||
if len(no_zero_list_h) == 0 or len(no_zero_list_w) == 0:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
left = max(no_zero_list_h[0] - bounder, 0)
|
||||
right = min(no_zero_list_h[-1] + bounder, img_width)
|
||||
top = max(no_zero_list_w[0] - bounder, 0)
|
||||
bottom = min(no_zero_list_w[-1] + bounder, img_height)
|
||||
return [left, right, top, bottom]
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DatasetSampler(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
self.image_home = config["StyleSampler"]["image_home"]
|
||||
label_file = config["StyleSampler"]["label_file"]
|
||||
self.dataset_with_label = config["StyleSampler"]["with_label"]
|
||||
self.height = config["Global"]["image_height"]
|
||||
self.index = 0
|
||||
with open(label_file, "r") as f:
|
||||
label_raw = f.read()
|
||||
self.path_label_list = label_raw.split("\n")[:-1]
|
||||
assert len(self.path_label_list) > 0
|
||||
random.shuffle(self.path_label_list)
|
||||
|
||||
def sample(self):
|
||||
if self.index >= len(self.path_label_list):
|
||||
random.shuffle(self.path_label_list)
|
||||
self.index = 0
|
||||
if self.dataset_with_label:
|
||||
path_label = self.path_label_list[self.index]
|
||||
rel_image_path, label = path_label.split('\t')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
rel_image_path = self.path_label_list[self.index]
|
||||
label = None
|
||||
img_path = "{}/{}".format(self.image_home, rel_image_path)
|
||||
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
|
||||
origin_height = image.shape[0]
|
||||
ratio = self.height / origin_height
|
||||
width = int(image.shape[1] * ratio)
|
||||
height = int(image.shape[0] * ratio)
|
||||
image = cv2.resize(image, (width, height))
|
||||
|
||||
self.index += 1
|
||||
if label:
|
||||
return {"image": image, "label": label}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return {"image": image}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def duplicate_image(image, width):
|
||||
image_width = image.shape[1]
|
||||
dup_num = width // image_width + 1
|
||||
image = np.tile(image, reps=[1, dup_num, 1])
|
||||
cropped_image = image[:, :width, :]
|
||||
return cropped_image
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
from utils.config import ArgsParser, load_config, override_config
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
from engine import style_samplers, corpus_generators, text_drawers, predictors, writers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImageSynthesiser(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.FLAGS = ArgsParser().parse_args()
|
||||
self.config = load_config(self.FLAGS.config)
|
||||
self.config = override_config(self.config, options=self.FLAGS.override)
|
||||
self.output_dir = self.config["Global"]["output_dir"]
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(self.output_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(self.output_dir)
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger(
|
||||
log_file='{}/predict.log'.format(self.output_dir))
|
||||
|
||||
self.text_drawer = text_drawers.StdTextDrawer(self.config)
|
||||
|
||||
predictor_method = self.config["Predictor"]["method"]
|
||||
assert predictor_method is not None
|
||||
self.predictor = getattr(predictors, predictor_method)(self.config)
|
||||
|
||||
def synth_image(self, corpus, style_input, language="en"):
|
||||
corpus_list, text_input_list = self.text_drawer.draw_text(
|
||||
corpus, language, style_input_width=style_input.shape[1])
|
||||
synth_result = self.predictor.predict(style_input, text_input_list)
|
||||
return synth_result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DatasetSynthesiser(ImageSynthesiser):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(DatasetSynthesiser, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.tag = self.FLAGS.tag
|
||||
self.output_num = self.config["Global"]["output_num"]
|
||||
corpus_generator_method = self.config["CorpusGenerator"]["method"]
|
||||
self.corpus_generator = getattr(corpus_generators,
|
||||
corpus_generator_method)(self.config)
|
||||
|
||||
style_sampler_method = self.config["StyleSampler"]["method"]
|
||||
assert style_sampler_method is not None
|
||||
self.style_sampler = style_samplers.DatasetSampler(self.config)
|
||||
self.writer = writers.SimpleWriter(self.config, self.tag)
|
||||
|
||||
def synth_dataset(self):
|
||||
for i in range(self.output_num):
|
||||
style_data = self.style_sampler.sample()
|
||||
style_input = style_data["image"]
|
||||
corpus_language, text_input_label = self.corpus_generator.generate()
|
||||
text_input_label_list, text_input_list = self.text_drawer.draw_text(
|
||||
text_input_label,
|
||||
corpus_language,
|
||||
style_input_width=style_input.shape[1])
|
||||
|
||||
text_input_label = "".join(text_input_label_list)
|
||||
|
||||
synth_result = self.predictor.predict(style_input, text_input_list)
|
||||
fake_fusion = synth_result["fake_fusion"]
|
||||
self.writer.save_image(fake_fusion, text_input_label)
|
||||
self.writer.save_label()
|
||||
self.writer.merge_label()
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
|||
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class StdTextDrawer(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.max_width = config["Global"]["image_width"]
|
||||
self.char_list = " 0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
|
||||
self.height = config["Global"]["image_height"]
|
||||
self.font_dict = {}
|
||||
self.load_fonts(config["TextDrawer"]["fonts"])
|
||||
self.support_languages = list(self.font_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_fonts(self, fonts_config):
|
||||
for language in fonts_config:
|
||||
font_path = fonts_config[language]
|
||||
font_height = self.get_valid_height(font_path)
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_height)
|
||||
self.font_dict[language] = font
|
||||
|
||||
def get_valid_height(self, font_path):
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, self.height - 4)
|
||||
left, top, right, bottom = font.getbbox(self.char_list)
|
||||
_, font_height = right - left, bottom - top
|
||||
if font_height <= self.height - 4:
|
||||
return self.height - 4
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return int((self.height - 4)**2 / font_height)
|
||||
|
||||
def draw_text(self,
|
||||
corpus,
|
||||
language="en",
|
||||
crop=True,
|
||||
style_input_width=None):
|
||||
if language not in self.support_languages:
|
||||
self.logger.warning(
|
||||
"language {} not supported, use en instead.".format(language))
|
||||
language = "en"
|
||||
if crop:
|
||||
width = min(self.max_width, len(corpus) * self.height) + 4
|
||||
else:
|
||||
width = len(corpus) * self.height + 4
|
||||
|
||||
if style_input_width is not None:
|
||||
width = min(width, style_input_width)
|
||||
|
||||
corpus_list = []
|
||||
text_input_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
while len(corpus) != 0:
|
||||
bg = Image.new("RGB", (width, self.height), color=(127, 127, 127))
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(bg)
|
||||
char_x = 2
|
||||
font = self.font_dict[language]
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
while i < len(corpus):
|
||||
char_i = corpus[i]
|
||||
char_size = font.getsize(char_i)[0]
|
||||
# split when char_x exceeds char size and index is not 0 (at least 1 char should be wroten on the image)
|
||||
if char_x + char_size >= width and i != 0:
|
||||
text_input = np.array(bg).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
text_input = text_input[:, 0:char_x, :]
|
||||
|
||||
corpus_list.append(corpus[0:i])
|
||||
text_input_list.append(text_input)
|
||||
corpus = corpus[i:]
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
break
|
||||
draw.text((char_x, 2), char_i, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
|
||||
char_x += char_size
|
||||
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
# the whole text is shorter than style input
|
||||
if i == len(corpus):
|
||||
text_input = np.array(bg).astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
text_input = text_input[:, 0:char_x, :]
|
||||
|
||||
corpus_list.append(corpus[0:i])
|
||||
text_input_list.append(text_input)
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
return corpus_list, text_input_list
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import glob
|
||||
|
||||
from utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SimpleWriter(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config, tag):
|
||||
self.logger = get_logger()
|
||||
self.output_dir = config["Global"]["output_dir"]
|
||||
self.counter = 0
|
||||
self.label_dict = {}
|
||||
self.tag = tag
|
||||
self.label_file_index = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def save_image(self, image, text_input_label):
|
||||
image_home = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "images", self.tag)
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(image_home):
|
||||
os.makedirs(image_home)
|
||||
|
||||
image_path = os.path.join(image_home, "{}.png".format(self.counter))
|
||||
# todo support continue synth
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(image_path, image)
|
||||
self.logger.info("generate image: {}".format(image_path))
|
||||
|
||||
image_name = os.path.join(self.tag, "{}.png".format(self.counter))
|
||||
self.label_dict[image_name] = text_input_label
|
||||
|
||||
self.counter += 1
|
||||
if not self.counter % 100:
|
||||
self.save_label()
|
||||
|
||||
def save_label(self):
|
||||
label_raw = ""
|
||||
label_home = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "label")
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(label_home):
|
||||
os.mkdir(label_home)
|
||||
for image_path in self.label_dict:
|
||||
label = self.label_dict[image_path]
|
||||
label_raw += "{}\t{}\n".format(image_path, label)
|
||||
label_file_path = os.path.join(label_home,
|
||||
"{}_label.txt".format(self.tag))
|
||||
with open(label_file_path, "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(label_raw)
|
||||
self.label_file_index += 1
|
||||
|
||||
def merge_label(self):
|
||||
label_raw = ""
|
||||
label_file_regex = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "label",
|
||||
"*_label.txt")
|
||||
label_file_list = glob.glob(label_file_regex)
|
||||
for label_file_i in label_file_list:
|
||||
with open(label_file_i, "r") as f:
|
||||
label_raw += f.read()
|
||||
label_file_path = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "label.txt")
|
||||
with open(label_file_path, "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(label_raw)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
Paddle
|
||||
飞桨文字识别
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
style_images/1.jpg NEATNESS
|
||||
style_images/2.jpg 锁店君和宾馆
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.5 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.3 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
__dir__ = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
|
||||
sys.path.append(__dir__)
|
||||
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(__dir__, '..')))
|
||||
|
||||
from engine.synthesisers import DatasetSynthesiser
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def synth_dataset():
|
||||
dataset_synthesiser = DatasetSynthesiser()
|
||||
dataset_synthesiser.synth_dataset()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
synth_dataset()
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import glob
|
||||
|
||||
__dir__ = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
|
||||
sys.path.append(__dir__)
|
||||
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(__dir__, '..')))
|
||||
|
||||
from utils.config import ArgsParser
|
||||
from engine.synthesisers import ImageSynthesiser
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def synth_image():
|
||||
args = ArgsParser().parse_args()
|
||||
image_synthesiser = ImageSynthesiser()
|
||||
style_image_path = args.style_image
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(style_image_path)
|
||||
text_corpus = args.text_corpus
|
||||
language = args.language
|
||||
|
||||
synth_result = image_synthesiser.synth_image(text_corpus, img, language)
|
||||
fake_fusion = synth_result["fake_fusion"]
|
||||
fake_text = synth_result["fake_text"]
|
||||
fake_bg = synth_result["fake_bg"]
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("fake_fusion.jpg", fake_fusion)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("fake_text.jpg", fake_text)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("fake_bg.jpg", fake_bg)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def batch_synth_images():
|
||||
image_synthesiser = ImageSynthesiser()
|
||||
|
||||
corpus_file = "../StyleTextRec_data/test_20201208/test_text_list.txt"
|
||||
style_data_dir = "../StyleTextRec_data/test_20201208/style_images/"
|
||||
save_path = "./output_data/"
|
||||
corpus_list = []
|
||||
with open(corpus_file, "rb") as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
substr = line.decode("utf-8").strip("\n").split("\t")
|
||||
corpus_list.append(substr)
|
||||
style_img_list = glob.glob("{}/*.jpg".format(style_data_dir))
|
||||
corpus_num = len(corpus_list)
|
||||
style_img_num = len(style_img_list)
|
||||
for cno in range(corpus_num):
|
||||
for sno in range(style_img_num):
|
||||
corpus, lang = corpus_list[cno]
|
||||
style_img_path = style_img_list[sno]
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(style_img_path)
|
||||
synth_result = image_synthesiser.synth_image(corpus, img, lang)
|
||||
fake_fusion = synth_result["fake_fusion"]
|
||||
fake_text = synth_result["fake_text"]
|
||||
fake_bg = synth_result["fake_bg"]
|
||||
for tp in range(2):
|
||||
if tp == 0:
|
||||
prefix = "%s/c%d_s%d_" % (save_path, cno, sno)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
prefix = "%s/s%d_c%d_" % (save_path, sno, cno)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("%s_fake_fusion.jpg" % prefix, fake_fusion)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("%s_fake_text.jpg" % prefix, fake_text)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("%s_fake_bg.jpg" % prefix, fake_bg)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite("%s_input_style.jpg" % prefix, img)
|
||||
print(cno, corpus_num, sno, style_img_num)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
# batch_synth_images()
|
||||
synth_image()
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import yaml
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from argparse import ArgumentParser, RawDescriptionHelpFormatter
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def override(dl, ks, v):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursively replace dict of list
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
dl(dict or list): dict or list to be replaced
|
||||
ks(list): list of keys
|
||||
v(str): value to be replaced
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def str2num(v):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return eval(v)
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
return v
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(dl, (list, dict)), ("{} should be a list or a dict")
|
||||
assert len(ks) > 0, ('lenght of keys should larger than 0')
|
||||
if isinstance(dl, list):
|
||||
k = str2num(ks[0])
|
||||
if len(ks) == 1:
|
||||
assert k < len(dl), ('index({}) out of range({})'.format(k, dl))
|
||||
dl[k] = str2num(v)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
override(dl[k], ks[1:], v)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if len(ks) == 1:
|
||||
#assert ks[0] in dl, ('{} is not exist in {}'.format(ks[0], dl))
|
||||
if not ks[0] in dl:
|
||||
logger.warning('A new filed ({}) detected!'.format(ks[0], dl))
|
||||
dl[ks[0]] = str2num(v)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert ks[0] in dl, (
|
||||
'({}) doesn\'t exist in {}, a new dict field is invalid'.
|
||||
format(ks[0], dl))
|
||||
override(dl[ks[0]], ks[1:], v)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def override_config(config, options=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursively override the config
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
config(dict): dict to be replaced
|
||||
options(list): list of pairs(key0.key1.idx.key2=value)
|
||||
such as: [
|
||||
'topk=2',
|
||||
'VALID.transforms.1.ResizeImage.resize_short=300'
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
config(dict): replaced config
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if options is not None:
|
||||
for opt in options:
|
||||
assert isinstance(opt, str), (
|
||||
"option({}) should be a str".format(opt))
|
||||
assert "=" in opt, (
|
||||
"option({}) should contain a ="
|
||||
"to distinguish between key and value".format(opt))
|
||||
pair = opt.split('=')
|
||||
assert len(pair) == 2, ("there can be only a = in the option")
|
||||
key, value = pair
|
||||
keys = key.split('.')
|
||||
override(config, keys, value)
|
||||
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ArgsParser(ArgumentParser):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(ArgsParser, self).__init__(
|
||||
formatter_class=RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
|
||||
self.add_argument("-c", "--config", help="configuration file to use")
|
||||
self.add_argument(
|
||||
"-t", "--tag", default="0", help="tag for marking worker")
|
||||
self.add_argument(
|
||||
'-o',
|
||||
'--override',
|
||||
action='append',
|
||||
default=[],
|
||||
help='config options to be overridden')
|
||||
self.add_argument(
|
||||
"--style_image", default="examples/style_images/1.jpg", help="tag for marking worker")
|
||||
self.add_argument(
|
||||
"--text_corpus", default="PaddleOCR", help="tag for marking worker")
|
||||
self.add_argument(
|
||||
"--language", default="en", help="tag for marking worker")
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_args(self, argv=None):
|
||||
args = super(ArgsParser, self).parse_args(argv)
|
||||
assert args.config is not None, \
|
||||
"Please specify --config=configure_file_path."
|
||||
return args
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_config(file_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Load config from yml/yaml file.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
file_path (str): Path of the config file to be loaded.
|
||||
Returns: config
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ext = os.path.splitext(file_path)[1]
|
||||
assert ext in ['.yml', '.yaml'], "only support yaml files for now"
|
||||
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
|
||||
config = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.Loader)
|
||||
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def gen_config():
|
||||
base_config = {
|
||||
"Global": {
|
||||
"algorithm": "SRNet",
|
||||
"use_gpu": True,
|
||||
"start_epoch": 1,
|
||||
"stage1_epoch_num": 100,
|
||||
"stage2_epoch_num": 100,
|
||||
"log_smooth_window": 20,
|
||||
"print_batch_step": 2,
|
||||
"save_model_dir": "./output/SRNet",
|
||||
"use_visualdl": False,
|
||||
"save_epoch_step": 10,
|
||||
"vgg_pretrain": "./pretrained/VGG19_pretrained",
|
||||
"vgg_load_static_pretrain": True
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Architecture": {
|
||||
"model_type": "data_aug",
|
||||
"algorithm": "SRNet",
|
||||
"net_g": {
|
||||
"name": "srnet_net_g",
|
||||
"encode_dim": 64,
|
||||
"norm": "batch",
|
||||
"use_dropout": False,
|
||||
"init_type": "xavier",
|
||||
"init_gain": 0.02,
|
||||
"use_dilation": 1
|
||||
},
|
||||
# input_nc, ndf, netD,
|
||||
# n_layers_D=3, norm='instance', use_sigmoid=False, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_id='cuda:0'
|
||||
"bg_discriminator": {
|
||||
"name": "srnet_bg_discriminator",
|
||||
"input_nc": 6,
|
||||
"ndf": 64,
|
||||
"netD": "basic",
|
||||
"norm": "none",
|
||||
"init_type": "xavier",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"fusion_discriminator": {
|
||||
"name": "srnet_fusion_discriminator",
|
||||
"input_nc": 6,
|
||||
"ndf": 64,
|
||||
"netD": "basic",
|
||||
"norm": "none",
|
||||
"init_type": "xavier",
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Loss": {
|
||||
"lamb": 10,
|
||||
"perceptual_lamb": 1,
|
||||
"muvar_lamb": 50,
|
||||
"style_lamb": 500
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Optimizer": {
|
||||
"name": "Adam",
|
||||
"learning_rate": {
|
||||
"name": "lambda",
|
||||
"lr": 0.0002,
|
||||
"lr_decay_iters": 50
|
||||
},
|
||||
"beta1": 0.5,
|
||||
"beta2": 0.999,
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Train": {
|
||||
"batch_size_per_card": 8,
|
||||
"num_workers_per_card": 4,
|
||||
"dataset": {
|
||||
"delimiter": "\t",
|
||||
"data_dir": "/",
|
||||
"label_file": "tmp/label.txt",
|
||||
"transforms": [{
|
||||
"DecodeImage": {
|
||||
"to_rgb": True,
|
||||
"to_np": False,
|
||||
"channel_first": False
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
"NormalizeImage": {
|
||||
"scale": 1. / 255.,
|
||||
"mean": [0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
|
||||
"std": [0.229, 0.224, 0.225],
|
||||
"order": None
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, {
|
||||
"ToCHWImage": None
|
||||
}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
with open("config.yml", "w") as f:
|
||||
yaml.dump(base_config, f)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
gen_config()
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ['load_dygraph_pretrain']
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_dygraph_pretrain(model, logger, path=None, load_static_weights=False):
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(path + '.pdparams'):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Model pretrain path {} does not "
|
||||
"exists.".format(path))
|
||||
param_state_dict = paddle.load(path + '.pdparams')
|
||||
model.set_state_dict(param_state_dict)
|
||||
logger.info("load pretrained model from {}".format(path))
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
import paddle.distributed as dist
|
||||
|
||||
logger_initialized = {}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@functools.lru_cache()
|
||||
def get_logger(name='srnet', log_file=None, log_level=logging.INFO):
|
||||
"""Initialize and get a logger by name.
|
||||
If the logger has not been initialized, this method will initialize the
|
||||
logger by adding one or two handlers, otherwise the initialized logger will
|
||||
be directly returned. During initialization, a StreamHandler will always be
|
||||
added. If `log_file` is specified a FileHandler will also be added.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
name (str): Logger name.
|
||||
log_file (str | None): The log filename. If specified, a FileHandler
|
||||
will be added to the logger.
|
||||
log_level (int): The logger level. Note that only the process of
|
||||
rank 0 is affected, and other processes will set the level to
|
||||
"Error" thus be silent most of the time.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
logging.Logger: The expected logger.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(name)
|
||||
if name in logger_initialized:
|
||||
return logger
|
||||
for logger_name in logger_initialized:
|
||||
if name.startswith(logger_name):
|
||||
return logger
|
||||
|
||||
formatter = logging.Formatter(
|
||||
'[%(asctime)s] %(name)s %(levelname)s: %(message)s',
|
||||
datefmt="%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
|
||||
|
||||
stream_handler = logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)
|
||||
stream_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
|
||||
logger.addHandler(stream_handler)
|
||||
if log_file is not None and dist.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
log_file_folder = os.path.split(log_file)[0]
|
||||
os.makedirs(log_file_folder, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
file_handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file, 'a')
|
||||
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
|
||||
logger.addHandler(file_handler)
|
||||
if dist.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
logger.setLevel(log_level)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
|
||||
logger_initialized[name] = True
|
||||
return logger
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_mean_covariance(img):
|
||||
batch_size = img.shape[0]
|
||||
channel_num = img.shape[1]
|
||||
height = img.shape[2]
|
||||
width = img.shape[3]
|
||||
num_pixels = height * width
|
||||
|
||||
# batch_size * channel_num * 1 * 1
|
||||
mu = img.mean(2, keepdim=True).mean(3, keepdim=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# batch_size * channel_num * num_pixels
|
||||
img_hat = img - mu.expand_as(img)
|
||||
img_hat = img_hat.reshape([batch_size, channel_num, num_pixels])
|
||||
# batch_size * num_pixels * channel_num
|
||||
img_hat_transpose = img_hat.transpose([0, 2, 1])
|
||||
# batch_size * channel_num * channel_num
|
||||
covariance = paddle.bmm(img_hat, img_hat_transpose)
|
||||
covariance = covariance / num_pixels
|
||||
|
||||
return mu, covariance
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dice_coefficient(y_true_cls, y_pred_cls, training_mask):
|
||||
eps = 1e-5
|
||||
intersection = paddle.sum(y_true_cls * y_pred_cls * training_mask)
|
||||
union = paddle.sum(y_true_cls * training_mask) + paddle.sum(
|
||||
y_pred_cls * training_mask) + eps
|
||||
loss = 1. - (2 * intersection / union)
|
||||
return loss
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import errno
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_check_global_params(mode):
|
||||
check_params = [
|
||||
'use_gpu', 'max_text_length', 'image_shape', 'image_shape',
|
||||
'character_type', 'loss_type'
|
||||
]
|
||||
if mode == "train_eval":
|
||||
check_params = check_params + [
|
||||
'train_batch_size_per_card', 'test_batch_size_per_card'
|
||||
]
|
||||
elif mode == "test":
|
||||
check_params = check_params + ['test_batch_size_per_card']
|
||||
return check_params
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_gpu(use_gpu):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Log error and exit when set use_gpu=true in paddlepaddle
|
||||
cpu version.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
err = "Config use_gpu cannot be set as true while you are " \
|
||||
"using paddlepaddle cpu version ! \nPlease try: \n" \
|
||||
"\t1. Install paddlepaddle-gpu to run model on GPU \n" \
|
||||
"\t2. Set use_gpu as false in config file to run " \
|
||||
"model on CPU"
|
||||
if use_gpu:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not paddle.is_compiled_with_cuda():
|
||||
print(err)
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print("Fail to check gpu state.")
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mkdir_if_not_exist(path, logger):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
mkdir if not exists, ignore the exception when multiprocess mkdir together
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(path):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
os.makedirs(path)
|
||||
except OSError as e:
|
||||
if e.errno == errno.EEXIST and os.path.isdir(path):
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
'be happy if some process has already created {}'.format(
|
||||
path))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise OSError('Failed to mkdir {}'.format(path))
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|||
# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from .paddleocr import *
|
||||
|
||||
__version__ = paddleocr.VERSION
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
'PaddleOCR', 'PPStructure', 'draw_ocr', 'draw_structure_result',
|
||||
'save_structure_res', 'download_with_progressbar', 'sorted_layout_boxes',
|
||||
'convert_info_docx', 'to_excel'
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,652 @@
|
|||
# 基于PP-OCRv3的PCB字符识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目介绍](#1-项目介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 安装说明](#2-安装说明)
|
||||
- [3. 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4. 文本检测](#4-文本检测)
|
||||
- [4.1 预训练模型直接评估](#41-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.2 预训练模型+验证集padding直接评估](#42-预训练模型验证集padding直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.3 预训练模型+fine-tune](#43-预训练模型fine-tune)
|
||||
- [5. 文本识别](#5-文本识别)
|
||||
- [5.1 预训练模型直接评估](#51-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [5.2 三种fine-tune方案](#52-三种fine-tune方案)
|
||||
- [6. 模型导出](#6-模型导出)
|
||||
- [7. 端对端评测](#7-端对端评测)
|
||||
- [8. Jetson部署](#8-Jetson部署)
|
||||
- [9. 总结](#9-总结)
|
||||
- [更多资源](#更多资源)
|
||||
|
||||
# 1. 项目介绍
|
||||
|
||||
印刷电路板(PCB)是电子产品中的核心器件,对于板件质量的测试与监控是生产中必不可少的环节。在一些场景中,通过PCB中信号灯颜色和文字组合可以定位PCB局部模块质量问题,PCB文字识别中存在如下难点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 裁剪出的PCB图片宽高比例较小
|
||||
- 文字区域整体面积也较小
|
||||
- 包含垂直、水平多种方向文本
|
||||
|
||||
针对本场景,PaddleOCR基于全新的PP-OCRv3通过合成数据、微调以及其他场景适配方法完成小字符文本识别任务,满足企业上线要求。PCB检测、识别效果如 **图1** 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/95d8e95bf1ab476987f2519c0f8f0c60a0cdc2c444804ed6ab08f2f7ab054880', width='500'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图1 PCB检测识别效果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
注:欢迎在AIStudio领取免费算力体验线上实训,项目链接: [基于PP-OCRv3实现PCB字符识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4008973)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. 安装说明
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddleOCR源码,安装依赖环境。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如仍需安装or安装更新,可以执行以下步骤
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 安装依赖包
|
||||
pip install -r /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过图片合成工具生成 **图2** 所示的PCB图片,整图只有高25、宽150左右、文字区域高9、宽45左右,包含垂直和水平2种方向的文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/bb7a345687814a3d83a29790f2a2b7d081495b3a920b43988c93da6039cad653" width="1000" ></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图2 数据集示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
暂时不开源生成的PCB数据集,但是通过更换背景,通过如下代码生成数据即可:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd gen_data
|
||||
python3 gen.py --num_img=10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成图片参数解释:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
num_img:生成图片数量
|
||||
font_min_size、font_max_size:字体最大、最小尺寸
|
||||
bg_path:文字区域背景存放路径
|
||||
det_bg_path:整图背景存放路径
|
||||
fonts_path:字体路径
|
||||
corpus_path:语料路径
|
||||
output_dir:生成图片存储路径
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里生成 **100张** 相同尺寸和文本的图片,如 **图3** 所示,方便大家跑通实验。通过如下代码解压数据集:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/3277b750159f4b68b2b58506bfec9005d49aeb5fb1d9411e83f96f9ff7eb66a5" width="1000" ></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图3 案例提供数据集示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tar xf ./data/data148165/dataset.tar -C ./
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在生成数据集的时需要生成检测和识别训练需求的格式:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本检测**
|
||||
|
||||
标注文件格式如下,中间用'\t'分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
" 图像文件名 json.dumps编码的图像标注信息"
|
||||
ch4_test_images/img_61.jpg [{"transcription": "MASA", "points": [[310, 104], [416, 141], [418, 216], [312, 179]]}, {...}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
json.dumps编码前的图像标注信息是包含多个字典的list,字典中的 `points` 表示文本框的四个点的坐标(x, y),从左上角的点开始顺时针排列。 `transcription` 表示当前文本框的文字,***当其内容为“###”时,表示该文本框无效,在训练时会跳过。***
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本识别**
|
||||
|
||||
标注文件的格式如下, txt文件中默认请将图片路径和图片标签用'\t'分割,如用其他方式分割将造成训练报错。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
" 图像文件名 图像标注信息 "
|
||||
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_001.jpg 简单可依赖
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_002.jpg 用科技让复杂的世界更简单
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 4. 文本检测
|
||||
|
||||
选用飞桨OCR开发套件[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)中的PP-OCRv3模型进行文本检测和识别。针对检测模型和识别模型,进行了共计9个方面的升级:
|
||||
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3检测模型对PP-OCRv2中的CML协同互学习文本检测蒸馏策略进行了升级,分别针对教师模型和学生模型进行进一步效果优化。其中,在对教师模型优化时,提出了大感受野的PAN结构LK-PAN和引入了DML蒸馏策略;在对学生模型优化时,提出了残差注意力机制的FPN结构RSE-FPN。
|
||||
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法SVTR优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。PP-OCRv3通过轻量级文本识别网络SVTR_LCNet、Attention损失指导CTC损失训练策略、挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略TextConAug、TextRotNet自监督预训练模型、UDML联合互学习策略、UIM无标注数据挖掘方案,6个方面进行模型加速和效果提升。
|
||||
|
||||
更多细节请参考PP-OCRv3[技术报告](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用 **3种方案** 进行检测模型的训练、评估:
|
||||
- **PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **验证集padding**直接评估
|
||||
- PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.1 预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
我们首先通过PaddleOCR提供的预训练模型在验证集上进行评估,如果评估指标能满足效果,可以直接使用预训练模型,不再需要训练。
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型直接评估步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR已经提供了PP-OCR系列模型,部分模型展示如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型简介 | 模型名称 | 推荐场景 | 检测模型 | 方向分类器 | 识别模型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(16.2M) | ch_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 英文超轻量PP-OCRv3模型(13.4M) | en_PP-OCRv3_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv2模型(13.0M) | ch_PP-OCRv2_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCR mobile模型(9.4M) | ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文通用PP-OCR server模型(143.4M) | ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_xx | 服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
更多模型下载(包括多语言),可以参[考PP-OCR系列模型下载](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md)
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们使用PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如果更换其他模型,更新下载链接和解压指令就可以
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
mkdir pretrain_models
|
||||
cd pretrain_models
|
||||
# 下载英文预训练模型
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/english/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar && rm -rf en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
%cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest: 尺寸
|
||||
limit_side_len: 48
|
||||
limit_type: 'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在验证集上进行评估,具体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.2 预训练模型+验证集padding直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
考虑到PCB图片比较小,宽度只有25左右、高度只有140-170左右,我们在原图的基础上进行padding,再进行检测评估,padding前后效果对比如 **图4** 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/e61e6ba685534eda992cea30a63a9c461646040ffd0c4d208a5eebb85897dcf7' width='600'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图4 padding前后对比图</div>
|
||||
|
||||
将图片都padding到300*300大小,因为坐标信息发生了变化,我们同时要修改标注文件,在`/home/aistudio/dataset`目录里也提供了padding之后的图片,大家也可以尝试训练和评估:
|
||||
|
||||
同上,我们需要修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_padding_val.txt
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest: 尺寸
|
||||
limit_side_len: 1100
|
||||
limit_type: 'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型评估。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **4.3 预训练模型+fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
基于预训练模型,在生成的1500图片上进行fine-tune训练和评估,其中train数据1200张,val数据300张,修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 这里设置为1,方便快速跑通,实际中根据数据量调整该值
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir:模型保存路径
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径,'./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student.pdparams'
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate:调整学习率,本实验设置为0.0005
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_train.txt'
|
||||
Train.dataset.transforms.EastRandomCropData.size:训练尺寸改为[480,64]
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset/'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
||||
limit_side_len: 64
|
||||
limit_type:'min'
|
||||
```
|
||||
执行下面命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./output/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/latest"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | hmean | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 64.64% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + 验证集padding | 72.13% |+7.49% | padding可以提升尺寸较小图片的检测效果|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | 100.00% | +27.87% | fine-tune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注:上述实验结果均是在1500张图片(1200张训练集,300张测试集)上训练、评估的得到,AIstudio只提供了100张数据,所以指标有所差异属于正常,只要策略有效、规律相同即可。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. 文本识别
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用如下4种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
|
||||
- **方案1**:**PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
- **方案2**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
- **方案3**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune + **公开通用识别数据集**
|
||||
- **方案4**:PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune + **增加PCB图像数量**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## **5.1 预训练模型直接评估**
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,我们首先使用PaddleOCR提供的识别预训练模型在PCB验证集上进行评估。
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型直接评估步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量文本识别模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如果更换其他模型,更新下载链接和解压指令就可以
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_distillation.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Metric.ignore_space: True:忽略空格
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录,'/home/aistudio/dataset'
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件,'/home/aistudio/dataset/rec_gt_val.txt'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用下载的预训练模型进行评估:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## **5.2 三种fine-tune方案**
|
||||
|
||||
方案2、3、4训练和评估方式是相同的,因此在我们了解每个技术方案之后,再具体看修改哪些参数是相同,哪些是不同的。
|
||||
|
||||
**方案介绍:**
|
||||
|
||||
1) **方案2**:预训练模型 + **fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
- 在预训练模型的基础上进行fine-tune,使用1500张PCB进行训练和评估,其中训练集1200张,验证集300张。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2) **方案3**:预训练模型 + fine-tune + **公开通用识别数据集**
|
||||
|
||||
- 当识别数据比较少的情况,可以考虑添加公开通用识别数据集。在方案2的基础上,添加公开通用识别数据集,如lsvt、rctw等。
|
||||
|
||||
3)**方案4**:预训练模型 + fine-tune + **增加PCB图像数量**
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果能够获取足够多真实场景,我们可以通过增加数据量提升模型效果。在方案2的基础上,增加PCB的数量到2W张左右。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参数修改:**
|
||||
|
||||
接着我们看需要修改的参数,以上方案均需要修改配置文件`configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml`的参数,**修改一次即可**:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径,'pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy'
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.values:学习率,本实验设置为0.0005
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card: batch size,默认128,因为数据量小于128,因此我们设置为8,数据量大可以按默认的训练
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card: batch size,默认128,设置为4
|
||||
Metric.ignore_space: 忽略空格,本实验设置为True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**更换不同的方案**每次需要修改的参数:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 这里设置为1,方便快速跑通,实际中根据数据量调整该值
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir:指向模型保存路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时**方案3**修改以下参数
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:添加公开通用识别数据标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.ratio_list:数据和公开通用识别数据每次采样比例,按实际修改即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
如 **图5** 所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0fa18b25819042d9bbf3397c3af0e21433b23d52f7a84b0a8681b8e6a308d433' wdith=''></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图5 添加公开通用识别数据配置文件示例</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们提取Student模型的参数,在PCB数据集上进行fine-tune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 学生模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("student_model."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "student_model." in key}
|
||||
# 查看学生模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改参数后,**每个方案**都执行如下命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./output/rec_ppocr_v3/latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
所有方案评估指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | acc | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估 | 46.67% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune | 42.02% |-4.65% | 在数据量不足的情况,反而比预训练模型效果低(也可以通过调整超参数再试试)|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 公开通用识别数据集 | 77.00% | +30.33% | 在数据量不足的情况下,可以考虑补充公开数据训练 |
|
||||
| 4 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 99.99% | +22.99% | 如果能获取更多数据量的情况,可以通过增加数据量提升效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注:上述实验结果均是在1500张图片(1200张训练集,300张测试集)、2W张图片、添加公开通用识别数据集上训练、评估的得到,AIstudio只提供了100张数据,所以指标有所差异属于正常,只要策略有效、规律相同即可。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 6. 模型导出
|
||||
|
||||
inference 模型(paddle.jit.save保存的模型) 一般是模型训练,把模型结构和模型参数保存在文件中的固化模型,多用于预测部署场景。 训练过程中保存的模型是checkpoints模型,保存的只有模型的参数,多用于恢复训练等。 与checkpoints模型相比,inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 导出检测模型
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/latest" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./inference_model/ch_PP-OCR_V3_det/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因为上述模型只训练了1个epoch,因此我们使用训练最优的模型进行预测,存储在`/home/aistudio/best_models/`目录下,解压即可
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/best_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/PCB/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB.tar
|
||||
tar xf /home/aistudio/best_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB.tar -C /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_det.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="/home/aistudio/dataset/imgs/0000.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_algorithm="DB" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB/" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果存储在`inference_results`目录下,检测如下图所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/5939ae15a1f0445aaeec15c68107dbd897740a1ddd284bf8b583bb6242099157' width=''></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图6 检测结果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
同理,导出识别模型并进行推理。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 导出识别模型
|
||||
python3 tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="./output/rec_ppocr_v3/latest" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./inference_model/rec_ppocr_v3/"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,识别模型也只训练了1个epoch,因此我们使用训练最优的模型进行预测,存储在`/home/aistudio/best_models/`目录下,解压即可
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/best_models/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/fanliku/PCB/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB.tar
|
||||
tar xf /home/aistudio/best_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB.tar -C /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain_models/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../test_imgs/0000_rec.jpg" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测+识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../test_imgs/0000.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--draw_img_save_dir=./det_rec_infer/ \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_angle_cls=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
端到端预测结果存储在`det_res_infer`文件夹内,结果如下图所示:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/c570f343c29846c792da56ebaca16c50708477514dd048cea8bef37ffa85d03f'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图7 检测+识别结果</div>
|
||||
|
||||
# 7. 端对端评测
|
||||
|
||||
接下来介绍文本检测+文本识别的端对端指标评估方式。主要分为三步:
|
||||
|
||||
1)首先运行`tools/infer/predict_system.py`,将`image_dir`改为需要评估的数据文件家,得到保存的结果:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 检测+识别模型inference模型预测
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="../dataset/imgs/" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./pretrain_models/det_ppocr_v3_en_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--det_limit_side_len=48 \
|
||||
--det_limit_type='min' \
|
||||
--det_db_unclip_ratio=2.5 \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./pretrain_models/rec_ppocr_v3_ch_infer_PCB" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 48, 320" \
|
||||
--draw_img_save_dir=./det_rec_infer/ \
|
||||
--use_space_char=False \
|
||||
--use_angle_cls=False \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到保存结果,文本检测识别可视化图保存在`det_rec_infer/`目录下,预测结果保存在`det_rec_infer/system_results.txt`中,格式如下:`0018.jpg [{"transcription": "E295", "points": [[88, 33], [137, 33], [137, 40], [88, 40]]}]`
|
||||
|
||||
2)然后将步骤一保存的数据转换为端对端评测需要的数据格式: 修改 `tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py`中的代码,convert_label函数中设置输入标签路径,Mode,保存标签路径等,对预测数据的GTlabel和预测结果的label格式进行转换。
|
||||
```
|
||||
ppocr_label_gt = "/home/aistudio/dataset/det_gt_val.txt"
|
||||
convert_label(ppocr_label_gt, "gt", "./save_gt_label/")
|
||||
|
||||
ppocr_label_gt = "/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/PCB_result/det_rec_infer/system_results.txt"
|
||||
convert_label(ppocr_label_gt, "pred", "./save_PPOCRV2_infer/")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行`convert_ppocr_label.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到如下结果:
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── ./save_gt_label/
|
||||
├── ./save_PPOCRV2_infer/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3) 最后,执行端对端评测,运行`tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py`计算端对端指标,运行方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pip install editdistance
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py ./save_gt_label/ ./save_PPOCRV2_infer/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用`预训练模型+fine-tune'检测模型`、`预训练模型 + 2W张PCB图片funetune`识别模型,在300张PCB图片上评估得到如下结果,fmeasure为主要关注的指标:
|
||||
<div align=center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/37206ea48a244212ae7a821d50d1fd51faf3d7fe97ac47a29f04dfcbb377b019', width='700'></div>
|
||||
<div align=center>图8 端到端评估指标</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
注: 使用上述命令不能跑出该结果,因为数据集不相同,可以更换为自己训练好的模型,按上述流程运行
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 8. Jetson部署
|
||||
|
||||
我们只需要以下步骤就可以完成Jetson nano部署模型,简单易操作:
|
||||
|
||||
**1、在Jetson nano开发版上环境准备:**
|
||||
|
||||
* 安装PaddlePaddle
|
||||
|
||||
* 下载PaddleOCR并安装依赖
|
||||
|
||||
**2、执行预测**
|
||||
|
||||
* 将推理模型下载到jetson
|
||||
|
||||
* 执行检测、识别、串联预测即可
|
||||
|
||||
详细[参考流程](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/deploy/Jetson/readme_ch.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
# 9. 总结
|
||||
|
||||
检测实验分别使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型在PCB数据集上进行了直接评估、验证集padding、 fine-tune 3种方案,识别实验分别使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型在PCB数据集上进行了直接评估、 fine-tune、添加公开通用识别数据集、增加PCB图片数量4种方案,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* 检测
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | hmean | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| ---- | -------------------------------------------------------- | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接评估 | 64.64% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + 验证集padding直接评估 | 72.13% | +7.49% | padding可以提升尺寸较小图片的检测效果 |
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | 100.00% | +27.87% | fine-tune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
* 识别
|
||||
|
||||
| 序号 | 方案 | acc | 效果提升 | 实验分析 |
|
||||
| ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接评估 | 46.67% | - | 提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune | 42.02% | -4.65% | 在数据量不足的情况,反而比预训练模型效果低(也可以通过调整超参数再试试) |
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 公开通用识别数据集 | 77.00% | +30.33% | 在数据量不足的情况下,可以考虑补充公开数据训练 |
|
||||
| 4 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 99.99% | +22.99% | 如果能获取更多数据量的情况,可以通过增加数据量提升效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
* 端到端
|
||||
|
||||
| det | rec | fmeasure |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv3英文超轻量检测预训练模型 + fine-tune | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + fine-tune + 增加PCB图像数量 | 93.30% |
|
||||
|
||||
*结论*
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的检测模型在未经过fine-tune的情况下,在PCB数据集上也有64.64%的精度,说明具有泛化能力。验证集padding之后,精度提升7.5%,在图片尺寸较小的情况,我们可以通过padding的方式提升检测效果。经过 fine-tune 后能够极大的提升检测效果,精度达到100%。
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模型方案1和方案2对比可以发现,当数据量不足的情况,预训练模型精度可能比fine-tune效果还要高,所以我们可以先尝试预训练模型直接评估。如果在数据量不足的情况下想进一步提升模型效果,可以通过添加公开通用识别数据集,识别效果提升30%,非常有效。最后如果我们能够采集足够多的真实场景数据集,可以通过增加数据量提升模型效果,精度达到99.99%。
|
||||
|
||||
# 更多资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多深度学习知识、产业案例、面试宝典等,请参考:[awesome-DeepLearning](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/awesome-DeepLearning)
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多PaddleOCR使用教程,请参考:[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/dygraph)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 飞桨框架相关资料,请参考:[飞桨深度学习平台](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/?fr=paddleEdu_aistudio)
|
||||
|
||||
# 参考
|
||||
|
||||
* 数据生成代码库:https://github.com/zcswdt/Color_OCR_image_generator
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.0 KiB |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||
5ZQ
|
||||
I4UL
|
||||
PWL
|
||||
SNOG
|
||||
ZL02
|
||||
1C30
|
||||
O3H
|
||||
YHRS
|
||||
N03S
|
||||
1U5Y
|
||||
JTK
|
||||
EN4F
|
||||
YKJ
|
||||
DWNH
|
||||
R42W
|
||||
X0V
|
||||
4OF5
|
||||
08AM
|
||||
Y93S
|
||||
GWE2
|
||||
0KR
|
||||
9U2A
|
||||
DBQ
|
||||
Y6J
|
||||
ROZ
|
||||
K06
|
||||
KIEY
|
||||
NZQJ
|
||||
UN1B
|
||||
6X4
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 145 B |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 141 B |
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,270 @@
|
|||
# copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This code is refer from:
|
||||
https://github.com/zcswdt/Color_OCR_image_generator
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_char_lines(txt_root_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:get corpus line
|
||||
"""
|
||||
txt_files = os.listdir(txt_root_path)
|
||||
char_lines = []
|
||||
for txt in txt_files:
|
||||
f = open(os.path.join(txt_root_path, txt), mode='r', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
char_lines.append(line.strip())
|
||||
return char_lines
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_horizontal_text_picture(image_file, chars, fonts_list, cf):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:gen horizontal text picture
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img = Image.open(image_file)
|
||||
if img.mode != 'RGB':
|
||||
img = img.convert('RGB')
|
||||
img_w, img_h = img.size
|
||||
|
||||
# random choice font
|
||||
font_path = random.choice(fonts_list)
|
||||
# random choice font size
|
||||
font_size = random.randint(cf.font_min_size, cf.font_max_size)
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
|
||||
|
||||
ch_w = []
|
||||
ch_h = []
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
if int(PIL.__version__.split('.')[0]) < 10:
|
||||
wt, ht = font.getsize(ch)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
left, top, right, bottom = font.getbbox(ch)
|
||||
wt, ht = right - left, bottom - top
|
||||
ch_w.append(wt)
|
||||
ch_h.append(ht)
|
||||
f_w = sum(ch_w)
|
||||
f_h = max(ch_h)
|
||||
|
||||
# add space
|
||||
char_space_width = max(ch_w)
|
||||
f_w += (char_space_width * (len(chars) - 1))
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = random.randint(0, img_w - f_w)
|
||||
y1 = random.randint(0, img_h - f_h)
|
||||
x2 = x1 + f_w
|
||||
y2 = y1 + f_h
|
||||
|
||||
crop_y1 = y1
|
||||
crop_x1 = x1
|
||||
crop_y2 = y2
|
||||
crop_x2 = x2
|
||||
|
||||
best_color = (0, 0, 0)
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
|
||||
for i, ch in enumerate(chars):
|
||||
draw.text((x1, y1), ch, best_color, font=font)
|
||||
x1 += (ch_w[i] + char_space_width)
|
||||
crop_img = img.crop((crop_x1, crop_y1, crop_x2, crop_y2))
|
||||
return crop_img, chars
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_vertical_text_picture(image_file, chars, fonts_list, cf):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc:gen vertical text picture
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img = Image.open(image_file)
|
||||
if img.mode != 'RGB':
|
||||
img = img.convert('RGB')
|
||||
img_w, img_h = img.size
|
||||
# random choice font
|
||||
font_path = random.choice(fonts_list)
|
||||
# random choice font size
|
||||
font_size = random.randint(cf.font_min_size, cf.font_max_size)
|
||||
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
|
||||
|
||||
ch_w = []
|
||||
ch_h = []
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
if int(PIL.__version__.split('.')[0]) < 10:
|
||||
wt, ht = font.getsize(ch)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
left, top, right, bottom = font.getbbox(ch)
|
||||
wt, ht = right - left, bottom - top
|
||||
ch_w.append(wt)
|
||||
ch_h.append(ht)
|
||||
f_w = max(ch_w)
|
||||
f_h = sum(ch_h)
|
||||
|
||||
x1 = random.randint(0, img_w - f_w)
|
||||
y1 = random.randint(0, img_h - f_h)
|
||||
x2 = x1 + f_w
|
||||
y2 = y1 + f_h
|
||||
|
||||
crop_y1 = y1
|
||||
crop_x1 = x1
|
||||
crop_y2 = y2
|
||||
crop_x2 = x2
|
||||
|
||||
best_color = (0, 0, 0)
|
||||
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
for ch in chars:
|
||||
draw.text((x1, y1), ch, best_color, font=font)
|
||||
y1 = y1 + ch_h[i]
|
||||
i = i + 1
|
||||
crop_img = img.crop((crop_x1, crop_y1, crop_x2, crop_y2))
|
||||
crop_img = crop_img.transpose(Image.ROTATE_90)
|
||||
return crop_img, chars
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_fonts(fonts_path):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
desc: get all fonts
|
||||
"""
|
||||
font_files = os.listdir(fonts_path)
|
||||
fonts_list=[]
|
||||
for font_file in font_files:
|
||||
font_path=os.path.join(fonts_path, font_file)
|
||||
fonts_list.append(font_path)
|
||||
return fonts_list
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--num_img', type=int, default=30, help="Number of images to generate")
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--font_min_size', type=int, default=11)
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--font_max_size', type=int, default=12,
|
||||
help="Help adjust the size of the generated text and the size of the picture")
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--bg_path', type=str, default='./background',
|
||||
help='The generated text pictures will be pasted onto the pictures of this folder')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--det_bg_path', type=str, default='./det_background',
|
||||
help='The generated text pictures will use the pictures of this folder as the background')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--fonts_path', type=str, default='../../StyleText/fonts',
|
||||
help='The font used to generate the picture')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--corpus_path', type=str, default='./corpus',
|
||||
help='The corpus used to generate the text picture')
|
||||
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default='./output/', help='Images save dir')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cf = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
# save path
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# get corpus
|
||||
txt_root_path = cf.corpus_path
|
||||
char_lines = get_char_lines(txt_root_path=txt_root_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# get all fonts
|
||||
fonts_path = cf.fonts_path
|
||||
fonts_list = get_fonts(fonts_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# rec bg
|
||||
img_root_path = cf.bg_path
|
||||
imnames=os.listdir(img_root_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# det bg
|
||||
det_bg_path = cf.det_bg_path
|
||||
bg_pics = os.listdir(det_bg_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# OCR det files
|
||||
det_val_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'det_gt_val.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
det_train_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'det_gt_train.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
# det imgs
|
||||
det_save_dir = 'imgs/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + det_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + det_save_dir)
|
||||
det_val_save_dir = 'imgs_val/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + det_val_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + det_val_save_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# OCR rec files
|
||||
rec_val_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'rec_gt_val.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
rec_train_file = open(cf.output_dir + 'rec_gt_train.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
# rec imgs
|
||||
rec_save_dir = 'rec_imgs/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + rec_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + rec_save_dir)
|
||||
rec_val_save_dir = 'rec_imgs_val/'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(cf.output_dir + rec_val_save_dir):
|
||||
os.mkdir(cf.output_dir + rec_val_save_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
val_ratio = cf.num_img * 0.2 # val dataset ratio
|
||||
|
||||
print('start generating...')
|
||||
for i in range(0, cf.num_img):
|
||||
imname = random.choice(imnames)
|
||||
img_path = os.path.join(img_root_path, imname)
|
||||
|
||||
rnd = random.random()
|
||||
# gen horizontal text picture
|
||||
if rnd < 0.5:
|
||||
gen_img, chars = get_horizontal_text_picture(img_path, char_lines[i], fonts_list, cf)
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
gen_img = gen_img.crop((0, 3, ori_w, ori_h))
|
||||
# gen vertical text picture
|
||||
else:
|
||||
gen_img, chars = get_vertical_text_picture(img_path, char_lines[i], fonts_list, cf)
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
gen_img = gen_img.crop((3, 0, ori_w, ori_h))
|
||||
|
||||
ori_w, ori_h = gen_img.size
|
||||
|
||||
# rec imgs
|
||||
save_img_name = str(i).zfill(4) + '.jpg'
|
||||
if i < val_ratio:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(rec_val_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
line = save_dir + '\t' + char_lines[i] + '\n'
|
||||
rec_val_file.write(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(rec_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
line = save_dir + '\t' + char_lines[i] + '\n'
|
||||
rec_train_file.write(line)
|
||||
gen_img.save(cf.output_dir + save_dir, quality = 95, subsampling=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# det img
|
||||
# random choice bg
|
||||
bg_pic = random.sample(bg_pics, 1)[0]
|
||||
det_img = Image.open(os.path.join(det_bg_path, bg_pic))
|
||||
# the PCB position is fixed, modify it according to your own scenario
|
||||
if bg_pic == '1.png':
|
||||
x1 = 38
|
||||
y1 = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x1 = 34
|
||||
y1 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
det_img.paste(gen_img, (x1, y1))
|
||||
# text pos
|
||||
chars_pos = [[x1, y1], [x1 + ori_w, y1], [x1 + ori_w, y1 + ori_h], [x1, y1 + ori_h]]
|
||||
label = [{"transcription":char_lines[i], "points":chars_pos}]
|
||||
if i < val_ratio:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(det_val_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
det_val_file.write(save_dir + '\t' + json.dumps(
|
||||
label, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
save_dir = os.path.join(det_save_dir, save_img_name)
|
||||
det_train_file.write(save_dir + '\t' + json.dumps(
|
||||
label, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
|
||||
det_img.save(cf.output_dir + save_dir, quality = 95, subsampling=0)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
|||
[English](README_en.md) | 简体中文
|
||||
|
||||
# 场景应用
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR场景应用覆盖通用,制造、金融、交通行业的主要OCR垂类应用,在PP-OCR、PP-Structure的通用能力基础之上,以notebook的形式展示利用场景数据微调、模型优化方法、数据增广等内容,为开发者快速落地OCR应用提供示范与启发。
|
||||
|
||||
- [教程文档](#1)
|
||||
- [通用](#11)
|
||||
- [制造](#12)
|
||||
- [金融](#13)
|
||||
- [交通](#14)
|
||||
|
||||
- [模型下载](#2)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 教程文档
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="11"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 通用
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 模型下载 | 教程 | 示例图 |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------- | --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 高精度中文识别模型SVTR | 比PP-OCRv3识别模型精度高3%,<br />可用于数据挖掘或对预测效率要求不高的场景。 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./高精度中文识别模型.md)/English | <img src="../doc/ppocr_v3/svtr_tiny.png" width=200> |
|
||||
| 手写体识别 | 新增字形支持 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./手写文字识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/7a8865b2836f42d382e7c3fdaedc4d307d797fa2bcd0466e9f8b7705efff5a7b" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="12"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 制造
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 模型下载 | 教程 | 示例图 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ------------------------------ | -------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 数码管识别 | 数码管数据合成、漏识别调优 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./光功率计数码管字符识别/光功率计数码管字符识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/7d5774a273f84efba5b9ce7fd3f86e9ef24b6473e046444db69fa3ca20ac0986" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| 液晶屏读数识别 | 检测模型蒸馏、Serving部署 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./液晶屏读数识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/901ab741cb46441ebec510b37e63b9d8d1b7c95f63cc4e5e8757f35179ae6373" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| 包装生产日期 | 点阵字符合成、过曝过暗文字识别 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./包装生产日期识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/d9e0533cc1df47ffa3bbe99de9e42639a3ebfa5bce834bafb1ca4574bf9db684" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| PCB文字识别 | 小尺寸文本检测与识别 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./PCB字符识别/PCB字符识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/95d8e95bf1ab476987f2519c0f8f0c60a0cdc2c444804ed6ab08f2f7ab054880" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| 电表识别 | 大分辨率图像检测调优 | [模型下载](#2) | | |
|
||||
| 液晶屏缺陷检测 | 非文字字符识别 | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="13"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 金融
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 模型下载 | 教程 | 示例图 |
|
||||
| -------------- | ----------------------------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 表单VQA | 多模态通用表单结构化提取 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./多模态表单识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/a3b25766f3074d2facdf88d4a60fc76612f51992fd124cf5bd846b213130665b" width = "200" height = "200" /> |
|
||||
| 增值税发票 | 关键信息抽取,SER、RE任务训练 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./发票关键信息抽取.md)/English | <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width = "200" /> |
|
||||
| 印章检测与识别 | 端到端弯曲文本识别 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./印章弯曲文字识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/498119182f0a414ab86ae2de752fa31c9ddc3a74a76847049cc57884602cb269" width = "150" /> |
|
||||
| 通用卡证识别 | 通用结构化提取 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./快速构建卡证类OCR.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/981640e17d05487e961162f8576c9e11634ca157f79048d4bd9d3bc21722afe8" width = "300" /> |
|
||||
| 身份证识别 | 结构化提取、图像阴影 | | | |
|
||||
| 合同比对 | 密集文本检测、NLP关键信息抽取 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./扫描合同关键信息提取.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/54f3053e6e1b47a39b26e757006fe2c44910d60a3809422ab76c25396b92e69b" width = "300" /> |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="14"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### 交通
|
||||
|
||||
| 类别 | 亮点 | 模型下载 | 教程 | 示例图 |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------ | -------------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 车牌识别 | 多角度图像、轻量模型、端侧部署 | [模型下载](#2) | [中文](./轻量级车牌识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/76b6a0939c2c4cf49039b6563c4b28e241e11285d7464e799e81c58c0f7707a7" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| 驾驶证/行驶证识别 | 尽请期待 | | | |
|
||||
| 快递单识别 | 尽请期待 | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## 模型下载
|
||||
|
||||
如需下载上述场景中已经训练好的垂类模型,可以扫描下方二维码,关注公众号填写问卷后,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取20G OCR学习大礼包(内含《动手学OCR》电子书、课程回放视频、前沿论文等重磅资料)
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
如果您是企业开发者且未在上述场景中找到合适的方案,可以填写[OCR应用合作调研问卷](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vj/QwF7GKw.aspx),免费与官方团队展开不同层次的合作,包括但不限于问题抽象、确定技术方案、项目答疑、共同研发等。如果您已经使用PaddleOCR落地项目,也可以填写此问卷,与飞桨平台共同宣传推广,提升企业技术品宣。期待您的提交!
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://trackgit.com">
|
||||
<img src="https://us-central1-trackgit-analytics.cloudfunctions.net/token/ping/l63cvzo0w09yxypc7ygl" alt="traffic" />
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||
English| [简体中文](README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
# Application
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR scene application covers general, manufacturing, finance, transportation industry of the main OCR vertical applications, on the basis of the general capabilities of PP-OCR, PP-Structure, in the form of notebook to show the use of scene data fine-tuning, model optimization methods, data augmentation and other content, for developers to quickly land OCR applications to provide demonstration and inspiration.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tutorial](#1)
|
||||
- [General](#11)
|
||||
- [Manufacturing](#12)
|
||||
- [Finance](#13)
|
||||
- [Transportation](#14)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Model Download](#2)
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="1"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="11"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### General
|
||||
|
||||
| Case | Feature | Model Download | Tutorial | Example |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------- | --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| High-precision Chineses recognition model SVTR | New model | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./高精度中文识别模型.md)/English | <img src="../doc/ppocr_v3/svtr_tiny.png" width=200> |
|
||||
| Chinese handwriting recognition | New font support | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./手写文字识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/7a8865b2836f42d382e7c3fdaedc4d307d797fa2bcd0466e9f8b7705efff5a7b" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="12"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Manufacturing
|
||||
|
||||
| Case | Feature | Model Download | Tutorial | Example |
|
||||
| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Digital tube | Digital tube data sythesis, recognition model fine-tuning | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./光功率计数码管字符识别/光功率计数码管字符识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/7d5774a273f84efba5b9ce7fd3f86e9ef24b6473e046444db69fa3ca20ac0986" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| LCD screen | Detection model distillation, serving deployment | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./液晶屏读数识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/901ab741cb46441ebec510b37e63b9d8d1b7c95f63cc4e5e8757f35179ae6373" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| Packaging production data | Dot matrix character synthesis, overexposure and overdark text recognition | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./包装生产日期识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/d9e0533cc1df47ffa3bbe99de9e42639a3ebfa5bce834bafb1ca4574bf9db684" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| PCB text recognition | Small size text detection and recognition | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./PCB字符识别/PCB字符识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/95d8e95bf1ab476987f2519c0f8f0c60a0cdc2c444804ed6ab08f2f7ab054880" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| Meter text recognition | High-resolution image detection fine-tuning | [Model Download](#2) | | |
|
||||
| LCD character defect detection | Non-text character recognition | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="13"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Finance
|
||||
|
||||
| Case | Feature | Model Download | Tutorial | Example |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------- | -------------------- | ----------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| Form visual question and answer | Multimodal general form structured extraction | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./多模态表单识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/a3b25766f3074d2facdf88d4a60fc76612f51992fd124cf5bd846b213130665b" width = "200" height = "200" /> |
|
||||
| VAT invoice | Key information extraction, SER, RE task fine-tune | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./发票关键信息抽取.md)/English | <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width = "200" /> |
|
||||
| Seal detection and recognition | End-to-end curved text recognition | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./印章弯曲文字识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/498119182f0a414ab86ae2de752fa31c9ddc3a74a76847049cc57884602cb269" width = "150" /> |
|
||||
| Universal card recognition | Universal structured extraction | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./快速构建卡证类OCR.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/981640e17d05487e961162f8576c9e11634ca157f79048d4bd9d3bc21722afe8" width = "300" /> |
|
||||
| ID card recognition | Structured extraction, image shading | | | |
|
||||
| Contract key information extraction | Dense text detection, NLP concatenation | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./扫描合同关键信息提取.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/54f3053e6e1b47a39b26e757006fe2c44910d60a3809422ab76c25396b92e69b" width = "300" /> |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="14"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Transportation
|
||||
|
||||
| Case | Feature | Model Download | Tutorial | Example |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------------- | ----------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| License plate recognition | Multi-angle images, lightweight models, edge-side deployment | [Model Download](#2) | [中文](./轻量级车牌识别.md)/English | <img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/76b6a0939c2c4cf49039b6563c4b28e241e11285d7464e799e81c58c0f7707a7" width = "200" height = "100" /> |
|
||||
| Driver's license/driving license identification | coming soon | | | |
|
||||
| Express text recognition | coming soon | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="2"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Model Download
|
||||
|
||||
- For international developers: We're building a way to download these trained models, and since the current tutorials are Chinese, if you are good at both Chinese and English, or willing to polish English documents, please let us know in [discussion](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/discussions).
|
||||
- For Chinese developer: If you want to download the trained application model in the above scenarios, scan the QR code below with your WeChat, follow the PaddlePaddle official account to fill in the questionnaire, and join the PaddleOCR official group to get the 20G OCR learning materials (including "Dive into OCR" e-book, course video, application models and other materials)
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are an enterprise developer and have not found a suitable solution in the above scenarios, you can fill in the [OCR Application Cooperation Survey Questionnaire](https://paddle.wjx.cn/vj/QwF7GKw.aspx) to carry out different levels of cooperation with the official team **for free**, including but not limited to problem abstraction, technical solution determination, project Q&A, joint research and development, etc. If you have already used paddleOCR in your project, you can also fill out this questionnaire to jointly promote with the PaddlePaddle and enhance the technical publicity of enterprises. Looking forward to your submission!
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://trackgit.com">
|
||||
<img src="https://us-central1-trackgit-analytics.cloudfunctions.net/token/ping/l6u6aszdfexs2jnrlil6" alt="trackgit-views" />
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,472 @@
|
|||
# 智能运营:通用中文表格识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 背景介绍](#1-背景介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 中文表格识别](#2-中文表格识别)
|
||||
- [2.1 环境准备](#21-环境准备)
|
||||
- [2.2 准备数据集](#22-准备数据集)
|
||||
- [2.2.1 划分训练测试集](#221-划分训练测试集)
|
||||
- [2.2.2 查看数据集](#222-查看数据集)
|
||||
- [2.3 训练](#23-训练)
|
||||
- [2.4 验证](#24-验证)
|
||||
- [2.5 训练引擎推理](#25-训练引擎推理)
|
||||
- [2.6 模型导出](#26-模型导出)
|
||||
- [2.7 预测引擎推理](#27-预测引擎推理)
|
||||
- [2.8 表格识别](#28-表格识别)
|
||||
- [3. 表格属性识别](#3-表格属性识别)
|
||||
- [3.1 代码、环境、数据准备](#31-代码环境数据准备)
|
||||
- [3.1.1 代码准备](#311-代码准备)
|
||||
- [3.1.2 环境准备](#312-环境准备)
|
||||
- [3.1.3 数据准备](#313-数据准备)
|
||||
- [3.2 表格属性识别训练](#32-表格属性识别训练)
|
||||
- [3.3 表格属性识别推理和部署](#33-表格属性识别推理和部署)
|
||||
- [3.3.1 模型转换](#331-模型转换)
|
||||
- [3.3.2 模型推理](#332-模型推理)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 背景介绍
|
||||
|
||||
中文表格识别在金融行业有着广泛的应用,如保险理赔、财报分析和信息录入等领域。当前,金融行业的表格识别主要以手动录入为主,开发一种自动表格识别成为丞待解决的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在金融行业中,表格图像主要有清单类的单元格密集型表格,申请表类的大单元格表格,拍照表格和倾斜表格四种主要形式。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
当前的表格识别算法不能很好的处理这些场景下的表格图像。在本例中,我们使用PP-StructureV2最新发布的表格识别模型SLANet来演示如何进行中文表格是识别。同时,为了方便作业流程,我们使用表格属性识别模型对表格图像的属性进行识别,对表格的难易程度进行判断,加快人工进行校对速度。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目AI Studio链接:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4588067
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 中文表格识别
|
||||
### 2.1 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 下载PaddleOCR代码
|
||||
! git clone -b dygraph https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 安装PaddleOCR环境
|
||||
! pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt --force-reinstall
|
||||
! pip install protobuf==3.19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 准备数据集
|
||||
|
||||
本例中使用的数据集采用表格[生成工具](https://github.com/WenmuZhou/TableGeneration)制作。
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令对数据集进行解压,并查看数据集大小
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! cd data/data165849 && tar -xf table_gen_dataset.tar && cd -
|
||||
! wc -l data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/gt.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2.1 划分训练测试集
|
||||
|
||||
使用下述命令将数据集划分为训练集和测试集, 这里将90%划分为训练集,10%划分为测试集
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
with open('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/gt.txt') as f:
|
||||
lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
random.shuffle(lines)
|
||||
train_len = int(len(lines)*0.9)
|
||||
train_list = lines[:train_len]
|
||||
val_list = lines[train_len:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 保存结果
|
||||
with open('/home/aistudio/train.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
|
||||
f.writelines(train_list)
|
||||
with open('/home/aistudio/val.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
|
||||
f.writelines(val_list)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
划分完成后,数据集信息如下
|
||||
|
||||
|类型|数量|图片地址|标注文件路径|
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|训练集|18000|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset|/home/aistudio/train.txt|
|
||||
|测试集|2000|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset|/home/aistudio/val.txt|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2.2 查看数据集
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import os, json
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
%matplotlib inline
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_line(data_dir, line):
|
||||
data_line = line.strip("\n")
|
||||
info = json.loads(data_line)
|
||||
file_name = info['filename']
|
||||
cells = info['html']['cells'].copy()
|
||||
structure = info['html']['structure']['tokens'].copy()
|
||||
|
||||
img_path = os.path.join(data_dir, file_name)
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
|
||||
print(img_path)
|
||||
return None
|
||||
data = {
|
||||
'img_path': img_path,
|
||||
'cells': cells,
|
||||
'structure': structure,
|
||||
'file_name': file_name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
def draw_bbox(img_path, points, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2):
|
||||
if isinstance(img_path, str):
|
||||
img_path = cv2.imread(img_path)
|
||||
img_path = img_path.copy()
|
||||
for point in points:
|
||||
cv2.polylines(img_path, [point.astype(int)], True, color, thickness)
|
||||
return img_path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rebuild_html(data):
|
||||
html_code = data['structure']
|
||||
cells = data['cells']
|
||||
to_insert = [i for i, tag in enumerate(html_code) if tag in ('<td>', '>')]
|
||||
|
||||
for i, cell in zip(to_insert[::-1], cells[::-1]):
|
||||
if cell['tokens']:
|
||||
text = ''.join(cell['tokens'])
|
||||
# skip empty text
|
||||
sp_char_list = ['<b>', '</b>', '\u2028', ' ', '<i>', '</i>']
|
||||
text_remove_style = skip_char(text, sp_char_list)
|
||||
if len(text_remove_style) == 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
html_code.insert(i + 1, text)
|
||||
|
||||
html_code = ''.join(html_code)
|
||||
return html_code
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def skip_char(text, sp_char_list):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
skip empty cell
|
||||
@param text: text in cell
|
||||
@param sp_char_list: style char and special code
|
||||
@return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for sp_char in sp_char_list:
|
||||
text = text.replace(sp_char, '')
|
||||
return text
|
||||
|
||||
save_dir = '/home/aistudio/vis'
|
||||
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
image_dir = '/home/aistudio/data/data165849/'
|
||||
html_str = '<table border="1">'
|
||||
|
||||
# 解析标注信息并还原html表格
|
||||
data = parse_line(image_dir, val_list[0])
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(data['img_path'])
|
||||
img_name = ''.join(os.path.basename(data['file_name']).split('.')[:-1])
|
||||
img_save_name = os.path.join(save_dir, img_name)
|
||||
boxes = [np.array(x['bbox']) for x in data['cells']]
|
||||
show_img = draw_bbox(data['img_path'], boxes)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(img_save_name + '_show.jpg', show_img)
|
||||
|
||||
html = rebuild_html(data)
|
||||
html_str += html
|
||||
html_str += '</table>'
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示标注的html字符串
|
||||
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
|
||||
display(HTML(html_str))
|
||||
# 显示单元格坐标
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.3 训练
|
||||
|
||||
这里选用PP-StructureV2中的表格识别模型[SLANet](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/configs/table/SLANet.yml)
|
||||
|
||||
SLANet是PP-StructureV2全新推出的表格识别模型,相比PP-StructureV1中TableRec-RARE,在速度不变的情况下精度提升4.7%。TEDS提升2%
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|算法|Acc|[TEDS(Tree-Edit-Distance-based Similarity)](https://github.com/ibm-aur-nlp/PubTabNet/tree/master/src)|Speed|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | ---|
|
||||
| EDD<sup>[2]</sup> |x| 88.30% |x|
|
||||
| TableRec-RARE(ours) | 71.73%| 93.88% |779ms|
|
||||
| SLANet(ours) | 76.31%| 95.89%|766ms|
|
||||
|
||||
进行训练之前先使用如下命令下载预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 进入PaddleOCR工作目录
|
||||
os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
|
||||
# 下载英文预训练模型
|
||||
! wget -nc -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/slanet/en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train.tar --no-check-certificate
|
||||
! cd ./pretrain_models/ && tar xf en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train.tar && cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令即可启动训练,需要修改的配置有
|
||||
|
||||
|字段|修改值|含义|
|
||||
|---|---|---|
|
||||
|Global.pretrained_model|./pretrain_models/en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train/best_accuracy.pdparams|指向英文表格预训练模型地址|
|
||||
|Global.eval_batch_step|562|模型多少step评估一次,一般设置为一个epoch总的step数|
|
||||
|Optimizer.lr.name|Const|学习率衰减器 |
|
||||
|Optimizer.lr.learning_rate|0.0005|学习率设为之前的0.05倍 |
|
||||
|Train.dataset.data_dir|/home/aistudio/data/data165849|指向训练集图片存放目录 |
|
||||
|Train.dataset.label_file_list|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/train.txt|指向训练集标注文件 |
|
||||
|Train.loader.batch_size_per_card|32|训练时每张卡的batch_size |
|
||||
|Train.loader.num_workers|1|训练集多进程数据读取的进程数,在aistudio中需要设为1 |
|
||||
|Eval.dataset.data_dir|/home/aistudio/data/data165849|指向测试集图片存放目录 |
|
||||
|Eval.dataset.label_file_list|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/val.txt|指向测试集标注文件 |
|
||||
|Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card|32|测试时每张卡的batch_size |
|
||||
|Eval.loader.num_workers|1|测试集多进程数据读取的进程数,在aistudio中需要设为1 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
已经修改好的配置存储在 `/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
|
||||
! python3 tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
大约在7个epoch后达到最高精度 97.49%
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.4 验证
|
||||
|
||||
训练完成后,可使用如下命令在测试集上评估最优模型的精度
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! python3 tools/eval.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.5 训练引擎推理
|
||||
使用如下命令可使用训练引擎对单张图片进行推理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os;os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
|
||||
! python3 tools/infer_table.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams Global.infer_img=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
%matplotlib inline
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示原图
|
||||
show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示预测的单元格
|
||||
show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/infer/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.6 模型导出
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令可将模型导出为inference模型
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! python3 tools/export_model.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams Global.save_inference_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.7 预测引擎推理
|
||||
使用如下命令可使用预测引擎对单张图片进行推理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure')
|
||||
! python3 table/predict_structure.py \
|
||||
--table_model_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer \
|
||||
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
|
||||
--image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg \
|
||||
--output=../output/inference
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 显示原图
|
||||
show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示预测的单元格
|
||||
show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/inference/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.8 表格识别
|
||||
|
||||
在表格结构模型训练完成后,可结合OCR检测识别模型,对表格内容进行识别。
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载PP-OCRv3文字检测识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 下载PP-OCRv3文本检测识别模型并解压
|
||||
! wget -nc -P ./inference/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer.tar --no-check-certificate
|
||||
! wget -nc -P ./inference/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer.tar --no-check-certificate
|
||||
! cd ./inference/ && tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer.tar && tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer.tar && cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
模型下载完成后,使用如下命令进行表格识别
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os;os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure')
|
||||
! python3 table/predict_table.py \
|
||||
--det_model_dir=inference/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir=inference/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer \
|
||||
--table_model_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer \
|
||||
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt \
|
||||
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
|
||||
--image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg \
|
||||
--output=../output/table
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 显示原图
|
||||
show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
|
||||
plt.imshow(show_img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示预测结果
|
||||
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
|
||||
display(HTML('<html><body><table><tr><td colspan="5">alleadersh</td><td rowspan="2">不贰过,推</td><td rowspan="2">从自己参与浙江数</td><td rowspan="2">。另一方</td></tr><tr><td>AnSha</td><td>自己越</td><td>共商共建工作协商</td><td>w.east </td><td>抓好改革试点任务</td></tr><tr><td>Edime</td><td>ImisesElec</td><td>怀天下”。</td><td></td><td>22.26 </td><td>31.61</td><td>4.30 </td><td>794.94</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="2">ip</td><td> Profundi</td><td>:2019年12月1</td><td>Horspro</td><td>444.48</td><td>2.41 </td><td>87</td><td>679.98</td></tr><tr><td> iehaiTrain</td><td>组长蒋蕊</td><td>Toafterdec</td><td>203.43</td><td>23.54 </td><td>4</td><td>4266.62</td></tr><tr><td>Tyint </td><td> roudlyRol</td><td>谢您的好意,我知道</td><td>ErChows</td><td></td><td>48.90</td><td>1031</td><td>6</td></tr><tr><td>NaFlint</td><td></td><td>一辈的</td><td>aterreclam</td><td>7823.86</td><td>9829.23</td><td>7.96 </td><td> 3068</td></tr><tr><td>家上下游企业,5</td><td>Tr</td><td>景象。当地球上的我们</td><td>Urelaw</td><td>799.62</td><td>354.96</td><td>12.98</td><td>33 </td></tr><tr><td>赛事(</td><td> uestCh</td><td>复制的业务模式并</td><td>Listicjust</td><td>9.23</td><td></td><td>92</td><td>53.22</td></tr><tr><td> Ca</td><td> Iskole</td><td>扶贫"之名引导</td><td> Papua </td><td>7191.90</td><td>1.65</td><td>3.62</td><td>48</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="2">避讳</td><td>ir</td><td>但由于</td><td>Fficeof</td><td>0.22</td><td>6.37</td><td>7.17</td><td>3397.75</td></tr><tr><td>ndaTurk</td><td>百处遗址</td><td>gMa</td><td>1288.34</td><td>2053.66</td><td>2.29</td><td>885.45</td></tr></table></body></html>'))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 表格属性识别
|
||||
### 3.1 代码、环境、数据准备
|
||||
#### 3.1.1 代码准备
|
||||
首先,我们需要准备训练表格属性的代码,PaddleClas集成了PULC方案,该方案可以快速获得一个在CPU上用时2ms的属性识别模型。PaddleClas代码可以clone下载得到。获取方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! git clone -b develop https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.1.2 环境准备
|
||||
其次,我们需要安装训练PaddleClas相关的依赖包
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
! pip install -r PaddleClas/requirements.txt --force-reinstall
|
||||
! pip install protobuf==3.20.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.1.3 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
最后,准备训练数据。在这里,我们一共定义了表格的6个属性,分别是表格来源、表格数量、表格颜色、表格清晰度、表格有无干扰、表格角度。其可视化如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们提供了一个表格属性的demo子集,可以快速迭代体验。下载方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd PaddleClas/dataset
|
||||
!wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/table_attribute.tar
|
||||
!tar -xf table_attribute.tar
|
||||
%cd ../PaddleClas/dataset
|
||||
%cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 表格属性识别训练
|
||||
表格属性训练整体pipelinie如下:
|
||||
|
||||
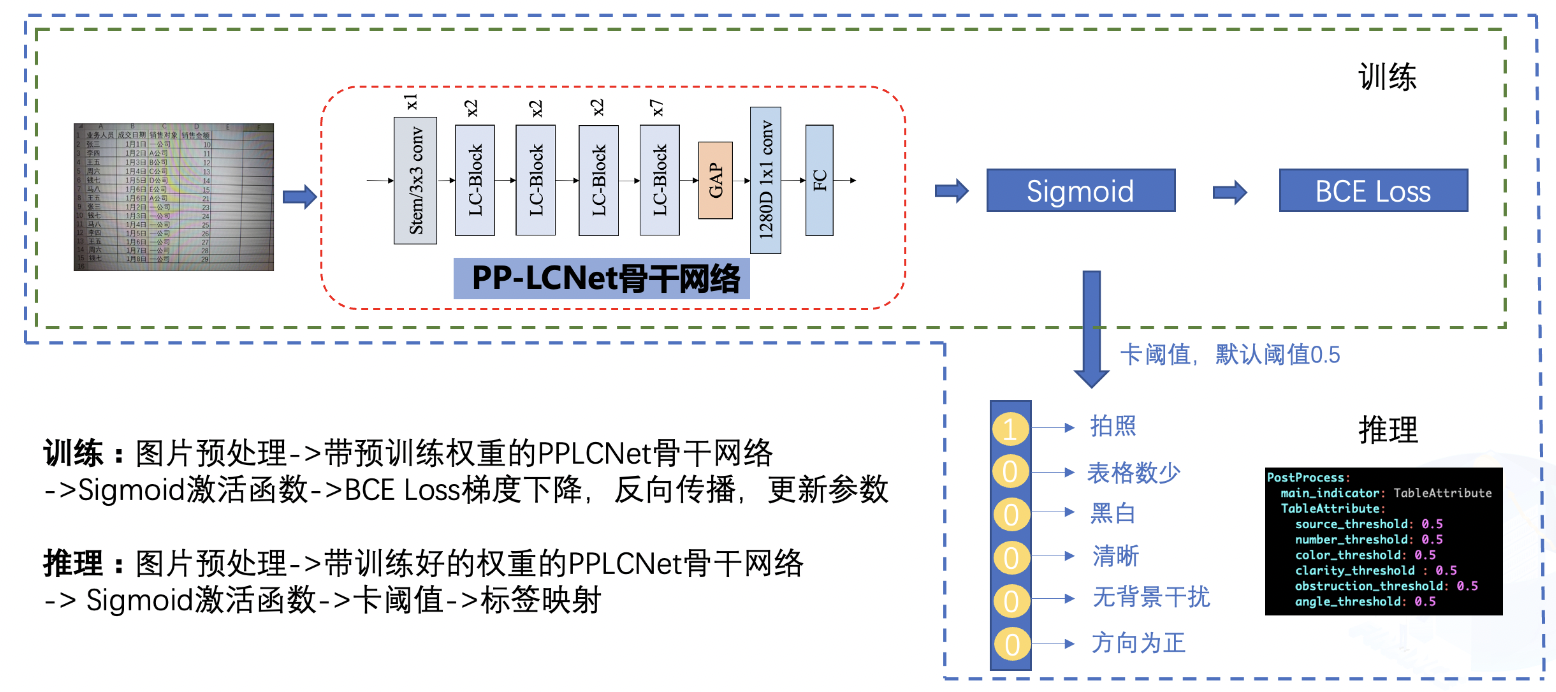
|
||||
|
||||
1.训练过程中,图片经过预处理之后,送入到骨干网络之中,骨干网络将抽取表格图片的特征,最终该特征连接输出的FC层,FC层经过Sigmoid激活函数后和真实标签做交叉熵损失函数,优化器通过对该损失函数做梯度下降来更新骨干网络的参数,经过多轮训练后,骨干网络的参数可以对为止图片做很好的预测;
|
||||
|
||||
2.推理过程中,图片经过预处理之后,送入到骨干网络之中,骨干网络加载学习好的权重后对该表格图片做出预测,预测的结果为一个6维向量,该向量中的每个元素反映了每个属性对应的概率值,通过对该值进一步卡阈值之后,得到最终的输出,最终的输出描述了该表格的6个属性。
|
||||
|
||||
当准备好相关的数据之后,可以一键启动表格属性的训练,训练代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
!python tools/train.py -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/table_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml -o Global.device=cpu -o Global.epochs=10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.3 表格属性识别推理和部署
|
||||
#### 3.3.1 模型转换
|
||||
当训练好模型之后,需要将模型转换为推理模型进行部署。转换脚本如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
!python tools/export_model.py -c ppcls/configs/PULC/table_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行以上命令之后,会在当前目录上生成`inference`文件夹,该文件夹中保存了当前精度最高的推理模型。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.3.2 模型推理
|
||||
安装推理需要的paddleclas包, 此时需要通过下载安装paddleclas的develop的whl包
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
!pip install https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/whl/paddleclas-0.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
进入`deploy`目录下即可对模型进行推理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd deploy/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
推理命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
!python python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/table_attribute/inference_table_attribute.yaml -o Global.inference_model_dir="../inference" -o Global.infer_imgs="../dataset/table_attribute/Table_val/val_9.jpg"
|
||||
!python python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/table_attribute/inference_table_attribute.yaml -o Global.inference_model_dir="../inference" -o Global.infer_imgs="../dataset/table_attribute/Table_val/val_3253.jpg"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
推理的表格图片:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
预测结果如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
val_9.jpg: {'attributes': ['Scanned', 'Little', 'Black-and-White', 'Clear', 'Without-Obstacles', 'Horizontal'], 'output': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
推理的表格图片:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
预测结果如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
val_3253.jpg: {'attributes': ['Photo', 'Little', 'Black-and-White', 'Blurry', 'Without-Obstacles', 'Tilted'], 'output': [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对比两张图片可以发现,第一张图片比较清晰,表格属性的结果也偏向于比较容易识别,我们可以更相信表格识别的结果,第二张图片比较模糊,且存在倾斜现象,表格识别可能存在错误,需要我们人工进一步校验。通过表格的属性识别能力,可以进一步将“人工”和“智能”很好的结合起来,为表格识别能力的落地的精度提供保障。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
|||
46.39
|
||||
40.08
|
||||
89.52
|
||||
-71.93
|
||||
23.19
|
||||
-81.02
|
||||
-34.09
|
||||
05.87
|
||||
-67.80
|
||||
-51.56
|
||||
-34.58
|
||||
37.91
|
||||
56.98
|
||||
29.01
|
||||
-90.13
|
||||
35.55
|
||||
66.07
|
||||
-90.35
|
||||
-50.93
|
||||
42.42
|
||||
21.40
|
||||
-30.99
|
||||
-71.78
|
||||
25.60
|
||||
-48.69
|
||||
-72.28
|
||||
-17.55
|
||||
-99.93
|
||||
-47.35
|
||||
-64.89
|
||||
-31.28
|
||||
-90.01
|
||||
05.17
|
||||
30.91
|
||||
30.56
|
||||
-06.90
|
||||
79.05
|
||||
67.74
|
||||
-32.31
|
||||
94.22
|
||||
28.75
|
||||
51.03
|
||||
-58.96
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,467 @@
|
|||
# 光功率计数码管字符识别
|
||||
|
||||
本案例将使用OCR技术自动识别光功率计显示屏文字,通过本章您可以掌握:
|
||||
|
||||
- PaddleOCR快速使用
|
||||
- 数据合成方法
|
||||
- 数据挖掘方法
|
||||
- 基于现有数据微调
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 背景介绍
|
||||
|
||||
光功率计(optical power meter )是指用于测量绝对光功率或通过一段光纤的光功率相对损耗的仪器。在光纤系统中,测量光功率是最基本的,非常像电子学中的万用表;在光纤测量中,光功率计是重负荷常用表。
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://bkimg.cdn.bcebos.com/pic/a08b87d6277f9e2f999f5e3e1c30e924b899f35a?x-bce-process=image/watermark,image_d2F0ZXIvYmFpa2U5Mg==,g_7,xp_5,yp_5/format,f_auto" width="400">
|
||||
|
||||
目前光功率计缺少将数据直接输出的功能,需要人工读数。这一项工作单调重复,如果可以使用机器替代人工,将节约大量成本。针对上述问题,希望通过摄像头拍照->智能读数的方式高效地完成此任务。
|
||||
|
||||
为实现智能读数,通常会采取文本检测+文本识别的方案:
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,使用文本检测模型定位出光功率计中的数字部分;
|
||||
|
||||
第二步,使用文本识别模型获得准确的数字和单位信息。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目主要介绍如何完成第二步文本识别部分,包括:真实评估集的建立、训练数据的合成、基于 PP-OCRv3 和 SVTR_Tiny 两个模型进行训练,以及评估和推理。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目难点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 光功率计数码管字符数据较少,难以获取。
|
||||
- 数码管中小数点占像素较少,容易漏识别。
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上问题, 本例选用 PP-OCRv3 和 SVTR_Tiny 两个高精度模型训练,同时提供了真实数据挖掘案例和数据合成案例。基于 PP-OCRv3 模型,在构建的真实评估集上精度从 52% 提升至 72%,SVTR_Tiny 模型精度可达到 78.9%。
|
||||
|
||||
aistudio项目链接: [光功率计数码管字符识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4049044?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. PaddleOCR 快速使用
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR 旨在打造一套丰富、领先、且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型,并应用落地。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
官方提供了适用于通用场景的高精轻量模型,首先使用官方提供的 PP-OCRv3 模型预测图片,验证下当前模型在光功率计场景上的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
- 准备环境
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U pip
|
||||
python3 -m pip install paddleocr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 测试效果
|
||||
|
||||
测试图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
paddleocr --lang=ch --det=Fase --image_dir=data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
得到如下测试结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
('.7000', 0.6885431408882141)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
发现数字识别较准,然而对负号和小数点识别不准确。 由于PP-OCRv3的训练数据大多为通用场景数据,在特定的场景上效果可能不够好。因此需要基于场景数据进行微调。
|
||||
|
||||
下面就主要介绍如何在光功率计(数码管)场景上微调训练。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
特定的工业场景往往很难获取开源的真实数据集,光功率计也是如此。在实际工业场景中,可以通过摄像头采集的方法收集大量真实数据,本例中重点介绍数据合成方法和真实数据挖掘方法,如何利用有限的数据优化模型精度。
|
||||
|
||||
数据集分为两个部分:合成数据,真实数据, 其中合成数据由 text_renderer 工具批量生成得到, 真实数据通过爬虫等方式在百度图片中搜索并使用 PPOCRLabel 标注得到。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 合成数据
|
||||
|
||||
本例中数据合成工具使用的是 [text_renderer](https://github.com/Sanster/text_renderer), 该工具可以合成用于文本识别训练的文本行数据:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export https_proxy=http://172.19.57.45:3128
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/oh-my-ocr/text_renderer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import os
|
||||
python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -r docker/requirements.txt
|
||||
python3 main.py \
|
||||
--config example_data/example.py \
|
||||
--dataset img \
|
||||
--num_processes 2 \
|
||||
--log_period 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
给定字体和语料,就可以合成较为丰富样式的文本行数据。 光功率计识别场景,目标是正确识别数码管文本,因此需要收集部分数码管字体,训练语料,用于合成文本识别数据。
|
||||
|
||||
将收集好的语料存放在 example_data 路径下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ln -s ./fonts/DS* text_renderer/example_data/font/
|
||||
ln -s ./corpus/digital.txt text_renderer/example_data/text/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改 text_renderer/example_data/font_list/font_list.txt ,选择需要的字体开始合成:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 main.py \
|
||||
--config example_data/digital_example.py \
|
||||
--dataset img \
|
||||
--num_processes 2 \
|
||||
--log_period 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
合成图片会被存在目录 text_renderer/example_data/digital/chn_data 下
|
||||
|
||||
查看合成的数据样例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 真实数据挖掘
|
||||
|
||||
模型训练需要使用真实数据作为评价指标,否则很容易过拟合到简单的合成数据中。没有开源数据的情况下,可以利用部分无标注数据+标注工具获得真实数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. 数据搜集
|
||||
|
||||
使用[爬虫工具](https://github.com/Joeclinton1/google-images-download.git)获得无标注数据
|
||||
|
||||
2. [PPOCRLabel](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/release/2.5/PPOCRLabel) 完成半自动标注
|
||||
|
||||
PPOCRLabel是一款适用于OCR领域的半自动化图形标注工具,内置PP-OCR模型对数据自动标注和重新识别。使用Python3和PyQT5编写,支持矩形框标注、表格标注、不规则文本标注、关键信息标注模式,导出格式可直接用于PaddleOCR检测和识别模型的训练。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
收集完数据后就可以进行分配了,验证集中一般都是真实数据,训练集中包含合成数据+真实数据。本例中标注了155张图片,其中训练集和验证集的数目为100和55。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
最终 `data` 文件夹应包含以下几部分:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|-data
|
||||
|- synth_train.txt
|
||||
|- real_train.txt
|
||||
|- real_eval.txt
|
||||
|- synthetic_data
|
||||
|- word_001.png
|
||||
|- word_002.jpg
|
||||
|- word_003.jpg
|
||||
| ...
|
||||
|- real_data
|
||||
|- word_001.png
|
||||
|- word_002.jpg
|
||||
|- word_003.jpg
|
||||
| ...
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 模型选择
|
||||
|
||||
本案例提供了2种文本识别模型:PP-OCRv3 识别模型 和 SVTR_Tiny:
|
||||
|
||||
[PP-OCRv3 识别模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md):PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法SVTR优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。并进行了一系列结构改进加速模型预测。
|
||||
|
||||
[SVTR_Tiny](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.00159):SVTR提出了一种用于场景文本识别的单视觉模型,该模型在patch-wise image tokenization框架内,完全摒弃了序列建模,在精度具有竞争力的前提下,模型参数量更少,速度更快。
|
||||
|
||||
以上两个策略在自建中文数据集上的精度和速度对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| ID | 策略 | 模型大小 | 精度 | 预测耗时(CPU + MKLDNN)|
|
||||
|-----|-----|--------|----| --- |
|
||||
| 01 | PP-OCRv2 | 8M | 74.80% | 8.54ms |
|
||||
| 02 | SVTR_Tiny | 21M | 80.10% | 97.00ms |
|
||||
| 03 | SVTR_LCNet(h32) | 12M | 71.90% | 6.60ms |
|
||||
| 04 | SVTR_LCNet(h48) | 12M | 73.98% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
| 05 | + GTC | 12M | 75.80% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
| 06 | + TextConAug | 12M | 76.30% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
| 07 | + TextRotNet | 12M | 76.90% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
| 08 | + UDML | 12M | 78.40% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
| 09 | + UIM | 12M | 79.40% | 7.60ms |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.3 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载 PaddleOCR 代码库
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone -b release/2.5 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR提供了训练脚本、评估脚本和预测脚本,本节将以 PP-OCRv3 中文识别模型为例:
|
||||
|
||||
**Step1:下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载 pretrain model,您可以下载训练好的模型在自定义数据上进行finetune
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR/
|
||||
# 下载PP-OCRv3 中文预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压模型参数
|
||||
cd pretrain_models
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Step2:自定义字典文件**
|
||||
|
||||
接下来需要提供一个字典({word_dict_name}.txt),使模型在训练时,可以将所有出现的字符映射为字典的索引。
|
||||
|
||||
因此字典需要包含所有希望被正确识别的字符,{word_dict_name}.txt需要写成如下格式,并以 `utf-8` 编码格式保存:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
2
|
||||
3
|
||||
4
|
||||
5
|
||||
6
|
||||
7
|
||||
8
|
||||
9
|
||||
-
|
||||
.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
word_dict.txt 每行有一个单字,将字符与数字索引映射在一起,“3.14” 将被映射成 [3, 11, 1, 4]
|
||||
|
||||
* 内置字典
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR内置了一部分字典,可以按需使用。
|
||||
|
||||
`ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt` 是一个包含6623个字符的中文字典
|
||||
|
||||
`ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt` 是一个包含36个字符的英文字典
|
||||
|
||||
* 自定义字典
|
||||
|
||||
内置字典面向通用场景,具体的工业场景中,可能需要识别特殊字符,或者只需识别某几个字符,此时自定义字典会更提升模型精度。例如在光功率计场景中,需要识别数字和单位。
|
||||
|
||||
遍历真实数据标签中的字符,制作字典`digital_dict.txt`如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-
|
||||
.
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
2
|
||||
3
|
||||
4
|
||||
5
|
||||
6
|
||||
7
|
||||
8
|
||||
9
|
||||
B
|
||||
E
|
||||
F
|
||||
H
|
||||
L
|
||||
N
|
||||
T
|
||||
W
|
||||
d
|
||||
k
|
||||
m
|
||||
n
|
||||
o
|
||||
z
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Step3:修改配置文件**
|
||||
|
||||
为了更好的使用预训练模型,训练推荐使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml](../../configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml)配置文件,并参考下列说明修改配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
以 `ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 为例:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 添加自定义字典,如修改字典请将路径指向新字典
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/dict/digital_dict.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 识别空格
|
||||
use_space_char: True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizer:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 添加学习率衰减策略
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.001
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 数据集格式,支持LMDBDataSet以及SimpleDataSet
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 数据集路径
|
||||
data_dir: ./data/
|
||||
# 训练集标签文件
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/digital_train.txt #11w
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/real_train.txt #100
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/dbm_img/dbm.txt #3w
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 0.3
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
...
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
# 修改 image_shape 以适应长文本
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 48, 320]
|
||||
...
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
...
|
||||
# 单卡训练的batch_size
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 数据集格式,支持LMDBDataSet以及SimpleDataSet
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 数据集路径
|
||||
data_dir: ./data
|
||||
# 验证集标签文件
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/digital_img/real_val.txt
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
...
|
||||
- RecResizeImg:
|
||||
# 修改 image_shape 以适应长文本
|
||||
image_shape: [3, 48, 320]
|
||||
...
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
# 单卡验证的batch_size
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 256
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
**注意,训练/预测/评估时的配置文件请务必与训练一致。**
|
||||
|
||||
**Step4:启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
*如果您安装的是cpu版本,请将配置文件中的 `use_gpu` 字段修改为false*
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU训练 支持单卡,多卡训练
|
||||
# 训练数码管数据 训练日志会自动保存为 "{save_model_dir}" 下的train.log
|
||||
|
||||
#单卡训练(训练周期长,不建议)
|
||||
python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
|
||||
#多卡训练,通过--gpus参数指定卡号
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1,2,3' tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrain_models/en_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR支持训练和评估交替进行, 可以在 `configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 中修改 `eval_batch_step` 设置评估频率,默认每500个iter评估一次。评估过程中默认将最佳acc模型,保存为 `output/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distill/best_accuracy` 。
|
||||
|
||||
如果验证集很大,测试将会比较耗时,建议减少评估次数,或训练完再进行评估。
|
||||
|
||||
### SVTR_Tiny 训练
|
||||
|
||||
SVTR_Tiny 训练步骤与上面一致,SVTR支持的配置和模型训练权重可以参考[算法介绍文档](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_svtr.md)
|
||||
|
||||
**Step1:下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 下载 SVTR_Tiny 中文识别预训练模型和配置文件
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压模型参数
|
||||
tar -xf rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar && rm -rf rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Step2:自定义字典文件**
|
||||
|
||||
字典依然使用自定义的 digital_dict.txt
|
||||
|
||||
**Step3:修改配置文件**
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件中对应修改字典路径和数据路径
|
||||
|
||||
**Step4:启动训练**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
## 单卡训练
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train/rec_svtr_tiny_6local_6global_stn_ch.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./rec_svtr_tiny_none_ctc_ch_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.4 验证效果
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理
|
||||
|
||||
* 指标评估
|
||||
|
||||
训练中模型参数默认保存在`Global.save_model_dir`目录下。在评估指标时,需要设置`Global.checkpoints`指向保存的参数文件。评估数据集可以通过 `configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml` 修改Eval中的 `label_file_path` 设置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# GPU 评估, Global.checkpoints 为待测权重
|
||||
python3 -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0' tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.checkpoints={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 测试识别效果
|
||||
|
||||
使用 PaddleOCR 训练好的模型,可以通过以下脚本进行快速预测。
|
||||
|
||||
默认预测图片存储在 `infer_img` 里,通过 `-o Global.checkpoints` 加载训练好的参数文件:
|
||||
|
||||
根据配置文件中设置的 `save_model_dir` 和 `save_epoch_step` 字段,会有以下几种参数被保存下来:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output/rec/
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.pdopt
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.pdparams
|
||||
├── best_accuracy.states
|
||||
├── config.yml
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.pdopt
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.pdparams
|
||||
├── iter_epoch_3.states
|
||||
├── latest.pdopt
|
||||
├── latest.pdparams
|
||||
├── latest.states
|
||||
└── train.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中 best_accuracy.* 是评估集上的最优模型;iter_epoch_x.* 是以 `save_epoch_step` 为间隔保存下来的模型;latest.* 是最后一个epoch的模型。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 预测英文结果
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model={path/to/weights}/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=test_digital.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测图片:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
得到输入图像的预测结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
infer_img: test_digital.png
|
||||
result: ('-70.00', 0.9998967)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,685 @@
|
|||
# 一种基于PaddleOCR的产品包装生产日期识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目介绍](#1-项目介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 环境搭建](#2-环境搭建)
|
||||
- [3. 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4. 直接使用PP-OCRv3模型评估](#4-直接使用PPOCRv3模型评估)
|
||||
- [5. 基于合成数据finetune](#5-基于合成数据finetune)
|
||||
- [5.1 Text Renderer数据合成方法](#51-TextRenderer数据合成方法)
|
||||
- [5.1.1 下载Text Renderer代码](#511-下载TextRenderer代码)
|
||||
- [5.1.2 准备背景图片](#512-准备背景图片)
|
||||
- [5.1.3 准备语料](#513-准备语料)
|
||||
- [5.1.4 下载字体](#514-下载字体)
|
||||
- [5.1.5 运行数据合成命令](#515-运行数据合成命令)
|
||||
- [5.2 模型训练](#52-模型训练)
|
||||
- [6. 基于真实数据finetune](#6-基于真实数据finetune)
|
||||
- [6.1 python爬虫获取数据](#61-python爬虫获取数据)
|
||||
- [6.2 数据挖掘](#62-数据挖掘)
|
||||
- [6.3 模型训练](#63-模型训练)
|
||||
- [7. 基于合成+真实数据finetune](#7-基于合成+真实数据finetune)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目介绍
|
||||
|
||||
产品包装生产日期是计算机视觉图像识别技术在工业场景中的一种应用。产品包装生产日期识别技术要求能够将产品生产日期从复杂背景中提取并识别出来,在物流管理、物资管理中得到广泛应用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 项目难点
|
||||
|
||||
1. 没有训练数据
|
||||
2. 图像质量层次不齐: 角度倾斜、图片模糊、光照不足、过曝等问题严重
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上问题, 本例选用PP-OCRv3这一开源超轻量OCR系统进行包装产品生产日期识别系统的开发。直接使用PP-OCRv3进行评估的精度为62.99%。为提升识别精度,我们首先使用数据合成工具合成了3k数据,基于这部分数据进行finetune,识别精度提升至73.66%。由于合成数据与真实数据之间的分布存在差异,为进一步提升精度,我们使用网络爬虫配合数据挖掘策略得到了1k带标签的真实数据,基于真实数据finetune的精度为71.33%。最后,我们综合使用合成数据和真实数据进行finetune,将识别精度提升至86.99%。各策略的精度提升效果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 策略 | 精度|
|
||||
| :--------------- | :-------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv3评估 | 62.99|
|
||||
| 合成数据finetune | 73.66|
|
||||
| 真实数据finetune | 71.33|
|
||||
| 真实+合成数据finetune | 86.99|
|
||||
|
||||
AIStudio项目链接: [一种基于PaddleOCR的包装生产日期识别方法](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4287736)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 环境搭建
|
||||
|
||||
本任务基于Aistudio完成, 具体环境如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统: Linux
|
||||
- PaddlePaddle: 2.3
|
||||
- PaddleOCR: Release/2.5
|
||||
- text_renderer: master
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddlleOCR代码并安装依赖库:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone -b dygraph https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装依赖库
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
本项目使用人工预标注的300张图像作为测试集。
|
||||
|
||||
部分数据示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
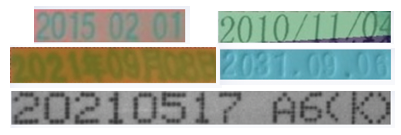
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
标签文件格式如下:
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
数据路径 标签(中间以制表符分隔)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|数据集类型|数量|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|测试集| 300|
|
||||
|
||||
数据集[下载链接](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/149770),下载后可以通过下方命令解压:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
tar -xvf data.tar
|
||||
mv data ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
数据解压后的文件结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── mining_images # 挖掘的真实数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── mining_train.list # 挖掘的真实数据文件列表
|
||||
│ ├── render_images # 合成数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── render_train.list # 合成数据文件列表
|
||||
│ ├── val # 测试集数据
|
||||
│ └── val.list # 测试集数据文件列表
|
||||
| ├── bg # 合成数据所需背景图像
|
||||
│ └── corpus # 合成数据所需语料
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 直接使用PP-OCRv3模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
准备好测试数据后,可以使用PaddleOCR的PP-OCRv3模型进行识别。
|
||||
|
||||
- 下载预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要下载PP-OCR v3中英文识别模型文件,下载链接可以在https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md#6 获取,下载命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
mkdir ckpt
|
||||
wget -nc -P ckpt https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
pushd ckpt/
|
||||
tar -xvf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
popd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令进行PP-OCRv3评估:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"]
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中各参数含义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-c: 指定使用的配置文件,ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml对应于OCRv3识别模型。
|
||||
-o: 覆盖配置文件中参数
|
||||
Global.checkpoints: 指定评估使用的模型文件路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir: 指定评估数据集路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list: 指定评估数据集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 基于合成数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1 Text Renderer数据合成方法
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.1 下载Text Renderer代码
|
||||
|
||||
首先从github或gitee下载Text Renderer代码,并安装相关依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://gitee.com/wowowoll/text_renderer.git
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装依赖库
|
||||
cd text_renderer
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用text renderer合成数据之前需要准备好背景图片、语料以及字体库,下面将逐一介绍各个步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.2 准备背景图片
|
||||
|
||||
观察日常生活中常见的包装生产日期图片,我们可以发现其背景相对简单。为此我们可以从网上找一下图片,截取部分图像块作为背景图像。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分图像作为背景图片,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的背景图像,示例如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
背景图像存放于如下位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
| ├── bg # 合成数据所需背景图像
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.3 准备语料
|
||||
|
||||
观察测试集生产日期图像,我们可以知道如下数据有如下特点:
|
||||
1. 由年月日组成,中间可能以“/”、“-”、“:”、“.”或者空格间隔,也可能以汉字年月日分隔
|
||||
2. 有些生产日期包含在产品批号中,此时可能包含具体时间、英文字母或数字标识
|
||||
|
||||
基于以上两点,我们编写语料生成脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from random import choice
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
cropus_num = 2000 #设置语料数量
|
||||
|
||||
def get_cropus(f):
|
||||
# 随机生成年份
|
||||
year = random.randint(0, 22)
|
||||
# 随机生成月份
|
||||
month = random.randint(1, 12)
|
||||
# 随机生成日期
|
||||
day_dict = {31: [1,3,5,7,8,10,12], 30: [4,6,9,11], 28: [2]}
|
||||
for item in day_dict:
|
||||
if month in day_dict[item]:
|
||||
day = random.randint(0, item)
|
||||
# 随机生成小时
|
||||
hours = random.randint(0, 24)
|
||||
# 随机生成分钟
|
||||
minute = random.randint(0, 60)
|
||||
# 随机生成秒数
|
||||
second = random.randint(0, 60)
|
||||
|
||||
# 随机生成产品标识字符
|
||||
length = random.randint(0, 6)
|
||||
file_id = []
|
||||
flag = 0
|
||||
my_dict = [i for i in range(48,58)] + [j for j in range(40, 42)] + [k for k in range(65,90)] # 大小写字母 + 括号
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, length):
|
||||
if flag:
|
||||
if i == flag+2: #括号匹配
|
||||
file_id.append(')')
|
||||
flag = 0
|
||||
continue
|
||||
sel = choice(my_dict)
|
||||
if sel == 41:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if sel == 40:
|
||||
if i == 1 or i > length-3:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
flag = i
|
||||
my_ascii = chr(sel)
|
||||
file_id.append(my_ascii)
|
||||
file_id_str = ''.join(file_id)
|
||||
|
||||
#随机生成产品标识字符
|
||||
file_id2 = random.randint(0, 9)
|
||||
|
||||
rad = random.random()
|
||||
if rad < 0.3:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}{:02d}{:02d} {}'.format(year, month, day, file_id_str))
|
||||
elif 0.3 < rad < 0.5:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}年{:02d}月{:02d}日'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.5 < rad < 0.7:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}/{:02d}/{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.7 < rad < 0.8:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}-{:02d}-{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
elif 0.8 < rad < 0.9:
|
||||
f.write('20{:02d}.{:02d}.{:02d}'.format(year, month, day))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
f.write('{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d} {:02d}'.format(hours, minute, second, file_id2))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
file_path = '/home/aistudio/text_renderer/my_data/cropus'
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
|
||||
os.makedirs(file_path)
|
||||
file_name = os.path.join(file_path, 'books.txt')
|
||||
f = open(file_name, 'w')
|
||||
for i in range(cropus_num):
|
||||
get_cropus(f)
|
||||
if i < cropus_num-1:
|
||||
f.write('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分语料,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的语料库,默认位置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ └── corpus #合成数据所需语料
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.4 下载字体
|
||||
|
||||
观察包装生产日期,我们可以发现其使用的字体为点阵体。字体可以在如下网址下载:
|
||||
https://www.fonts.net.cn/fonts-en/tag-dianzhen-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
本项目已准备了部分字体,在第3部分完成数据准备后,可以得到我们准备好的字体,默认位置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ └── fonts #合成数据所需字体
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载好字体后,还需要在list文件中指定字体文件存放路径,脚本如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd text_renderer/my_data/
|
||||
touch fonts.list
|
||||
ls /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/fonts/* > fonts.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.5 运行数据合成命令
|
||||
|
||||
完成数据准备后,my_data文件结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
my_data/
|
||||
├── cropus
|
||||
│ └── books.txt #语料库
|
||||
├── eng.txt #字符列表
|
||||
└── fonts.list #字体列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在运行合成数据命令之前,还有两处细节需要手动修改:
|
||||
1. 将默认配置文件`text_renderer/configs/default.yaml`中第9行enable的值设为`true`,即允许合成彩色图像。否则合成的都是灰度图。
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# color boundary is in R,G,B format
|
||||
font_color:
|
||||
+ enable: true #false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 将`text_renderer/textrenderer/renderer.py`第184行作如下修改,取消padding。否则图片两端会有一些空白。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
padding = random.randint(s_bbox_width // 10, s_bbox_width // 8) #修改前
|
||||
padding = 0 #修改后
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行数据合成命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/text_renderer/
|
||||
python main.py --num_img=3000 \
|
||||
--fonts_list='./my_data/fonts.list' \
|
||||
--corpus_dir "./my_data/cropus" \
|
||||
--corpus_mode "list" \
|
||||
--bg_dir "/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/bg/" \
|
||||
--img_width 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
合成好的数据默认保存在`text_renderer/output`目录下,可进入该目录查看合成的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
合成数据示例如下
|
||||
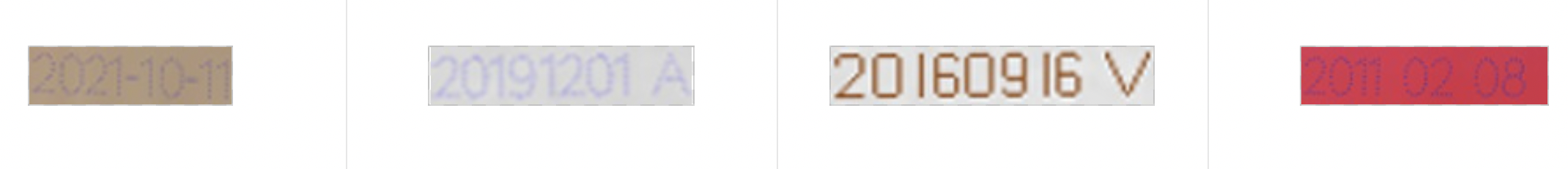
|
||||
|
||||
数据合成好后,还需要生成如下格式的训练所需的标注文件,
|
||||
```
|
||||
图像路径 标签
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下脚本即可生成标注文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
abspath = '/home/aistudio/text_renderer/output/default/'
|
||||
|
||||
#标注文件生成路径
|
||||
fout = open('./render_train.list', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
with open('./output/default/tmp_labels.txt','r') as f:
|
||||
lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
for item in lines:
|
||||
label = item[9:]
|
||||
filename = item[:8] + '.jpg'
|
||||
fout.write(abspath + filename + '\t' + label)
|
||||
|
||||
fout.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
经过以上步骤,我们便完成了包装生产日期数据合成。
|
||||
数据位于`text_renderer/output`,标注文件位于`text_renderer/render_train.list`。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目提供了生成好的数据供大家体验,完成步骤3的数据准备后,可得数据路径位于:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── render_images # 合成数据示例
|
||||
│ ├── render_train.list #合成数据文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
准备好合成数据后,我们可以使用以下命令,利用合成数据进行finetune:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=20 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/render_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中各参数含义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
-c: 指定使用的配置文件,ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml对应于OCRv3识别模型。
|
||||
-o: 覆盖配置文件中参数
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model: 指定finetune使用的预训练模型
|
||||
Global.epoch_num: 指定训练的epoch数
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step: 间隔多少step做一次评估
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card: 训练单卡batch size
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir: 评估数据集路径
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list: 评估数据集文件列表
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card: 评估单卡batch size
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. 基于真实数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用合成数据finetune能提升我们模型的识别精度,但由于合成数据和真实数据之间的分布可能有一定差异,因此作用有限。为进一步提高识别精度,本节介绍如何挖掘真实数据进行模型finetune。
|
||||
|
||||
数据挖掘的整体思路如下:
|
||||
1. 使用python爬虫从网上获取大量无标签数据
|
||||
2. 使用模型从大量无标签数据中构建出有效训练集
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.1 python爬虫获取数据
|
||||
|
||||
- 推荐使用[爬虫工具](https://github.com/Joeclinton1/google-images-download)获取无标签图片。
|
||||
|
||||
图片获取后,可按如下目录格式组织:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
sprider
|
||||
├── file.list
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── 00000.jpg
|
||||
│ ├── 00001.jpg
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.2 数据挖掘
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用PaddleOCR对获取到的图片进行挖掘,具体步骤如下:
|
||||
1. 使用 PP-OCRv3检测模型+svtr-tiny识别模型,对每张图片进行预测。
|
||||
2. 使用数据挖掘策略,得到有效图片。
|
||||
3. 将有效图片对应的图像区域和标签提取出来,构建训练集。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载预训练模型,PP-OCRv3检测模型下载链接:https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取svtr-tiny高精度中文识别预训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
完成下载后,可将模型存储于如下位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PaddleOCR
|
||||
├── data
|
||||
│ ├── rec_vit_sub_64_363_all/ # svtr_tiny高精度识别模型
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 下载解压PP-OCRv3检测模型
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
wget -nc -P ckpt https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
pushd ckpt
|
||||
tar -xvf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar
|
||||
popd ckpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在使用PPOCRv3检测模型+svtr-tiny识别模型进行预测之前,有如下两处细节需要手动修改:
|
||||
1. 将`tools/infer/predict_rec.py`中第110行`imgW`修改为`320`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#imgW = int((imgH * max_wh_ratio))
|
||||
imgW = 320
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 将`tools/infer/predict_system.py`第169行添加如下一行,将预测分数也写入结果文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
"scores": rec_res[idx][1],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
模型预测命令:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="/home/aistudio/sprider/data" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer/" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/rec_vit_sub_64_363_all/" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3,32,320"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
获得预测结果后,我们使用数据挖掘策略得到有效图片。具体挖掘策略如下:
|
||||
1. 预测置信度高于95%
|
||||
2. 识别结果包含字符‘20’,即年份
|
||||
3. 没有中文,或者有中文并且‘日’和'月'同时在识别结果中
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 获取有效预测
|
||||
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
zh_pattern = re.compile(u'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+') #正则表达式,筛选字符是否包含中文
|
||||
|
||||
file_path = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/inference_results/system_results.txt'
|
||||
out_path = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/selected_results.txt'
|
||||
f_out = open(out_path, 'w')
|
||||
|
||||
with open(file_path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
flag = False
|
||||
# 读取文件内容
|
||||
file_name, json_file = line.strip().split('\t')
|
||||
preds = json.loads(json_file)
|
||||
res = []
|
||||
for item in preds:
|
||||
transcription = item['transcription'] #获取识别结果
|
||||
scores = item['scores'] #获取识别得分
|
||||
# 挖掘策略
|
||||
if scores > 0.95:
|
||||
if '20' in transcription and len(transcription) > 4 and len(transcription) < 12:
|
||||
word = transcription
|
||||
if not(zh_pattern.search(word) and ('日' not in word or '月' not in word)):
|
||||
flag = True
|
||||
res.append(item)
|
||||
save_pred = file_name + "\t" + json.dumps(
|
||||
res, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n"
|
||||
if flag ==True:
|
||||
f_out.write(save_pred)
|
||||
|
||||
f_out.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后将有效预测对应的图像区域和标签提取出来,构建训练集。具体实现脚本如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
PATH = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/inference_results/' #数据原始路径
|
||||
SAVE_PATH = '/home/aistudio/mining_images/' #裁剪后数据保存路径
|
||||
file_list = '/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/selected_results.txt' #数据预测结果
|
||||
label_file = '/home/aistudio/mining_images/mining_train.list' #输出真实数据训练集标签list
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(SAVE_PATH):
|
||||
os.mkdir(SAVE_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
f_label = open(label_file, 'w')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rotate_crop_image(img, points):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
根据检测结果points,从输入图像img中裁剪出相应的区域
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert len(points) == 4, "shape of points must be 4*2"
|
||||
img_crop_width = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3])))
|
||||
img_crop_height = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2])))
|
||||
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
|
||||
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
|
||||
[0, img_crop_height]])
|
||||
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
|
||||
# 形变或倾斜,会做透视变换,reshape成矩形
|
||||
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
|
||||
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
|
||||
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
|
||||
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
|
||||
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)
|
||||
return dst_img
|
||||
|
||||
def crop_and_get_filelist(file_list):
|
||||
with open(file_list, "r", encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
|
||||
img_num = 0
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
img_name, json_file = line.strip().split('\t')
|
||||
preds = json.loads(json_file)
|
||||
for item in preds:
|
||||
transcription = item['transcription']
|
||||
points = item['points']
|
||||
points = np.array(points).astype('float32')
|
||||
#print('processing {}...'.format(img_name))
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(PATH+img_name)
|
||||
dst_img = get_rotate_crop_image(img, points)
|
||||
h, w, c = dst_img.shape
|
||||
newWidth = int((32. / h) * w)
|
||||
newImg = cv2.resize(dst_img, (newWidth, 32))
|
||||
new_img_name = '{:05d}.jpg'.format(img_num)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(SAVE_PATH+new_img_name, dst_img)
|
||||
f_label.write(SAVE_PATH+new_img_name+'\t'+transcription+'\n')
|
||||
img_num += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
crop_and_get_filelist(file_list)
|
||||
f_label.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.3 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
通过数据挖掘,我们得到了真实场景数据和对应的标签。接下来使用真实数据finetune,观察精度提升效果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
利用真实数据进行finetune:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=20 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/mining_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
各参数含义参考第6部分合成数据finetune,只需要对训练数据路径做相应的修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
示例使用我们提供的真实数据进行finetune,如想换成自己的数据,只需要相应的修改`Train.dataset.data_dir`和`Train.dataset.label_file_list`参数即可。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数据量不大,这里仅训练20个epoch即可。训练完成后,可以得到合成数据finetune后的精度为best acc=**71.33%**。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数量比较少,精度会比合成数据finetue的略低。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. 基于合成+真实数据finetune
|
||||
|
||||
为进一步提升模型精度,我们结合使用合成数据和挖掘到的真实数据进行finetune。
|
||||
|
||||
利用合成+真实数据进行finetune,各参数含义参考第6部分合成数据finetune,只需要对训练数据路径做相应的修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir: 训练数据集路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list: 训练集文件列表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成训练list文件:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 生成训练集文件list
|
||||
cat /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/render_train.list /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/mining_train.list > /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/data/render_mining_train.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动训练:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ${PaddleOCR_root}
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./ckpt/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.epoch_num=40 \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step='[0, 20]' \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=['./data/render_mining_train.list'] \
|
||||
Train.loader.batch_size_per_card=64 \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=./data \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=["./data/val.list"] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card=64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
示例使用我们提供的真实+合成数据进行finetune,如想换成自己的数据,只需要相应的修改Train.dataset.data_dir和Train.dataset.label_file_list参数即可。
|
||||
|
||||
由于数据量不大,这里仅训练40个epoch即可。训练完成后,可以得到合成数据finetune后的精度为best acc=**86.99%**。
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,相较于原始PP-OCRv3的识别精度62.99%,使用合成数据+真实数据finetune后,识别精度能提升24%。
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,可以同样扫描上方二维码下载,将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
模型的推理部署方法可以参考repo文档: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/deploy/README_ch.md
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# 基于VI-LayoutXLM的发票关键信息抽取
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目背景及意义](#1-项目背景及意义)
|
||||
- [2. 项目内容](#2-项目内容)
|
||||
- [3. 安装环境](#3-安装环境)
|
||||
- [4. 关键信息抽取](#4-关键信息抽取)
|
||||
- [4.1 文本检测](#41-文本检测)
|
||||
- [4.2 文本识别](#42-文本识别)
|
||||
- [4.3 语义实体识别](#43-语义实体识别)
|
||||
- [4.4 关系抽取](#44-关系抽取)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目背景及意义
|
||||
|
||||
关键信息抽取在文档场景中被广泛使用,如身份证中的姓名、住址信息抽取,快递单中的姓名、联系方式等关键字段内容的抽取。传统基于模板匹配的方案需要针对不同的场景制定模板并进行适配,较为繁琐,不够鲁棒。基于该问题,我们借助飞桨提供的PaddleOCR套件中的关键信息抽取方案,实现对增值税发票场景的关键信息抽取。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 项目内容
|
||||
|
||||
本项目基于PaddleOCR开源套件,以VI-LayoutXLM多模态关键信息抽取模型为基础,针对增值税发票场景进行适配,提取该场景的关键信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 安装环境
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 首先git官方的PaddleOCR项目,安装需要的依赖
|
||||
# 第一次运行打开该注释
|
||||
git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
# 安装PaddleOCR的依赖
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
# 安装关键信息抽取任务的依赖
|
||||
pip install -r ./ppstructure/kie/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 关键信息抽取
|
||||
|
||||
基于文档图像的关键信息抽取包含3个部分:(1)文本检测(2)文本识别(3)关键信息抽取方法,包括语义实体识别或者关系抽取,下面分别进行介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 文本检测
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本文重点关注发票的关键信息抽取模型训练与预测过程,因此在关键信息抽取过程中,直接使用标注的文本检测与识别标注信息进行测试,如果你希望自定义该场景的文本检测模型,完成端到端的关键信息抽取部分,请参考[文本检测模型训练教程](../doc/doc_ch/detection.md),按照训练数据格式准备数据,并完成该场景下垂类文本检测模型的微调过程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 文本识别
|
||||
|
||||
本文重点关注发票的关键信息抽取模型训练与预测过程,因此在关键信息抽取过程中,直接使用提供的文本检测与识别标注信息进行测试,如果你希望自定义该场景的文本检测模型,完成端到端的关键信息抽取部分,请参考[文本识别模型训练教程](../doc/doc_ch/recognition.md),按照训练数据格式准备数据,并完成该场景下垂类文本识别模型的微调过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition)
|
||||
|
||||
语义实体识别指的是给定一段文本行,确定其类别(如`姓名`、`住址`等类别)。PaddleOCR中提供了基于VI-LayoutXLM的多模态语义实体识别方法,融合文本、位置与版面信息,相比LayoutXLM多模态模型,去除了其中的视觉骨干网络特征提取部分,引入符合阅读顺序的文本行排序方法,同时使用UDML联合互蒸馏方法进行训练,最终在精度与速度方面均超越LayoutXLM。更多关于VI-LayoutXLM的算法介绍与精度指标,请参考:[VI-LayoutXLM算法介绍](../doc/doc_ch/algorithm_kie_vi_layoutxlm.md)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.1 准备数据
|
||||
|
||||
发票场景为例,我们首先需要标注出其中的关键字段,我们将其标注为`问题-答案`的key-value pair,如下,编号No为12270830,则`No`字段标注为question,`12270830`字段标注为answer。如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185381131-76b6e260-04fe-46d9-baca-6bdd7fe0d0ce.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
|
||||
* 如果文本检测模型数据标注过程中,没有标注 **非关键信息内容** 的检测框,那么在标注关键信息抽取任务的时候,也不需要标注该部分,如上图所示;如果标注的过程,如果同时标注了**非关键信息内容** 的检测框,那么我们需要将该部分的label记为other。
|
||||
* 标注过程中,需要以文本行为单位进行标注,无需标注单个字符的位置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
已经处理好的增值税发票数据集从这里下载:[增值税发票数据集下载链接](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/165561)。
|
||||
|
||||
下载好发票数据集,并解压在train_data目录下,目录结构如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
train_data
|
||||
|--zzsfp
|
||||
|---class_list.txt
|
||||
|---imgs/
|
||||
|---train.json
|
||||
|---val.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中`class_list.txt`是包含`other`, `question`, `answer`,3个种类的的类别列表(不区分大小写),`imgs`目录底下,`train.json`与`val.json`分别表示训练与评估集合的标注文件。训练集中包含30张图片,验证集中包含8张图片。部分标注如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
b33.jpg [{"transcription": "No", "label": "question", "points": [[2882, 472], [3026, 472], [3026, 588], [2882, 588]], }, {"transcription": "12269563", "label": "answer", "points": [[3066, 448], [3598, 448], [3598, 576], [3066, 576]], ]}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
相比于OCR检测的标注,仅多了`label`字段。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.2 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
VI-LayoutXLM的配置为[ser_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh_udml.yml](../configs/kie/vi_layoutxlm/ser_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh_udml.yml),需要修改数据、类别数目以及配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
Architecture:
|
||||
model_type: &model_type "kie"
|
||||
name: DistillationModel
|
||||
algorithm: Distillation
|
||||
Models:
|
||||
Teacher:
|
||||
pretrained:
|
||||
freeze_params: false
|
||||
return_all_feats: true
|
||||
model_type: *model_type
|
||||
algorithm: &algorithm "LayoutXLM"
|
||||
Transform:
|
||||
Backbone:
|
||||
name: LayoutXLMForSer
|
||||
pretrained: True
|
||||
# one of base or vi
|
||||
mode: vi
|
||||
checkpoints:
|
||||
# 定义类别数目
|
||||
num_classes: &num_classes 5
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
PostProcess:
|
||||
name: DistillationSerPostProcess
|
||||
model_name: ["Student", "Teacher"]
|
||||
key: backbone_out
|
||||
# 定义类别文件
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/zzsfp/class_list.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 定义训练数据目录与标注文件
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/zzsfp/imgs
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/zzsfp/train.json
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 定义评估数据目录与标注文件
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/zzsfp/imgs
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/zzsfp/val.json
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
LayoutXLM与VI-LayoutXLM针对该场景的训练结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型 | 迭代轮数 | Hmean |
|
||||
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| LayoutXLM | 50 | 100.00% |
|
||||
| VI-LayoutXLM | 50 | 100.00% |
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出,由于当前数据量较少,场景比较简单,因此2个模型的Hmean均达到了100%。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.3 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
模型训练过程中,使用的是知识蒸馏的策略,最终保留了学生模型的参数,在评估时,我们需要针对学生模型的配置文件进行修改: [ser_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh.yml](../configs/kie/vi_layoutxlm/ser_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh.yml),修改内容与训练配置相同,包括**类别数、类别映射文件、数据目录**。
|
||||
|
||||
修改完成后,执行下面的命令完成评估过程。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 注意:需要根据你的配置文件地址与保存的模型地址,对评估命令进行修改
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py -c ./fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[2022/08/18 08:49:58] ppocr INFO: metric eval ***************
|
||||
[2022/08/18 08:49:58] ppocr INFO: precision:1.0
|
||||
[2022/08/18 08:49:58] ppocr INFO: recall:1.0
|
||||
[2022/08/18 08:49:58] ppocr INFO: hmean:1.0
|
||||
[2022/08/18 08:49:58] ppocr INFO: fps:1.9740402401574881
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.4 模型预测
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令进行预测。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser.py -c fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/XFUND/zh_val/val.json Global.infer_mode=False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测结果会保存在配置文件中的`Global.save_res_path`目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
部分预测结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185310636-6ce02f7c-790d-479f-b163-ea97a5a04808.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 注意:在预测时,使用的文本检测与识别结果为标注的结果,直接从json文件里面进行读取。
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望使用OCR引擎结果得到的结果进行推理,则可以使用下面的命令进行推理。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser.py -c fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/zzsfp/imgs/b25.jpg Global.infer_mode=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185384321-61153faa-e407-45c4-8e7c-a39540248189.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
它会使用PP-OCRv3的文本检测与识别模型进行获取文本位置与内容信息。
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出,由于训练的过程中,没有标注额外的字段为other类别,所以大多数检测出来的字段被预测为question或者answer。
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望构建基于你在垂类场景训练得到的OCR检测与识别模型,可以使用下面的方法传入检测与识别的inference 模型路径,即可完成OCR文本检测与识别以及SER的串联过程。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser.py -c fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/zzsfp/imgs/b25.jpg Global.infer_mode=True Global.kie_rec_model_dir="your_rec_model" Global.kie_det_model_dir="your_det_model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.4 关系抽取(Relation Extraction)
|
||||
|
||||
使用SER模型,可以获取图像中所有的question与answer的字段,继续这些字段的类别,我们需要进一步获取question与answer之间的连接,因此需要进一步训练关系抽取模型,解决该问题。本文也基于VI-LayoutXLM多模态预训练模型,进行下游RE任务的模型训练。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.4.1 准备数据
|
||||
|
||||
以发票场景为例,相比于SER任务,RE中还需要标记每个文本行的id信息以及链接关系linking,如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185387870-dc9125a0-9ceb-4036-abf3-184b6e65dc7d.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
标注文件的部分内容如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
b33.jpg [{"transcription": "No", "label": "question", "points": [[2882, 472], [3026, 472], [3026, 588], [2882, 588]], "id": 0, "linking": [[0, 1]]}, {"transcription": "12269563", "label": "answer", "points": [[3066, 448], [3598, 448], [3598, 576], [3066, 576]], "id": 1, "linking": [[0, 1]]}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
相比与SER的标注,多了`id`与`linking`的信息,分别表示唯一标识以及连接关系。
|
||||
|
||||
已经处理好的增值税发票数据集从这里下载:[增值税发票数据集下载链接](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/165561)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.4.2 开始训练
|
||||
|
||||
基于VI-LayoutXLM的RE任务配置为[re_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh_udml.yml](../configs/kie/vi_layoutxlm/re_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh_udml.yml),需要修改**数据路径、类别列表文件**。
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
# 定义训练数据目录与标注文件
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/zzsfp/imgs
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/zzsfp/train.json
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- DecodeImage: # load image
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
channel_first: False
|
||||
- VQATokenLabelEncode: # Class handling label
|
||||
contains_re: True
|
||||
algorithm: *algorithm
|
||||
class_path: &class_path train_data/zzsfp/class_list.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
# 定义评估数据目录与标注文件
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: train_data/zzsfp/imgs
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- train_data/zzsfp/val.json
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
LayoutXLM与VI-LayoutXLM针对该场景的训练结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型 | 迭代轮数 | Hmean |
|
||||
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| LayoutXLM | 50 | 98.00% |
|
||||
| VI-LayoutXLM | 50 | 99.30% |
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出,对于VI-LayoutXLM相比LayoutXLM的Hmean高了1.3%。
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.4.3 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
模型训练过程中,使用的是知识蒸馏的策略,最终保留了学生模型的参数,在评估时,我们需要针对学生模型的配置文件进行修改: [re_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh.yml](../configs/kie/vi_layoutxlm/re_vi_layoutxlm_xfund_zh.yml),修改内容与训练配置相同,包括**类别映射文件、数据目录**。
|
||||
|
||||
修改完成后,执行下面的命令完成评估过程。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 注意:需要根据你的配置文件地址与保存的模型地址,对评估命令进行修改
|
||||
python3 tools/eval.py -c ./fapiao/re_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/re_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
[2022/08/18 12:17:14] ppocr INFO: metric eval ***************
|
||||
[2022/08/18 12:17:14] ppocr INFO: precision:1.0
|
||||
[2022/08/18 12:17:14] ppocr INFO: recall:0.9873417721518988
|
||||
[2022/08/18 12:17:14] ppocr INFO: hmean:0.9936305732484078
|
||||
[2022/08/18 12:17:14] ppocr INFO: fps:2.765963539771157
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.4.4 模型预测
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令进行预测。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# -c 后面的是RE任务的配置文件
|
||||
# -o 后面的字段是RE任务的配置
|
||||
# -c_ser 后面的是SER任务的配置文件
|
||||
# -c_ser 后面的字段是SER任务的配置
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser_re.py -c fapiao/re_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/re_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_trained/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/zzsfp/val.json Global.infer_mode=False -c_ser fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o_ser Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_trained/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测结果会保存在配置文件中的`Global.save_res_path`目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
部分预测结果如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/14270174/185393805-c67ff571-cf7e-4217-a4b0-8b396c4f22bb.jpg" width="800">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 注意:在预测时,使用的文本检测与识别结果为标注的结果,直接从json文件里面进行读取。
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望使用OCR引擎结果得到的结果进行推理,则可以使用下面的命令进行推理。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser_re.py -c fapiao/re_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/re_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/zzsfp/val.json Global.infer_mode=True -c_ser fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o_ser Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望构建基于你在垂类场景训练得到的OCR检测与识别模型,可以使用下面的方法传入,即可完成SER + RE的串联过程。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/infer_kie_token_ser_re.py -c fapiao/re_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/re_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./train_data/zzsfp/val.json Global.infer_mode=True -c_ser fapiao/ser_vi_layoutxlm.yml -o_ser Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=fapiao/models/ser_vi_layoutxlm_fapiao_udml/best_accuracy Global.kie_rec_model_dir="your_rec_model" Global.kie_det_model_dir="your_det_model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,899 @@
|
|||
# 多模态表单识别
|
||||
- [多模态表单识别](#多模态表单识别)
|
||||
- [1 项目说明](#1-项目说明)
|
||||
- [2 安装说明](#2-安装说明)
|
||||
- [3 数据准备](#3-数据准备)
|
||||
- [3.1 下载处理好的数据集](#31-下载处理好的数据集)
|
||||
- [3.2 转换为PaddleOCR检测和识别格式](#32-转换为paddleocr检测和识别格式)
|
||||
- [4 OCR](#4-ocr)
|
||||
- [4.1 文本检测](#41-文本检测)
|
||||
- [4.1.1 方案1:预训练模型](#411-方案1预训练模型)
|
||||
- [4.1.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+fine-tune](#412-方案2xfund数据集fine-tune)
|
||||
- [4.2 文本识别](#42-文本识别)
|
||||
- [4.2.1 方案1:预训练模型](#421-方案1预训练模型)
|
||||
- [4.2.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+finetune](#422-方案2xfund数据集finetune)
|
||||
- [4.2.3 方案3:XFUND数据集+finetune+真实通用识别数据](#423-方案3xfund数据集finetune真实通用识别数据)
|
||||
- [5 文档视觉问答(DOC-VQA)](#5-文档视觉问答doc-vqa)
|
||||
- [5.1 SER](#51-ser)
|
||||
- [5.1.1 模型训练](#511-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.1.2 模型评估](#512-模型评估)
|
||||
- [5.1.3 模型预测](#513-模型预测)
|
||||
- [5.2 RE](#52-re)
|
||||
- [5.2.1 模型训练](#521-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.2.2 模型评估](#522-模型评估)
|
||||
- [5.2.3 模型预测](#523-模型预测)
|
||||
- [6 导出Excel](#6-导出excel)
|
||||
- [获得模型](#获得模型)
|
||||
- [更多资源](#更多资源)
|
||||
- [参考链接](#参考链接)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1 项目说明
|
||||
|
||||
计算机视觉在金融领域的应用覆盖文字识别、图像识别、视频识别等,其中文字识别(OCR)是金融领域中的核心AI能力,其应用覆盖客户服务、风险防控、运营管理等各项业务,针对的对象包括通用卡证票据识别(银行卡、身份证、营业执照等)、通用文本表格识别(印刷体、多语言、手写体等)以及一些金融特色票据凭证。通过因此如果能够在结构化信息提取时同时利用文字、页面布局等信息,便可增强不同版式下的泛化性。
|
||||
|
||||
表单识别旨在识别各种具有表格性质的证件、房产证、营业执照、个人信息表、发票等关键键值对(如姓名-张三),其广泛应用于银行、证券、公司财务等领域,具有很高的商业价值。本次范例项目开源了全流程表单识别方案,能够在多个场景快速实现迁移能力。表单识别通常存在以下难点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 人工摘录工作效率低;
|
||||
- 国内常见表单版式多;
|
||||
- 传统技术方案泛化效果不满足。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
表单识别包含两大阶段:OCR阶段和文档视觉问答阶段。
|
||||
|
||||
其中,OCR阶段选取了PaddleOCR的PP-OCRv2模型,主要由文本检测和文本识别两个模块组成。DOC-VQA文档视觉问答阶段基于PaddleNLP自然语言处理算法库实现的LayoutXLM模型,支持基于多模态方法的语义实体识别(Semantic Entity Recognition, SER)以及关系抽取(Relation Extraction, RE)任务。本案例流程如 **图1** 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/9bd844b970f94e5ba0bc0c5799bd819ea9b1861bb306471fabc2d628864d418e'></center>
|
||||
<center>图1 多模态表单识别流程图</center>
|
||||
|
||||
注:欢迎再AIStudio领取免费算力体验线上实训,项目链接: [多模态表单识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3884375?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2 安装说明
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下载PaddleOCR源码,上述AIStudio项目中已经帮大家打包好的PaddleOCR(已经修改好配置文件),无需下载解压即可,只需安装依赖环境~
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
unzip -q PaddleOCR.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 如仍需安装or安装更新,可以执行以下步骤
|
||||
# git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b dygraph
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 安装依赖包
|
||||
pip install -U pip
|
||||
pip install -r /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install paddleocr
|
||||
|
||||
pip install yacs gnureadline paddlenlp==2.2.1
|
||||
pip install xlsxwriter
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3 数据准备
|
||||
|
||||
这里使用[XFUN数据集](https://github.com/doc-analysis/XFUND)做为实验数据集。 XFUN数据集是微软提出的一个用于KIE任务的多语言数据集,共包含七个数据集,每个数据集包含149张训练集和50张验证集
|
||||
|
||||
分别为:ZH(中文)、JA(日语)、ES(西班牙)、FR(法语)、IT(意大利)、DE(德语)、PT(葡萄牙)
|
||||
|
||||
本次实验选取中文数据集作为我们的演示数据集。法语数据集作为实践课程的数据集,数据集样例图如 **图2** 所示。
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0f84137778cd4ab6899c64109d452290e9c678ccf01744978bc9c0647adbba45" width="1000" ></center>
|
||||
<center>图2 数据集样例,左中文,右法语</center>
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 下载处理好的数据集
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
处理好的XFUND中文数据集下载地址:[https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar) ,可以运行如下指令完成中文数据集下载和解压。
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/31e3dbee31d441d2a36d45b5af660e832dfa2f437f4d49a1914312a15b6a29a7"></center>
|
||||
<center>图3 下载数据集</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dataset/XFUND.tar
|
||||
tar -xf XFUND.tar
|
||||
|
||||
# XFUN其他数据集使用下面的代码进行转换
|
||||
# 代码链接:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release%2F2.4/ppstructure/vqa/helper/trans_xfun_data.py
|
||||
# %cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
# python3 ppstructure/vqa/tools/trans_xfun_data.py --ori_gt_path=path/to/json_path --output_path=path/to/save_path
|
||||
# %cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行上述指令后在 /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure/vqa/XFUND 目录下有2个文件夹,目录结构如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure/vqa/XFUND
|
||||
└─ zh_train/ 训练集
|
||||
├── image/ 图片存放文件夹
|
||||
├── xfun_normalize_train.json 标注信息
|
||||
└─ zh_val/ 验证集
|
||||
├── image/ 图片存放文件夹
|
||||
├── xfun_normalize_val.json 标注信息
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该数据集的标注格式为
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
{
|
||||
"height": 3508, # 图像高度
|
||||
"width": 2480, # 图像宽度
|
||||
"ocr_info": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "邮政地址:", # 单个文本内容
|
||||
"label": "question", # 文本所属类别
|
||||
"bbox": [261, 802, 483, 859], # 单个文本框
|
||||
"id": 54, # 文本索引
|
||||
"linking": [[54, 60]], # 当前文本和其他文本的关系 [question, answer]
|
||||
"words": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "湖南省怀化市市辖区",
|
||||
"label": "answer",
|
||||
"bbox": [487, 810, 862, 859],
|
||||
"id": 60,
|
||||
"linking": [[54, 60]],
|
||||
"words": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 转换为PaddleOCR检测和识别格式
|
||||
|
||||
使用XFUND训练PaddleOCR检测和识别模型,需要将数据集格式改为训练需求的格式。
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/9a709f19e7174725a8cfb09fd922ade74f8e9eb73ae1438596cbb2facef9c24a"></center>
|
||||
<center>图4 转换为OCR格式</center>
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本检测** 标注文件格式如下,中间用'\t'分隔:
|
||||
|
||||
" 图像文件名 json.dumps编码的图像标注信息"
|
||||
ch4_test_images/img_61.jpg [{"transcription": "MASA", "points": [[310, 104], [416, 141], [418, 216], [312, 179]]}, {...}]
|
||||
|
||||
json.dumps编码前的图像标注信息是包含多个字典的list,字典中的 `points` 表示文本框的四个点的坐标(x, y),从左上角的点开始顺时针排列。 `transcription` 表示当前文本框的文字,***当其内容为“###”时,表示该文本框无效,在训练时会跳过。***
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本识别** 标注文件的格式如下, txt文件中默认请将图片路径和图片标签用'\t'分割,如用其他方式分割将造成训练报错。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
" 图像文件名 图像标注信息 "
|
||||
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_001.jpg 简单可依赖
|
||||
train_data/rec/train/word_002.jpg 用科技让复杂的世界更简单
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
unzip -q /home/aistudio/data/data140302/XFUND_ori.zip -d /home/aistudio/data/data140302/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
已经提供转换脚本,执行如下代码即可转换成功:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/
|
||||
python trans_xfund_data.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4 OCR
|
||||
|
||||
选用飞桨OCR开发套件[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/README_ch.md)中的PP-OCRv2模型进行文本检测和识别。PP-OCRv2在PP-OCR的基础上,进一步在5个方面重点优化,检测模型采用CML协同互学习知识蒸馏策略和CopyPaste数据增广策略;识别模型采用LCNet轻量级骨干网络、UDML 改进知识蒸馏策略和[Enhanced CTC loss](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/doc/doc_ch/enhanced_ctc_loss.md)损失函数改进,进一步在推理速度和预测效果上取得明显提升。更多细节请参考PP-OCRv2[技术报告](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.03144)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 文本检测
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用2种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
- **PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型**
|
||||
- **XFUND数据集+fine-tune**
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.1.1 方案1:预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/2aff41ee8fce4e9bac8295cc00720217bde2aeee7ee7473689848bed0b6fde05"></center>
|
||||
<center>图5 文本检测方案1-下载预训练模型</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR已经提供了PP-OCR系列模型,部分模型展示如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 模型简介 | 模型名称 | 推荐场景 | 检测模型 | 方向分类器 | 识别模型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCRv2模型(13.0M) | ch_PP-OCRv2_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文超轻量PP-OCR mobile模型(9.4M) | ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_xx | 移动端&服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
| 中英文通用PP-OCR server模型(143.4M) | ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_xx | 服务器端 | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_det_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_cls_train.tar) | [推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_infer.tar) / [预训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_server_v2.0_rec_pre.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
更多模型下载(包括多语言),可以参考[PP-OCR 系列模型下载](./doc/doc_ch/models_list.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们使用PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
% cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**2)模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/75b0e977dfb74a83851f8828460759f337b1b7a0c33c47a08a30f3570e1e2e74"></center>
|
||||
<center>图6 文本检测方案1-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
接着使用下载的超轻量检测模型在XFUND验证集上进行评估,由于蒸馏需要包含多个网络,甚至多个Student网络,在计算指标的时候只需要计算一个Student网络的指标即可,key字段设置为Student则表示只计算Student网络的精度。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Metric:
|
||||
name: DistillationMetric
|
||||
base_metric_name: DetMetric
|
||||
main_indicator: hmean
|
||||
key: "Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
然后在XFUND验证集上进行评估,具体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="./pretrain_models/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | hmeans |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 77.26% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用文本检测预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,达到77%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.1.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR提供的蒸馏预训练模型包含了多个模型的参数,我们提取Student模型的参数,在XFUND数据集上进行finetune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
# print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 学生模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("student_model."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "student_model." in key}
|
||||
# 查看学生模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_distill_train/student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**1)模型训练**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/560c44b8dd604da7987bd25da0a882156ffcfb7f6bcb44108fe9bde77512e572"></center>
|
||||
<center>图7 文本检测方案2-模型训练</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate:调整学习率,本实验设置为0.005
|
||||
Train.dataset.transforms.EastRandomCropData.size:训练尺寸改为[1600, 1600]
|
||||
Eval.dataset.transforms.DetResizeForTest:评估尺寸,添加如下参数
|
||||
limit_side_len: 1600
|
||||
limit_type: 'min'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
执行下面命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**2)模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/5a75137c5f924dfeb6956b5818812298cc3dc7992ac84954b4175be9adf83c77"></center>
|
||||
<center>图8 文本检测方案2-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`。如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时我们提供了未finetuen的模型,配置文件参数(`pretrained_model`设置为空,`learning_rate` 设置为0.001)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | hmeans |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集 | 79.27% |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune | 85.24% |
|
||||
|
||||
对比仅使用XFUND数据集训练的模型,使用XFUND数据集+finetune训练,在验证集上评估达到85%左右,说明 finetune会提升垂类场景效果。
|
||||
|
||||
**3)导出模型**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/07c3b060c54e4b00be7de8d41a8a4696ff53835343cc4981aab0555183306e79"></center>
|
||||
<center>图9 文本检测方案2-模型导出</center>
|
||||
|
||||
在模型训练过程中保存的模型文件是包含前向预测和反向传播的过程,在实际的工业部署则不需要反向传播,因此需要将模型进行导成部署需要的模型格式。 执行下面命令,即可导出模型。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 加载配置文件`ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml`,从`pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune`目录下加载`best_accuracy`模型
|
||||
# inference模型保存在`./output/det_db_inference`目录下
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_det_student.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model="pretrain/ch_db_mv3-student1600-finetune/best_accuracy" \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir="./output/det_db_inference/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/inference/rec_crnn/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**4)模型预测**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0d582de9aa46474791e08654f84a614a6510e98bfe5f4ad3a26501cbf49ec151"></center>
|
||||
<center>图10 文本检测方案2-模型预测</center>
|
||||
|
||||
加载上面导出的模型,执行如下命令对验证集或测试集图片进行预测:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
det_model_dir:预测模型
|
||||
image_dir:测试图片路径
|
||||
use_gpu:是否使用GPU
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
检测可视化结果保存在`/home/aistudio/inference_results/`目录下,查看检测效果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%pwd
|
||||
!python tools/infer/predict_det.py \
|
||||
--det_algorithm="DB" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./output/det_db_inference/" \
|
||||
--image_dir="./doc/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg" \
|
||||
--use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
总结,我们分别使用PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型、XFUND数据集+finetune2种方案进行评估、训练等,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | hmeans | 结果分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 | 77.26% | ppocr提供的预训练模型有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集 | 79.27% | |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+finetune | 85.24% | finetune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 文本识别
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用如下3种方案进行训练、评估:
|
||||
|
||||
- PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型
|
||||
- XFUND数据集+fine-tune
|
||||
- XFUND数据集+fine-tune+真实通用识别数据
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.1 方案1:预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
**1)下载预训练模型**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/b7230e9964074181837e1132029f9da8178bf564ac5c43a9a93a30e975c0d8b4"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图11 文本识别方案1-下载预训练模型</center>
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量文本识别模型,下载并解压预训练模型:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/pretrain/
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv2/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar && rm -rf ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train.tar
|
||||
% cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**2)模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/166ce56d634c4c7589fe68fbc6e7ae663305dcc82ba144c781507341ffae7fe8"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图12 文本识别方案1-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
首先修改配置文件`configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_distillation.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用下载的预训练模型进行评估:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_distillation.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | acc |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 | 67.48% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用文本预训练模型在XFUND验证集上评估,acc达到67%左右,充分说明ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.2 方案2:XFUND数据集+finetune
|
||||
|
||||
同检测模型,我们提取Student模型的参数,在XFUND数据集上进行finetune,可以参考如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 学生模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Student."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Student." in key}
|
||||
# 查看学生模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "pretrain/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec_train/student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**1)模型训练**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/06dad690219b42a59a27c84a060af1436bcd05de10b843209c6270e04e4dda10"></center>
|
||||
<center>图13 文本识别方案2-模型训练</center>
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置文件`configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml`中的以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model:指向预训练模型路径
|
||||
Global.character_dict_path: 字典路径
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.values:学习率
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
执行如下命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**2)模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/c07c88f708ad43cc8cd615861626d0e8333c0e3d4dda49ac8cba1f8939fa8a94"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图14 文本识别方案2-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`,这里为大家提供训练好的模型`./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-finetune/best_accuracy`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-finetune/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | acc |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+finetune | 72.33% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用XFUND数据集+finetune训练,在验证集上评估达到72%左右,说明 finetune会提升垂类场景效果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.3 方案3:XFUND数据集+finetune+真实通用识别数据
|
||||
|
||||
接着我们在上述`XFUND数据集+finetune`实验的基础上,添加真实通用识别数据,进一步提升识别效果。首先准备真实通用识别数据,并上传到AIStudio:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)模型训练**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/45f288ce8b2c45d8aa5407785b4b40f4876fc3da23744bd7a78060797fba0190"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图15 文本识别方案3-模型训练</center>
|
||||
|
||||
在上述`XFUND数据集+finetune`实验中修改配置文件`configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml`的基础上,继续修改以下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向真实识别训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.ratio_list:动态采样
|
||||
```
|
||||
执行如下命令启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**2)模型评估**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/965db9f758614c6f9be301286cd5918f21110603c8aa4a1dbf5371e3afeec782"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图16 文本识别方案3-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用训练好的模型进行评估,更新模型路径`Global.checkpoints`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.checkpoints=./pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-realdata/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | acc |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune+真实通用识别数据 | 85.29% |
|
||||
|
||||
使用XFUND数据集+finetune训练,在验证集上评估达到85%左右,说明真实通用识别数据对于性能提升很有帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
**3)导出模型**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/3dc7f69fac174cde96b9d08b5e2353a1d88dc63e7be9410894c0783660b35b76"></center>
|
||||
<center>图17 文本识别方案3-导出模型</center>
|
||||
|
||||
导出模型只保留前向预测的过程:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
!python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/rec/ch_PP-OCRv2/ch_PP-OCRv2_rec.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=pretrain/rec_mobile_pp-OCRv2-student-realdata/best_accuracy \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=./output/rec_crnn_inference/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**4)模型预测**
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/60b95b4945954f81a080a8f308cee66f83146479cd1142b9b6b1290938fd1df8"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图18 文本识别方案3-模型预测</center>
|
||||
|
||||
加载上面导出的模型,执行如下命令对验证集或测试集图片进行预测,检测可视化结果保存在`/home/aistudio/inference_results/`目录下,查看检测、识别效果。需要通过`--rec_char_dict_path`指定使用的字典路径
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--image_dir="./doc/vqa/input/zh_val_21.jpg" \
|
||||
--det_model_dir="./output/det_db_inference/" \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir="./output/rec_crnn_inference/" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape="3, 32, 320" \
|
||||
--rec_char_dict_path="/home/aistudio/XFUND/word_dict.txt"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
总结,我们分别使用PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量检测预训练模型、XFUND数据集+finetune2种方案进行评估、训练等,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 | acc | 结果分析 |
|
||||
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
|
||||
| PP-OCRv2中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 | 67.48% | ppocr提供的预训练模型具有泛化能力 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune |72.33% | finetune会提升垂类场景效果 |
|
||||
| XFUND数据集+fine-tune+真实通用识别数据 | 85.29% | 真实通用识别数据对于性能提升很有帮助 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 5 文档视觉问答(DOC-VQA)
|
||||
|
||||
VQA指视觉问答,主要针对图像内容进行提问和回答,DOC-VQA是VQA任务中的一种,DOC-VQA主要针对文本图像的文字内容提出问题。
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR中DOC-VQA系列算法基于PaddleNLP自然语言处理算法库实现LayoutXLM论文,支持基于多模态方法的 **语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition, SER)** 以及 **关系抽取 (Relation Extraction, RE)** 任务。
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望直接体验预测过程,可以下载我们提供的预训练模型,跳过训练过程,直接预测即可。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd pretrain
|
||||
#下载SER模型
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
#下载RE模型
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/pplayout/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar && tar -xvf re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh.tar
|
||||
%cd ../
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1 SER
|
||||
|
||||
SER: 语义实体识别 (Semantic Entity Recognition), 可以完成对图像中的文本识别与分类。
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/a3b25766f3074d2facdf88d4a60fc76612f51992fd124cf5bd846b213130665b' width='700'></center>
|
||||
<center>图19 SER测试效果图</center>
|
||||
|
||||
**图19** 中不同颜色的框表示不同的类别,对于XFUND数据集,有QUESTION, ANSWER, HEADER 3种类别
|
||||
|
||||
- 深紫色:HEADER
|
||||
- 浅紫色:QUESTION
|
||||
- 军绿色:ANSWER
|
||||
|
||||
在OCR检测框的左上方也标出了对应的类别和OCR识别结果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.1 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/2e45f297c9d44ca5b8718ae100a365f7348eaeed4cb8495b904f28a9c8075d8a"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图20 SER-模型训练</center>
|
||||
|
||||
启动训练之前,需要修改配置文件 `configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml` 以下四个字段:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
2. Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
3. Eval.dataset.data_dir:指指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
4. Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标。 在`./output/ser_layoutxlm/`文件夹中会保存训练日志,最优的模型和最新epoch的模型。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.2 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/5df160ac39ee4d9e92a937094bc53a737272f9f2abeb4ddfaebb48e8eccf1be2"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图21 SER-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用下载的预训练模型进行评估,如果使用自己训练好的模型进行评估,将待评估的模型所在文件夹路径赋值给 `Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints` 字段即可。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标,预训练模型评估指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/2854aee557a74079a82dd5cd57e48bc2ce97974d5637477fb4deea137d0e312c' width='700'></center>
|
||||
<center>图 SER预训练模型评估指标</center>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.1.3 模型预测
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/0f7d50a0fb924b408b93e1fbd6ca64148eed34a2e6724280acd3e113fef7dc48"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图22 SER-模型预测</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令即可完成`OCR引擎 + SER`的串联预测, 以SER预训练模型为例:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python tools/infer_vqa_token_ser.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/ \
|
||||
Global.infer_img=doc/vqa/input/zh_val_42.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会在`config.Global.save_res_path`字段所配置的目录下保存预测结果可视化图像以及预测结果文本文件,预测结果文本文件名为`infer_results.txt`。通过如下命令查看预测图片:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
# 在notebook中使用matplotlib.pyplot绘图时,需要添加该命令进行显示
|
||||
%matplotlib inline
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.imread('output/ser/zh_val_42_ser.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(48,24))
|
||||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2 RE
|
||||
|
||||
基于 RE 任务,可以完成对图象中的文本内容的关系提取,如判断问题对(pair)。
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/4de19ca3e54343e88961e816cad28bbacdc807f40b9440be914d871b0a914570' width='700'></center>
|
||||
<center>图23 RE预测效果图</center>
|
||||
|
||||
图中红色框表示问题,蓝色框表示答案,问题和答案之间使用绿色线连接。在OCR检测框的左上方也标出了对应的类别和OCR识别结果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.2.1 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/268c707a62c54e93958d2b2ab29e0932953aad41819e44aaaaa05c8ad85c6491"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图24 RE-模型训练</center>
|
||||
|
||||
启动训练之前,需要修改配置文件`configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml`中的以下四个字段
|
||||
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir:指指向验证集图片存放目录
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向验证集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/train.py -c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标。 在`./output/re_layoutxlm/`文件夹中会保存训练日志,最优的模型和最新epoch的模型
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.2.2 模型评估
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/93c66a43a69e472899c1c6732408b7a42e99a43721e94e9ca3c0a64e080306e4"></center>
|
||||
<center>图25 RE-模型评估</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用下载的预训练模型进行评估,如果使用自己训练好的模型进行评估,将待评估的模型所在文件夹路径赋值给 `Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints` 字段即可。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/eval.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会打印出`precision`, `recall`, `hmean`等指标,预训练模型评估指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/f99af54fb2d14691a73b1a748e0ca22618aeddfded0c4da58bbbb03edb8c2340' width='700'></center>
|
||||
<center>图 RE预训练模型评估指标</center>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5.2.3 模型预测
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/bab32d32bdec4339b9a3e5f911e4b41f77996f3faabc40bd8309b5b20cad31e4"></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>图26 RE-模型预测</center>
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令即可完成OCR引擎 + SER + RE的串联预测, 以预训练SER和RE模型为例,
|
||||
|
||||
最终会在config.Global.save_res_path字段所配置的目录下保存预测结果可视化图像以及预测结果文本文件,预测结果文本文件名为infer_results.txt。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 tools/infer_vqa_token_ser_re.py \
|
||||
-c configs/vqa/re/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/re_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/ \
|
||||
Global.infer_img=test_imgs/ \
|
||||
-c_ser configs/vqa/ser/layoutxlm.yml \
|
||||
-o_ser Architecture.Backbone.checkpoints=pretrain/ser_LayoutXLM_xfun_zh/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最终会在config.Global.save_res_path字段所配置的目录下保存预测结果可视化图像以及预测结果文本文件,预测结果文本文件名为infer_results.txt, 每一行表示一张图片的结果,每张图片的结果如下所示,前面表示测试图片路径,后面为测试结果:key字段及对应的value字段。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
test_imgs/t131.jpg {"政治面税": "群众", "性别": "男", "籍贯": "河北省邯郸市", "婚姻状况": "亏末婚口已婚口已娇", "通讯地址": "邯郸市阳光苑7号楼003", "民族": "汉族", "毕业院校": "河南工业大学", "户口性质": "口农村城镇", "户口地址": "河北省邯郸市", "联系电话": "13288888888", "健康状况": "健康", "姓名": "小六", "好高cm": "180", "出生年月": "1996年8月9日", "文化程度": "本科", "身份证号码": "458933777777777777"}
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
展示预测结果
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
%matplotlib inline
|
||||
|
||||
img = cv2.imread('./output/re/t131_ser.jpg')
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(48,24))
|
||||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6 导出Excel
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/ab93d3d90d77437a81c9534b2dd1d3e39ef81e8473054fd3aeff6e837ebfb827"></center>
|
||||
<center>图27 导出Excel</center>
|
||||
|
||||
为了输出信息匹配对,我们修改`tools/infer_vqa_token_ser_re.py`文件中的`line 194-197`。
|
||||
```
|
||||
fout.write(img_path + "\t" + json.dumps(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ser_result": result,
|
||||
}, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
更改为
|
||||
```
|
||||
result_key = {}
|
||||
for ocr_info_head, ocr_info_tail in result:
|
||||
result_key[ocr_info_head['text']] = ocr_info_tail['text']
|
||||
|
||||
fout.write(img_path + "\t" + json.dumps(
|
||||
result_key, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同时将输出结果导出到Excel中,效果如 图28 所示:
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src='https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/9f45d3eef75e4842a0828bb9e518c2438300264aec0646cc9addfce860a04196' width='700'></center>
|
||||
<center>图28 Excel效果图</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import xlsxwriter as xw
|
||||
|
||||
workbook = xw.Workbook('output/re/infer_results.xlsx')
|
||||
format1 = workbook.add_format({
|
||||
'align': 'center',
|
||||
'valign': 'vcenter',
|
||||
'text_wrap': True,
|
||||
})
|
||||
worksheet1 = workbook.add_worksheet('sheet1')
|
||||
worksheet1.activate()
|
||||
title = ['姓名', '性别', '民族', '文化程度', '身份证号码', '联系电话', '通讯地址']
|
||||
worksheet1.write_row('A1', title)
|
||||
i = 2
|
||||
|
||||
with open('output/re/infer_results.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fin:
|
||||
lines = fin.readlines()
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
img_path, result = line.strip().split('\t')
|
||||
result_key = json.loads(result)
|
||||
# 写入Excel
|
||||
row_data = [result_key['姓名'], result_key['性别'], result_key['民族'], result_key['文化程度'], result_key['身份证号码'],
|
||||
result_key['联系电话'], result_key['通讯地址']]
|
||||
row = 'A' + str(i)
|
||||
worksheet1.write_row(row, row_data, format1)
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
workbook.close()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 更多资源
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多深度学习知识、产业案例、面试宝典等,请参考:[awesome-DeepLearning](https://github.com/paddlepaddle/awesome-DeepLearning)
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多PaddleOCR使用教程,请参考:[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/tree/dygraph)
|
||||
|
||||
- 更多PaddleNLP使用教程,请参考:[PaddleNLP](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP)
|
||||
|
||||
- 飞桨框架相关资料,请参考:[飞桨深度学习平台](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/?fr=paddleEdu_aistudio)
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考链接
|
||||
|
||||
- LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.08836.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
- microsoft/unilm/layoutxlm, https://github.com/microsoft/unilm/tree/master/layoutxlm
|
||||
|
||||
- XFUND dataset, https://github.com/doc-analysis/XFUND
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,775 @@
|
|||
# 快速构建卡证类OCR
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [快速构建卡证类OCR](#快速构建卡证类ocr)
|
||||
- [1. 金融行业卡证识别应用](#1-金融行业卡证识别应用)
|
||||
- [1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术](#11-金融行业中的ocr相关技术)
|
||||
- [1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍](#12-金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍)
|
||||
- [1.3 OCR落地挑战](#13-ocr落地挑战)
|
||||
- [2. 卡证识别技术解析](#2-卡证识别技术解析)
|
||||
- [2.1 卡证分类模型](#21-卡证分类模型)
|
||||
- [2.2 卡证识别模型](#22-卡证识别模型)
|
||||
- [3. OCR技术拆解](#3-ocr技术拆解)
|
||||
- [3.1技术流程](#31技术流程)
|
||||
- [3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类](#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证分类)
|
||||
- [卡证分类:数据、模型准备](#卡证分类数据模型准备)
|
||||
- [卡证分类---修改配置文件](#卡证分类---修改配置文件)
|
||||
- [卡证分类---训练](#卡证分类---训练)
|
||||
- [3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别](#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证识别)
|
||||
- [身份证识别:检测+分类](#身份证识别检测分类)
|
||||
- [数据标注](#数据标注)
|
||||
- [4 . 项目实践](#4--项目实践)
|
||||
- [4.1 环境准备](#41-环境准备)
|
||||
- [4.2 配置文件修改](#42-配置文件修改)
|
||||
- [4.3 代码修改](#43-代码修改)
|
||||
- [4.3.1 数据读取](#431-数据读取)
|
||||
- [4.3.2 head修改](#432--head修改)
|
||||
- [4.3.3 修改loss](#433-修改loss)
|
||||
- [4.3.4 后处理](#434-后处理)
|
||||
- [4.4. 模型启动](#44-模型启动)
|
||||
- [5 总结](#5-总结)
|
||||
- [References](#references)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 金融行业卡证识别应用
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术
|
||||
|
||||
* 《“十四五”数字经济发展规划》指出,2020年我国数字经济核心产业增加值占GDP比重达7.8%,随着数字经济迈向全面扩展,到2025年该比例将提升至10%。
|
||||
|
||||
* 在过去数年的跨越发展与积累沉淀中,数字金融、金融科技已在对金融业的重塑与再造中充分印证了其自身价值。
|
||||
|
||||
* 以智能为目标,提升金融数字化水平,实现业务流程自动化,降低人力成本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍
|
||||
|
||||
应用场景:身份证、银行卡、营业执照、驾驶证等。
|
||||
|
||||
应用难点:由于数据的采集来源多样,以及实际采集数据各种噪声:反光、褶皱、模糊、倾斜等各种问题干扰。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.3 OCR落地挑战
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
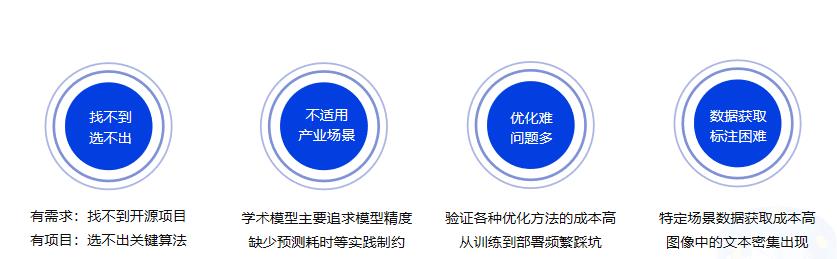
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 卡证识别技术解析
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
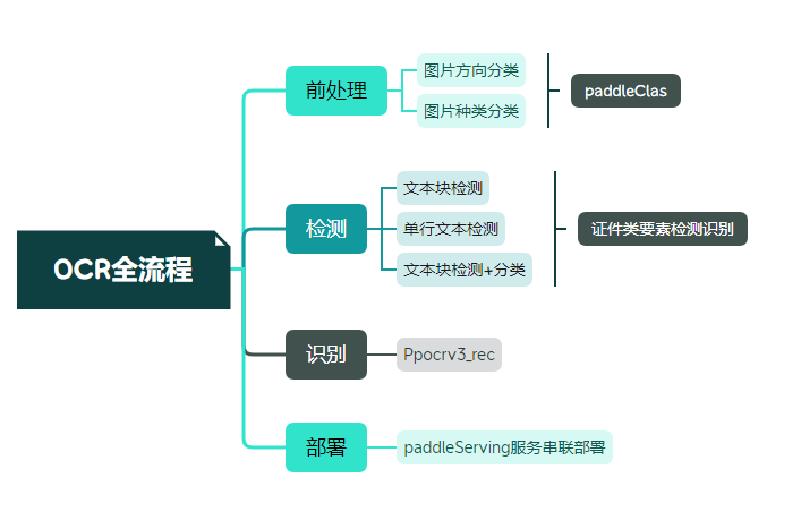
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1 卡证分类模型
|
||||
|
||||
卡证分类:基于PPLCNet
|
||||
|
||||
与其他轻量级模型相比在CPU环境下ImageNet数据集上的表现
|
||||
|
||||
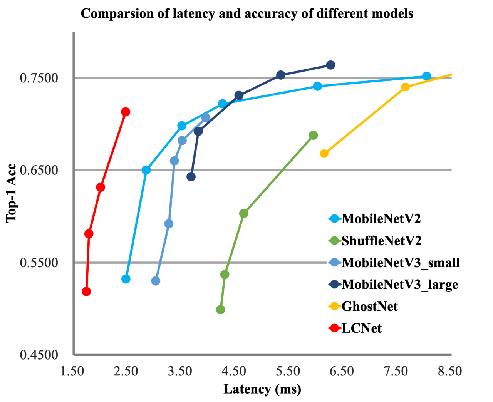
|
||||
|
||||
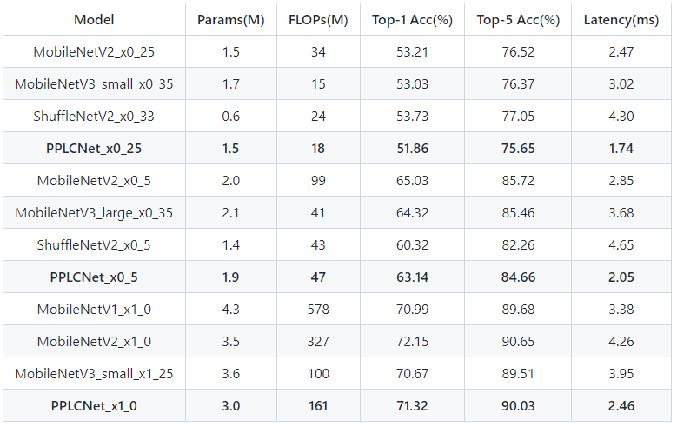
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 模型来自模型库PaddleClas,它是一个图像识别和图像分类任务的工具集,助力使用者训练出更好的视觉模型和应用落地。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 卡证识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
* 检测:DBNet 识别:SVRT
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* PPOCRv3在文本检测、识别进行了一系列改进优化,在保证精度的同时提升预测效率
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
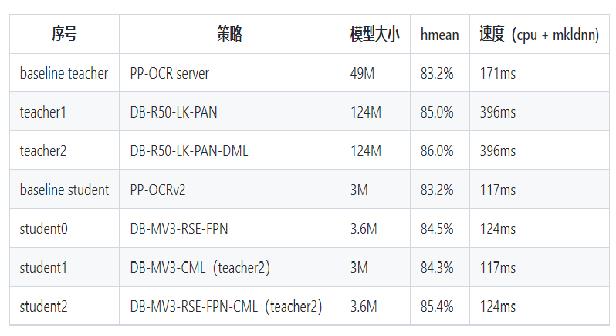
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
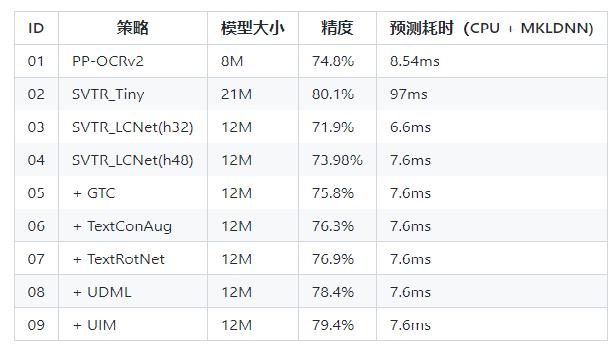
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. OCR技术拆解
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1技术流程
|
||||
|
||||
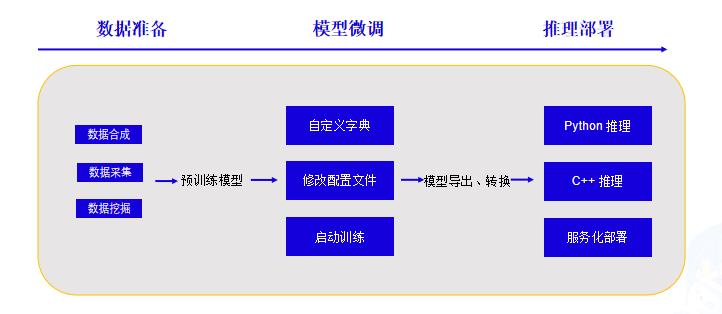
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类
|
||||
|
||||
#### 卡证分类:数据、模型准备
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
A 使用爬虫获取无标注数据,将相同类别的放在同一文件夹下,文件名从0开始命名。具体格式如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
注:卡证类数据,建议每个类别数据量在500张以上
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
B 一行命令生成标签文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tree -r -i -f | grep -E "jpg|JPG|jpeg|JPEG|png|PNG|webp" | awk -F "/" '{print $0" "$2}' > train_list.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
C [下载预训练模型 ](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/zh_CN/models/PP-LCNet.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 卡证分类---修改配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件主要修改三个部分:
|
||||
|
||||
全局参数:预训练模型路径/训练轮次/图像尺寸
|
||||
|
||||
模型结构:分类数
|
||||
|
||||
数据处理:训练/评估数据路径
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 卡证分类---训练
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
指定配置文件启动训练:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
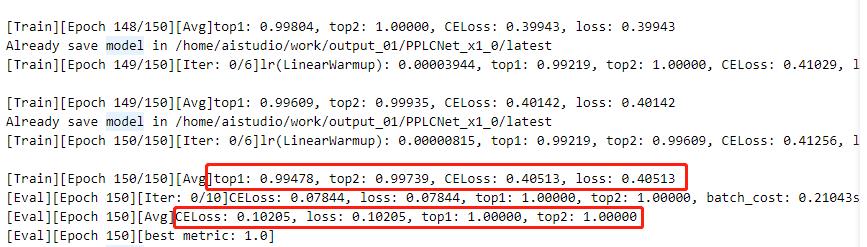
|
||||
|
||||
注:日志中显示了训练结果和评估结果(训练时可以设置固定轮数评估一次)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别
|
||||
|
||||
卡证识别(以身份证检测为例)
|
||||
存在的困难及问题:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在自然场景下,由于各种拍摄设备以及光线、角度不同等影响导致实际得到的证件影像千差万别。
|
||||
|
||||
* 如何快速提取需要的关键信息
|
||||
|
||||
* 多行的文本信息,检测结果如何正确拼接
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* OCR技术拆解---OCR工具库
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR是一个丰富、领先且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型并应用落地
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
身份证识别:用现有的方法识别
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 身份证识别:检测+分类
|
||||
|
||||
> 方法:基于现有的dbnet检测模型,加入分类方法。检测同时进行分类,从一定程度上优化识别流程
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据标注
|
||||
|
||||
使用PaddleOCRLable进行快速标注
|
||||
|
||||
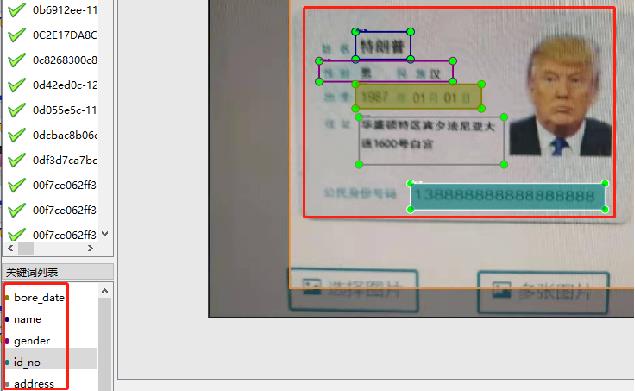
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 修改PPOCRLabel.py,将下图中的kie参数设置为True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
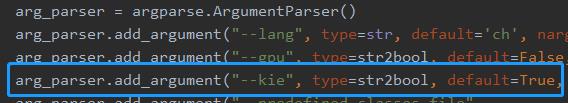
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 数据标注踩坑分享
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
注:两者只有标注有差别,训练参数数据集都相同
|
||||
|
||||
## 4 . 项目实践
|
||||
|
||||
AIStudio项目链接:[快速构建卡证类OCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4459116)
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
1)拉取[paddleocr](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)项目,如果从github上拉取速度慢可以选择从gitee上获取。
|
||||
```
|
||||
!git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b release/2.6 /home/aistudio/work/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2)获取并解压预训练模型,如果要使用其他模型可以从模型库里自主选择合适模型。
|
||||
```
|
||||
!wget -P work/pre_trained/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
!tar -vxf /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar -C /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained
|
||||
```
|
||||
3) 安装必要依赖
|
||||
```
|
||||
!pip install -r /home/aistudio/work/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 配置文件修改
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置文件 *work/configs/det/detmv3db.yml*
|
||||
|
||||
具体修改说明如下:
|
||||
|
||||
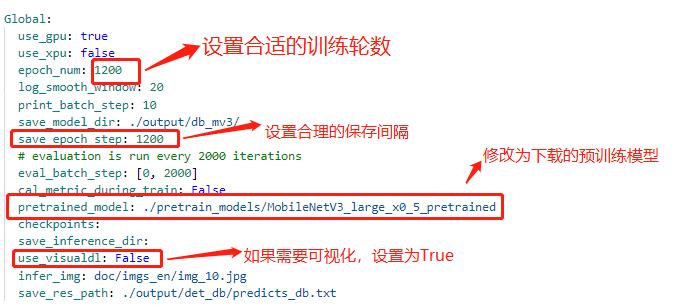
|
||||
|
||||
注:在上述的配置文件的Global变量中需要添加以下两个参数:
|
||||
|
||||
label_list 为标签表
|
||||
num_classes 为分类数
|
||||
上述两个参数根据实际的情况配置即可
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
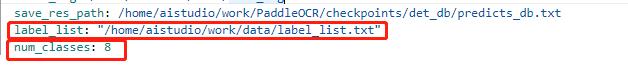
|
||||
|
||||
其中lable_list内容如下例所示,***建议第一个参数设置为 background,不要设置为实际要提取的关键信息种类***:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件中的其他设置说明
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
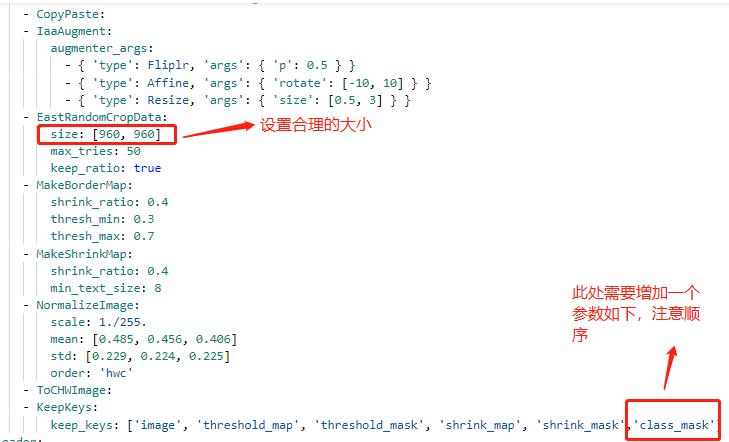
|
||||
|
||||
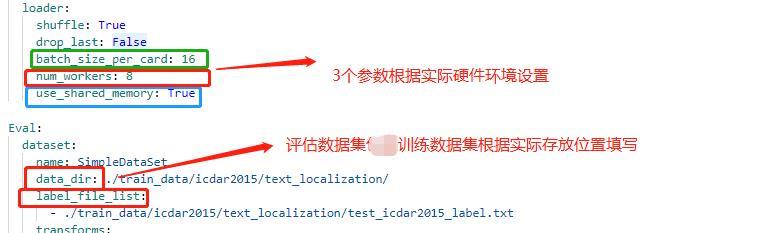
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3 代码修改
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.1 数据读取
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/label_ops.py中的DetLabelEncode
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class DetLabelEncode(object):
|
||||
|
||||
# 修改检测标签的编码处,新增了参数分类数:num_classes,重写初始化方法,以及分类标签的读取
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, label_list, num_classes=8, **kwargs):
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes
|
||||
self.label_list = []
|
||||
if label_list:
|
||||
if isinstance(label_list, str):
|
||||
with open(label_list, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
|
||||
for line in f.readlines():
|
||||
self.label_list.append(line.replace("\n", ""))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.label_list = label_list
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert ' please check label_list whether it is none or config is right'
|
||||
|
||||
if num_classes != len(self.label_list): # 校验分类数和标签的一致性
|
||||
assert 'label_list length is not equal to the num_classes'
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, data):
|
||||
label = data['label']
|
||||
label = json.loads(label)
|
||||
nBox = len(label)
|
||||
boxes, txts, txt_tags, classes = [], [], [], []
|
||||
for bno in range(0, nBox):
|
||||
box = label[bno]['points']
|
||||
txt = label[bno]['key_cls'] # 此处将kie中的参数作为分类读取
|
||||
boxes.append(box)
|
||||
txts.append(txt)
|
||||
|
||||
if txt in ['*', '###']:
|
||||
txt_tags.append(True)
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
classes.append(-2)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
txt_tags.append(False)
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1: # 将KIE内容的key标签作为分类标签使用
|
||||
classes.append(int(self.label_list.index(txt)))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(boxes) == 0:
|
||||
|
||||
return None
|
||||
boxes = self.expand_points_num(boxes)
|
||||
boxes = np.array(boxes, dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
txt_tags = np.array(txt_tags, dtype=np.bool_)
|
||||
classes = classes
|
||||
data['polys'] = boxes
|
||||
data['texts'] = txts
|
||||
data['ignore_tags'] = txt_tags
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
data['classes'] = classes
|
||||
return data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/make_shrink_map.py中的MakeShrinkMap类。这里需要注意的是,如果我们设置的label_list中的第一个参数为要检测的信息那么会得到如下的mask,
|
||||
|
||||
举例说明:
|
||||
这是检测的mask图,图中有四个mask那么实际对应的分类应该是4类
|
||||
|
||||
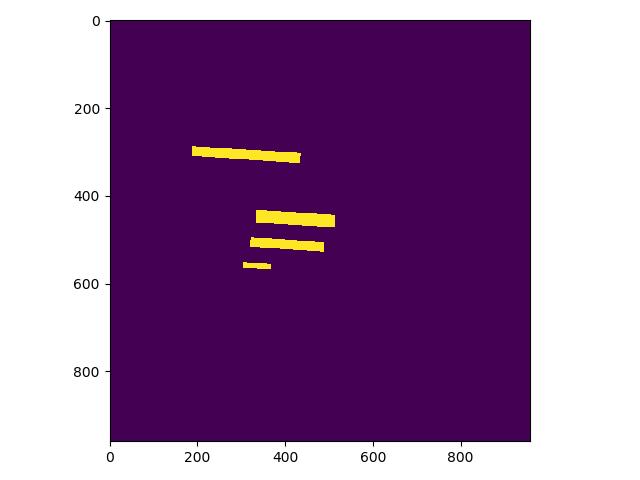
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
label_list中第一个为关键分类,则得到的分类Mask实际如下,与上图相比,少了一个box:
|
||||
|
||||
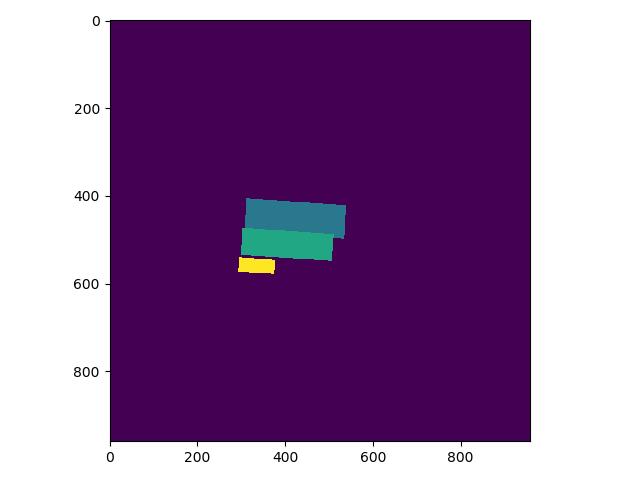
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class MakeShrinkMap(object):
|
||||
r'''
|
||||
Making binary mask from detection data with ICDAR format.
|
||||
Typically following the process of class `MakeICDARData`.
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, min_text_size=8, shrink_ratio=0.4, num_classes=8, **kwargs):
|
||||
self.min_text_size = min_text_size
|
||||
self.shrink_ratio = shrink_ratio
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes # 添加了分类
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, data):
|
||||
image = data['image']
|
||||
text_polys = data['polys']
|
||||
ignore_tags = data['ignore_tags']
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
classes = data['classes']
|
||||
|
||||
h, w = image.shape[:2]
|
||||
text_polys, ignore_tags = self.validate_polygons(text_polys,
|
||||
ignore_tags, h, w)
|
||||
gt = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
mask = np.ones((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
gt_class = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32) # 新增分类
|
||||
for i in range(len(text_polys)):
|
||||
polygon = text_polys[i]
|
||||
height = max(polygon[:, 1]) - min(polygon[:, 1])
|
||||
width = max(polygon[:, 0]) - min(polygon[:, 0])
|
||||
if ignore_tags[i] or min(height, width) < self.min_text_size:
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(mask,
|
||||
polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], 0)
|
||||
ignore_tags[i] = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
polygon_shape = Polygon(polygon)
|
||||
subject = [tuple(l) for l in polygon]
|
||||
padding = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
|
||||
padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_ROUND,
|
||||
pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
|
||||
shrinked = []
|
||||
|
||||
# Increase the shrink ratio every time we get multiple polygon returned back
|
||||
possible_ratios = np.arange(self.shrink_ratio, 1,
|
||||
self.shrink_ratio)
|
||||
np.append(possible_ratios, 1)
|
||||
for ratio in possible_ratios:
|
||||
distance = polygon_shape.area * (
|
||||
1 - np.power(ratio, 2)) / polygon_shape.length
|
||||
shrinked = padding.Execute(-distance)
|
||||
if len(shrinked) == 1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if shrinked == []:
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(mask,
|
||||
polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], 0)
|
||||
ignore_tags[i] = True
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
for each_shirnk in shrinked:
|
||||
shirnk = np.array(each_shirnk).reshape(-1, 2)
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(gt, [shirnk.astype(np.int32)], 1)
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1: # 绘制分类的mask
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(gt_class, polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], classes[i])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
data['shrink_map'] = gt
|
||||
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
data['class_mask'] = gt_class
|
||||
|
||||
data['shrink_mask'] = mask
|
||||
return data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于在训练数据中会对数据进行resize设置,yml中的操作为:EastRandomCropData,所以需要修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/random_crop_data.py中的EastRandomCropData
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class EastRandomCropData(object):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
size=(640, 640),
|
||||
max_tries=10,
|
||||
min_crop_side_ratio=0.1,
|
||||
keep_ratio=True,
|
||||
num_classes=8,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
self.size = size
|
||||
self.max_tries = max_tries
|
||||
self.min_crop_side_ratio = min_crop_side_ratio
|
||||
self.keep_ratio = keep_ratio
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, data):
|
||||
img = data['image']
|
||||
text_polys = data['polys']
|
||||
ignore_tags = data['ignore_tags']
|
||||
texts = data['texts']
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
classes = data['classes']
|
||||
all_care_polys = [
|
||||
text_polys[i] for i, tag in enumerate(ignore_tags) if not tag
|
||||
]
|
||||
# 计算crop区域
|
||||
crop_x, crop_y, crop_w, crop_h = crop_area(
|
||||
img, all_care_polys, self.min_crop_side_ratio, self.max_tries)
|
||||
# crop 图片 保持比例填充
|
||||
scale_w = self.size[0] / crop_w
|
||||
scale_h = self.size[1] / crop_h
|
||||
scale = min(scale_w, scale_h)
|
||||
h = int(crop_h * scale)
|
||||
w = int(crop_w * scale)
|
||||
if self.keep_ratio:
|
||||
padimg = np.zeros((self.size[1], self.size[0], img.shape[2]),
|
||||
img.dtype)
|
||||
padimg[:h, :w] = cv2.resize(
|
||||
img[crop_y:crop_y + crop_h, crop_x:crop_x + crop_w], (w, h))
|
||||
img = padimg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img = cv2.resize(
|
||||
img[crop_y:crop_y + crop_h, crop_x:crop_x + crop_w],
|
||||
tuple(self.size))
|
||||
# crop 文本框
|
||||
text_polys_crop = []
|
||||
ignore_tags_crop = []
|
||||
texts_crop = []
|
||||
classes_crop = []
|
||||
for poly, text, tag,class_index in zip(text_polys, texts, ignore_tags,classes):
|
||||
poly = ((poly - (crop_x, crop_y)) * scale).tolist()
|
||||
if not is_poly_outside_rect(poly, 0, 0, w, h):
|
||||
text_polys_crop.append(poly)
|
||||
ignore_tags_crop.append(tag)
|
||||
texts_crop.append(text)
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
classes_crop.append(class_index)
|
||||
data['image'] = img
|
||||
data['polys'] = np.array(text_polys_crop)
|
||||
data['ignore_tags'] = ignore_tags_crop
|
||||
data['texts'] = texts_crop
|
||||
if self.num_classes > 1:
|
||||
data['classes'] = classes_crop
|
||||
return data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.2 head修改
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
主要修改 ppocr/modeling/heads/det_db_head.py,将Head类中的最后一层的输出修改为实际的分类数,同时在DBHead中新增分类的head。
|
||||
|
||||
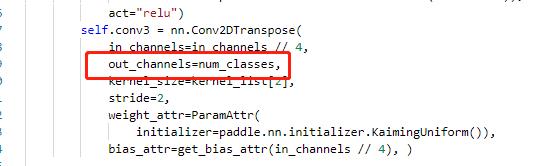
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.3 修改loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/losses/det_db_loss.py中的DBLoss类,分类采用交叉熵损失函数进行计算。
|
||||
|
||||
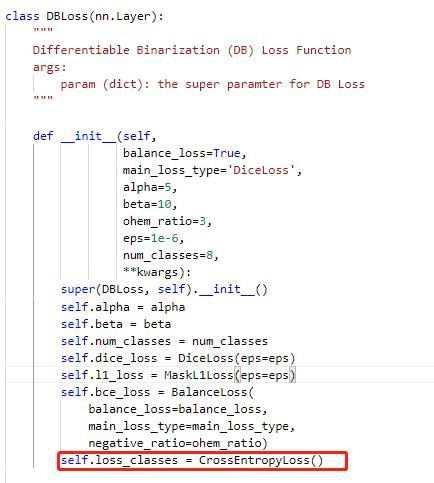
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.4 后处理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
由于涉及到eval以及后续推理能否正常使用,我们需要修改后处理的相关代码,修改位置 PaddleOCR/ppocr/postprocess/db_postprocess.py中的DBPostProcess类
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class DBPostProcess(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The post process for Differentiable Binarization (DB).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
thresh=0.3,
|
||||
box_thresh=0.7,
|
||||
max_candidates=1000,
|
||||
unclip_ratio=2.0,
|
||||
use_dilation=False,
|
||||
score_mode="fast",
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
self.thresh = thresh
|
||||
self.box_thresh = box_thresh
|
||||
self.max_candidates = max_candidates
|
||||
self.unclip_ratio = unclip_ratio
|
||||
self.min_size = 3
|
||||
self.score_mode = score_mode
|
||||
assert score_mode in [
|
||||
"slow", "fast"
|
||||
], "Score mode must be in [slow, fast] but got: {}".format(score_mode)
|
||||
|
||||
self.dilation_kernel = None if not use_dilation else np.array(
|
||||
[[1, 1], [1, 1]])
|
||||
|
||||
def boxes_from_bitmap(self, pred, _bitmap, classes, dest_width, dest_height):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_bitmap: single map with shape (1, H, W),
|
||||
whose values are binarized as {0, 1}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
bitmap = _bitmap
|
||||
height, width = bitmap.shape
|
||||
|
||||
outs = cv2.findContours((bitmap * 255).astype(np.uint8), cv2.RETR_LIST,
|
||||
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
|
||||
if len(outs) == 3:
|
||||
img, contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1], outs[2]
|
||||
elif len(outs) == 2:
|
||||
contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1]
|
||||
|
||||
num_contours = min(len(contours), self.max_candidates)
|
||||
|
||||
boxes = []
|
||||
scores = []
|
||||
class_indexes = []
|
||||
class_scores = []
|
||||
for index in range(num_contours):
|
||||
contour = contours[index]
|
||||
points, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(contour)
|
||||
if sside < self.min_size:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
points = np.array(points)
|
||||
if self.score_mode == "fast":
|
||||
score, class_index, class_score = self.box_score_fast(pred, points.reshape(-1, 2), classes)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
score, class_index, class_score = self.box_score_slow(pred, contour, classes)
|
||||
if self.box_thresh > score:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
box = self.unclip(points).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
|
||||
box, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(box)
|
||||
if sside < self.min_size + 2:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
box = np.array(box)
|
||||
|
||||
box[:, 0] = np.clip(
|
||||
np.round(box[:, 0] / width * dest_width), 0, dest_width)
|
||||
box[:, 1] = np.clip(
|
||||
np.round(box[:, 1] / height * dest_height), 0, dest_height)
|
||||
|
||||
boxes.append(box.astype(np.int16))
|
||||
scores.append(score)
|
||||
|
||||
class_indexes.append(class_index)
|
||||
class_scores.append(class_score)
|
||||
|
||||
if classes is None:
|
||||
return np.array(boxes, dtype=np.int16), scores
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return np.array(boxes, dtype=np.int16), scores, class_indexes, class_scores
|
||||
|
||||
def unclip(self, box):
|
||||
unclip_ratio = self.unclip_ratio
|
||||
poly = Polygon(box)
|
||||
distance = poly.area * unclip_ratio / poly.length
|
||||
offset = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
|
||||
offset.AddPath(box, pyclipper.JT_ROUND, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
|
||||
expanded = np.array(offset.Execute(distance))
|
||||
return expanded
|
||||
|
||||
def get_mini_boxes(self, contour):
|
||||
bounding_box = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
|
||||
points = sorted(list(cv2.boxPoints(bounding_box)), key=lambda x: x[0])
|
||||
|
||||
index_1, index_2, index_3, index_4 = 0, 1, 2, 3
|
||||
if points[1][1] > points[0][1]:
|
||||
index_1 = 0
|
||||
index_4 = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_1 = 1
|
||||
index_4 = 0
|
||||
if points[3][1] > points[2][1]:
|
||||
index_2 = 2
|
||||
index_3 = 3
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index_2 = 3
|
||||
index_3 = 2
|
||||
|
||||
box = [
|
||||
points[index_1], points[index_2], points[index_3], points[index_4]
|
||||
]
|
||||
return box, min(bounding_box[1])
|
||||
|
||||
def box_score_fast(self, bitmap, _box, classes):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
box_score_fast: use bbox mean score as the mean score
|
||||
'''
|
||||
h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
|
||||
box = _box.copy()
|
||||
xmin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 0].min()).astype(np.int32), 0, w - 1)
|
||||
xmax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 0].max()).astype(np.int32), 0, w - 1)
|
||||
ymin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 1].min()).astype(np.int32), 0, h - 1)
|
||||
ymax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 1].max()).astype(np.int32), 0, h - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
box[:, 0] = box[:, 0] - xmin
|
||||
box[:, 1] = box[:, 1] - ymin
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(mask, box.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
if classes is None:
|
||||
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], None, None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
k = 999
|
||||
class_mask = np.full((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), k, dtype=np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(class_mask, box.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 0)
|
||||
classes = classes[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_classes = classes + class_mask
|
||||
a = new_classes.reshape(-1)
|
||||
b = np.where(a >= k)
|
||||
classes = np.delete(a, b[0].tolist())
|
||||
|
||||
class_index = np.argmax(np.bincount(classes))
|
||||
class_score = np.sum(classes == class_index) / len(classes)
|
||||
|
||||
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], class_index, class_score
|
||||
|
||||
def box_score_slow(self, bitmap, contour, classes):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
box_score_slow: use polyon mean score as the mean score
|
||||
"""
|
||||
h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
|
||||
contour = contour.copy()
|
||||
contour = np.reshape(contour, (-1, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
xmin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
|
||||
xmax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
|
||||
ymin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
|
||||
ymax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
contour[:, 0] = contour[:, 0] - xmin
|
||||
contour[:, 1] = contour[:, 1] - ymin
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(mask, contour.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
if classes is None:
|
||||
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], None, None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
k = 999
|
||||
class_mask = np.full((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), k, dtype=np.int32)
|
||||
|
||||
cv2.fillPoly(class_mask, contour.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 0)
|
||||
classes = classes[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_classes = classes + class_mask
|
||||
a = new_classes.reshape(-1)
|
||||
b = np.where(a >= k)
|
||||
classes = np.delete(a, b[0].tolist())
|
||||
|
||||
class_index = np.argmax(np.bincount(classes))
|
||||
class_score = np.sum(classes == class_index) / len(classes)
|
||||
|
||||
return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], class_index, class_score
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, outs_dict, shape_list):
|
||||
pred = outs_dict['maps']
|
||||
if isinstance(pred, paddle.Tensor):
|
||||
pred = pred.numpy()
|
||||
pred = pred[:, 0, :, :]
|
||||
segmentation = pred > self.thresh
|
||||
|
||||
if "classes" in outs_dict:
|
||||
classes = outs_dict['classes']
|
||||
if isinstance(classes, paddle.Tensor):
|
||||
classes = classes.numpy()
|
||||
classes = classes[:, 0, :, :]
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
classes = None
|
||||
|
||||
boxes_batch = []
|
||||
for batch_index in range(pred.shape[0]):
|
||||
src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[batch_index]
|
||||
if self.dilation_kernel is not None:
|
||||
mask = cv2.dilate(
|
||||
np.array(segmentation[batch_index]).astype(np.uint8),
|
||||
self.dilation_kernel)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
mask = segmentation[batch_index]
|
||||
|
||||
if classes is None:
|
||||
boxes, scores = self.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask, None,
|
||||
src_w, src_h)
|
||||
boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes})
|
||||
else:
|
||||
boxes, scores, class_indexes, class_scores = self.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask,
|
||||
classes[batch_index],
|
||||
src_w, src_h)
|
||||
boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes, "classes": class_indexes, "class_scores": class_scores})
|
||||
|
||||
return boxes_batch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.4. 模型启动
|
||||
|
||||
在完成上述步骤后我们就可以正常启动训练
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其他命令:
|
||||
```
|
||||
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/eval.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
|
||||
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer_det.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
模型推理
|
||||
```
|
||||
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="/home/aistudio/work/test_img/" --det_model_dir="/home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/output/infer"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5 总结
|
||||
|
||||
1. 分类+检测在一定程度上能够缩短用时,具体的模型选取要根据业务场景恰当选择。
|
||||
2. 数据标注需要多次进行测试调整标注方法,一般进行检测模型微调,需要标注至少上百张。
|
||||
3. 设置合理的batch_size以及resize大小,同时注意lr设置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
1 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
|
||||
2 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas
|
||||
|
||||
3 https://blog.csdn.net/YY007H/article/details/124491217
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
|||
# 基于PP-OCRv3的手写文字识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目背景及意义](#1-项目背景及意义)
|
||||
- [2. 项目内容](#2-项目内容)
|
||||
- [3. PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍](#3-PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍)
|
||||
- [4. 安装环境](#4-安装环境)
|
||||
- [5. 数据准备](#5-数据准备)
|
||||
- [6. 模型训练](#6-模型训练)
|
||||
- [6.1 下载预训练模型](#61-下载预训练模型)
|
||||
- [6.2 修改配置文件](#62-修改配置文件)
|
||||
- [6.3 开始训练](#63-开始训练)
|
||||
- [7. 模型评估](#7-模型评估)
|
||||
- [8. 模型导出推理](#8-模型导出推理)
|
||||
- [8.1 模型导出](#81-模型导出)
|
||||
- [8.2 模型推理](#82-模型推理)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目背景及意义
|
||||
目前光学字符识别(OCR)技术在我们的生活当中被广泛使用,但是大多数模型在通用场景下的准确性还有待提高。针对于此我们借助飞桨提供的PaddleOCR套件较容易的实现了在垂类场景下的应用。手写体在日常生活中较为常见,然而手写体的识别却存在着很大的挑战,因为每个人的手写字体风格不一样,这对于视觉模型来说还是相当有挑战的。因此训练一个手写体识别模型具有很好的现实意义。下面给出一些手写体的示例图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 项目内容
|
||||
本项目基于PaddleOCR套件,以PP-OCRv3识别模型为基础,针对手写文字识别场景进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
Aistudio项目链接:[OCR手写文字识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4330587)
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法[SVTR](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.00159)优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。如下图所示,PP-OCRv3采用了6个优化策略。
|
||||
|
||||
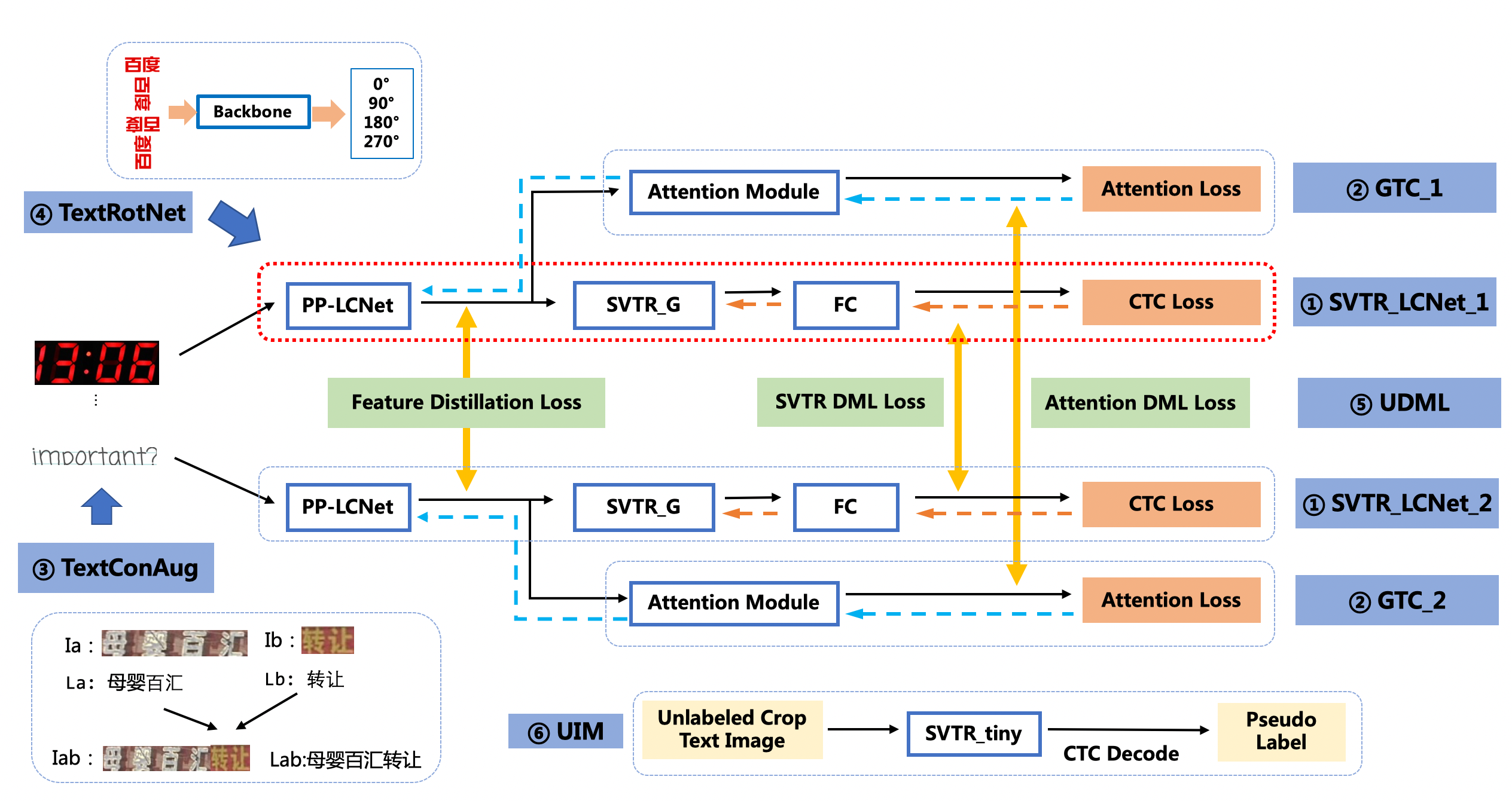
|
||||
|
||||
优化策略汇总如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* SVTR_LCNet:轻量级文本识别网络
|
||||
* GTC:Attention指导CTC训练策略
|
||||
* TextConAug:挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略
|
||||
* TextRotNet:自监督的预训练模型
|
||||
* UDML:联合互学习策略
|
||||
* UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案
|
||||
|
||||
详细优化策略描述请参考[PP-OCRv3优化策略](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md#3-%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96)
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 安装环境
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 首先git官方的PaddleOCR项目,安装需要的依赖
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 数据准备
|
||||
本项目使用公开的手写文本识别数据集,包含Chinese OCR, 中科院自动化研究所-手写中文数据集[CASIA-HWDB2.x](http://www.nlpr.ia.ac.cn/databases/handwriting/Download.html),以及由中科院手写数据和网上开源数据合并组合的[数据集](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/102884/0)等,该项目已经挂载处理好的数据集,可直接下载使用进行训练。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
下载并解压数据
|
||||
tar -xf hw_data.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. 模型训练
|
||||
### 6.1 下载预训练模型
|
||||
首先需要下载我们需要的PP-OCRv3识别预训练模型,更多选择请自行选择其他的[文字识别模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md#2-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 使用该指令下载需要的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrained_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压预训练模型文件
|
||||
tar -xf ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar -C pretrained_models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.2 修改配置文件
|
||||
我们使用`configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml`,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch_num: 100 # 训练epoch数
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 10
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 100] # 评估间隔,每隔100step评估一次
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy # 预训练模型路径
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine # 修改学习率衰减策略为Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.0001 # 修改fine-tune的学习率
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2 # 修改warmup轮数
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data # 训练集图片路径
|
||||
ext_op_transform_idx: 1
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/chineseocr-data/rec_hand_line_all_label_train.txt # 训练集标签
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.0Train_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.1Train_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.2Train_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/hwdb_ic13/handwriting_hwdb_train_labels.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HW_Chinese/train_hw.txt
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 0.1
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
- 0.02
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
drop_last: true
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data # 测试集图片路径
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/chineseocr-data/rec_hand_line_all_label_val.txt # 测试集标签
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.0Test_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.1Test_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.2Test_label.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/hwdb_ic13/handwriting_hwdb_val_labels.txt
|
||||
- ./train_data/handwrite/HW_Chinese/test_hw.txt
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
由于数据集大多是长文本,因此需要**注释**掉下面的数据增广策略,以便训练出更好的模型。
|
||||
```
|
||||
- RecConAug:
|
||||
prob: 0.5
|
||||
ext_data_num: 2
|
||||
image_shape: [48, 320, 3]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.3 开始训练
|
||||
我们使用上面修改好的配置文件`configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml`,预训练模型,数据集路径,学习率,训练轮数等都已经设置完毕后,可以使用下面命令开始训练。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 开始训练识别模型
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. 模型评估
|
||||
在训练之前,我们可以直接使用下面命令来评估预训练模型的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:46:22] ppocr INFO: load pretrain successful from ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
eval model:: 100%|████████████████████████████| 687/687 [03:29<00:00, 3.27it/s]
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: metric eval ***************
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: acc:0.03724954461811258
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: norm_edit_dis:0.4859541065843199
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: Teacher_acc:0.0371584699368947
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: Teacher_norm_edit_dis:0.48718814890536477
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:49:52] ppocr INFO: fps:947.8562684823883
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出,直接加载预训练模型进行评估,效果较差,因为预训练模型并不是基于手写文字进行单独训练的,所以我们需要基于预训练模型进行finetune。
|
||||
训练完成后,可以进行测试评估,评估命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估finetune效果
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估结果如下,可以看出识别准确率为54.3%。
|
||||
```
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: metric eval ***************
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: acc:0.5430100180913
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: norm_edit_dis:0.9203322593158589
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: Teacher_acc:0.5401183969626324
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: Teacher_norm_edit_dis:0.919827504507755
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:54:06] ppocr INFO: fps:928.948733797251
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
## 8. 模型导出推理
|
||||
训练完成后,可以将训练模型转换成inference模型。inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 8.1 模型导出
|
||||
导出命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 转化为推理模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy" Global.save_inference_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 8.2 模型推理
|
||||
导出模型后,可以使用如下命令进行推理预测:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 推理预测
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.0Test_images/104-P16_4.jpg" --rec_model_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:55:56] ppocr INFO: In PP-OCRv3, rec_image_shape parameter defaults to '3, 48, 320', if you are using recognition model with PP-OCRv2 or an older version, please set --rec_image_shape='3,32,320
|
||||
[2022/07/14 10:55:58] ppocr INFO: Predicts of train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.0Test_images/104-P16_4.jpg:('品结构,差异化的多品牌渗透使欧莱雅确立了其在中国化妆', 0.9904912114143372)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 可视化文字识别图片
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_path = 'train_data/handwrite/HWDB2.0Test_images/104-P16_4.jpg'
|
||||
|
||||
def vis(img_path):
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_path)
|
||||
plt.imshow(image)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
# image = image.resize([208, 208])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
vis(img_path)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
|
|||
# 金融智能核验:扫描合同关键信息抽取
|
||||
|
||||
本案例将使用OCR技术和通用信息抽取技术,实现合同关键信息审核和比对。通过本章的学习,你可以快速掌握:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用PaddleOCR提取扫描文本内容
|
||||
2. 使用PaddleNLP抽取自定义信息
|
||||
|
||||
点击进入 [AI Studio 项目](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4545772)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目背景
|
||||
合同审核广泛应用于大中型企业、上市公司、证券、基金公司中,是规避风险的重要任务。
|
||||
- 合同内容对比:合同审核场景中,快速找出不同版本合同修改区域、版本差异;如合同盖章归档场景中有效识别实际签署的纸质合同、电子版合同差异。
|
||||
|
||||
- 合规性检查:法务人员进行合同审核,如合同完备性检查、大小写金额检查、签约主体一致性检查、双方权利和义务对等性分析等。
|
||||
|
||||
- 风险点识别:通过合同审核可识别事实倾向型风险点和数值计算型风险点等,例如交付地点约定不明、合同总价款不一致、重要条款缺失等风险点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
传统业务中大多使用人工进行纸质版合同审核,存在成本高,工作量大,效率低的问题,且一旦出错将造成巨额损失。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本项目针对以上场景,使用PaddleOCR+PaddleNLP快速提取文本内容,经过少量数据微调即可准确抽取关键信息,**高效完成合同内容对比、合规性检查、风险点识别等任务,提高效率,降低风险**。
|
||||
|
||||
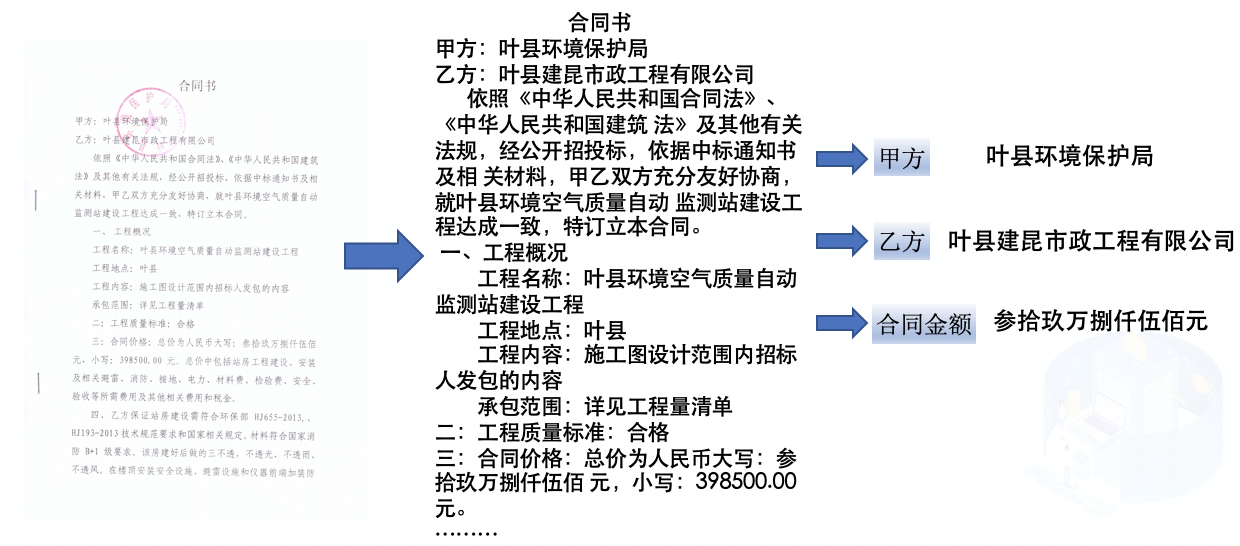
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1 扫描合同文本内容提取
|
||||
|
||||
使用PaddleOCR开源的模型可以快速完成扫描文档的文本内容提取,在清晰文档上识别准确率可达到95%+。下面来快速体验一下:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1.1 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)提供了适用于通用场景的高精轻量模型,提供数据预处理-模型推理-后处理全流程,支持pip安装:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python -m pip install paddleocr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1.2 效果测试
|
||||
|
||||
使用一张合同图片作为测试样本,感受ppocrv3模型效果:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src=https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/46258d0dc9dc40bab3ea0e70434e4a905646df8a647f4c49921e217de5142def width=300>
|
||||
|
||||
使用中文检测+识别模型提取文本,实例化PaddleOCR类:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from paddleocr import PaddleOCR, draw_ocr
|
||||
|
||||
# paddleocr目前支持中英文、英文、法语、德语、韩语、日语等80个语种,可以通过修改lang参数进行切换
|
||||
ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch") # need to run only once to download and load model into memory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
一行命令启动预测,预测结果包括`检测框`和`文本识别内容`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
img_path = "./test_img/hetong2.jpg"
|
||||
result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
|
||||
for line in result:
|
||||
print(line)
|
||||
|
||||
# 可视化结果
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
|
||||
boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
|
||||
im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
|
||||
im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
|
||||
im_show.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1.3 图片预处理
|
||||
|
||||
通过上图可视化结果可以看到,印章部分造成的文本遮盖,影响了文本识别结果,因此可以考虑通道提取,去除图片中的红色印章:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
#读入图像,三通道
|
||||
image=cv2.imread("./test_img/hetong2.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) #timg.jpeg
|
||||
|
||||
#获得三个通道
|
||||
Bch,Gch,Rch=cv2.split(image)
|
||||
|
||||
#保存三通道图片
|
||||
cv2.imwrite('blue_channel.jpg',Bch)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite('green_channel.jpg',Gch)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite('red_channel.jpg',Rch)
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### 2.1.4 合同文本信息提取
|
||||
|
||||
经过2.1.3的预处理后,合同照片的红色通道被分离,获得了一张相对更干净的图片,此时可以再次使用ppocr模型提取文本内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_path = './red_channel.jpg'
|
||||
result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
|
||||
|
||||
# 可视化结果
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
|
||||
boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
|
||||
im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
|
||||
im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
|
||||
vis = np.array(im_show)
|
||||
im_show.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
忽略检测框内容,提取完整的合同文本:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
all_context = "\n".join(txts)
|
||||
print(all_context)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上环节就完成了扫描合同关键信息抽取的第一步:文本内容提取,接下来可以基于识别出的文本内容抽取关键信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 合同关键信息抽取
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2.1 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
安装PaddleNLP
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install --upgrade paddlenlp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2.2 合同关键信息抽取
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleNLP 使用 Taskflow 统一管理多场景任务的预测功能,其中`information_extraction` 通过大量的有标签样本进行训练,在通用的场景中一般可以直接使用,只需更换关键字即可。例如在合同信息抽取中,我们重新定义抽取关键字:
|
||||
|
||||
甲方、乙方、币种、金额、付款方式
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
将使用OCR提取好的文本作为输入,使用三行命令可以对上文中提取到的合同文本进行关键信息抽取:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from paddlenlp import Taskflow
|
||||
schema = ["甲方","乙方","总价"]
|
||||
ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
|
||||
ie.set_schema(schema)
|
||||
ie(all_context)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到UIE模型可以准确的提取出关键信息,用于后续的信息比对或审核。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.效果优化
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 文本识别后处理调优
|
||||
|
||||
实际图片采集过程中,可能出现部分图片弯曲等问题,导致使用默认参数识别文本时存在漏检,影响关键信息获取。
|
||||
|
||||
例如下图:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/fe350481be0241c58736d487d1bf06c2e65911bf01254a79944be629c4c10091" height="300" width="300">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
直接进行预测:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
|
||||
# 预测结果
|
||||
result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
|
||||
# 可视化结果
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
|
||||
boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
|
||||
im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
|
||||
im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
|
||||
im_show.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可视化结果可以看到,弯曲图片存在漏检,一般来说可以通过调整后处理参数解决,无需重新训练模型。漏检问题往往是因为检测模型获得的分割图太小,生成框的得分过低被过滤掉了,通常有两种方式调整参数:
|
||||
- 开启`use_dilatiion=True` 膨胀分割区域
|
||||
- 调小`det_db_box_thresh`阈值
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 重新实例化 PaddleOCR
|
||||
ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch", det_db_box_thresh=0.3, use_dilation=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# 预测并可视化
|
||||
img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
|
||||
# 预测结果
|
||||
result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
|
||||
# 可视化结果
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
|
||||
boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
|
||||
im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
|
||||
im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
|
||||
im_show.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到漏检问题被很好的解决,提取完整的文本内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
|
||||
context = "\n".join(txts)
|
||||
print(context)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 关键信息提取调优
|
||||
|
||||
UIE通过大量有标签样本进行训练,得到了一个开箱即用的高精模型。 然而针对不同场景,可能会出现部分实体无法被抽取的情况。通常来说有以下几个方法进行效果调优:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 修改 schema
|
||||
- 添加正则方法
|
||||
- 标注小样本微调模型
|
||||
|
||||
**修改schema**
|
||||
|
||||
Prompt和原文描述越像,抽取效果越好,例如
|
||||
```
|
||||
三:合同价格:总价为人民币大写:参拾玖万捌仟伍佰
|
||||
元,小写:398500.00元。总价中包括站房工程建设、安装
|
||||
及相关避雷、消防、接地、电力、材料费、检验费、安全、
|
||||
验收等所需费用及其他相关费用和税金。
|
||||
```
|
||||
schema = ["总金额"] 时无法准确抽取,与原文描述差异较大。 修改 schema = ["总价"] 再次尝试:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from paddlenlp import Taskflow
|
||||
# schema = ["总金额"]
|
||||
schema = ["总价"]
|
||||
ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
|
||||
ie.set_schema(schema)
|
||||
ie(all_context)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**模型微调**
|
||||
|
||||
UIE的建模方式主要是通过 `Prompt` 方式来建模, `Prompt` 在小样本上进行微调效果非常有效。详细的数据标注+模型微调步骤可以参考项目:
|
||||
|
||||
[PaddleNLP信息抽取技术重磅升级!](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?channelType=0&channel=0)
|
||||
|
||||
[工单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
[快递单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4038499?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
扫描合同的关键信息提取可以使用 PaddleOCR + PaddleNLP 组合实现,两个工具均有以下优势:
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用简单:whl包一键安装,3行命令调用
|
||||
* 效果领先:优秀的模型效果可覆盖几乎全部的应用场景
|
||||
* 调优成本低:OCR模型可通过后处理参数的调整适配略有偏差的扫描文本, UIE模型可以通过极少的标注样本微调,成本很低。
|
||||
|
||||
## 作业
|
||||
|
||||
尝试自己解析出 `test_img/homework.png` 扫描合同中的 [甲方、乙方] 关键词:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<img src=https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/50a49a3c9f8348bfa04e8c8b97d3cce0d0dd6b14040f43939268d120688ef7ca width=300 hight=400>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
更多场景下的垂类模型获取,请扫下图二维码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
|
||||
<img src=https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/606538b59ea845cb99943b1dec6efe724e78f75c1e9c49228c7bf7da9f8837f5 width=300 hight=300>
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,616 @@
|
|||
# 基于PP-OCRv3的液晶屏读数识别
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目背景及意义](#1-项目背景及意义)
|
||||
- [2. 项目内容](#2-项目内容)
|
||||
- [3. 安装环境](#3-安装环境)
|
||||
- [4. 文字检测](#4-文字检测)
|
||||
- [4.1 PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍](#41-PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍)
|
||||
- [4.2 数据准备](#42-数据准备)
|
||||
- [4.3 模型训练](#43-模型训练)
|
||||
- [4.3.1 预训练模型直接评估](#431-预训练模型直接评估)
|
||||
- [4.3.2 预训练模型直接finetune](#432-预训练模型直接finetune)
|
||||
- [4.3.3 基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型](#433-基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型)
|
||||
- [4.3.4 基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型](#434-基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型)
|
||||
- [4.3.5 采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度](#435-采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度)
|
||||
- [4.3.6 模型导出推理](#436-4.3.6-模型导出推理)
|
||||
- [5. 文字识别](#5-文字识别)
|
||||
- [5.1 PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍](#51-PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍)
|
||||
- [5.2 数据准备](#52-数据准备)
|
||||
- [5.3 模型训练](#53-模型训练)
|
||||
- [5.4 模型导出推理](#54-模型导出推理)
|
||||
- [6. 系统串联](#6-系统串联)
|
||||
- [6.1 后处理](#61-后处理)
|
||||
- [7. PaddleServing部署](#7-PaddleServing部署)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目背景及意义
|
||||
目前光学字符识别(OCR)技术在我们的生活当中被广泛使用,但是大多数模型在通用场景下的准确性还有待提高,针对于此我们借助飞桨提供的PaddleOCR套件较容易的实现了在垂类场景下的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
该项目以国家质量基础(NQI)为准绳,充分利用大数据、云计算、物联网等高新技术,构建覆盖计量端、实验室端、数据端和硬件端的完整计量解决方案,解决传统计量校准中存在的难题,拓宽计量检测服务体系和服务领域;解决无数传接口或数传接口不统一、不公开的计量设备,以及计量设备所处的环境比较恶劣,不适合人工读取数据。通过OCR技术实现远程计量,引领计量行业向智慧计量转型和发展。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 项目内容
|
||||
本项目基于PaddleOCR开源套件,以PP-OCRv3检测和识别模型为基础,针对液晶屏读数识别场景进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
Aistudio项目链接:[OCR液晶屏读数识别](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4080130)
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 安装环境
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 首先git官方的PaddleOCR项目,安装需要的依赖
|
||||
# 第一次运行打开该注释
|
||||
# git clone https://gitee.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git
|
||||
cd PaddleOCR
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 文字检测
|
||||
文本检测的任务是定位出输入图像中的文字区域。近年来学术界关于文本检测的研究非常丰富,一类方法将文本检测视为目标检测中的一个特定场景,基于通用目标检测算法进行改进适配,如TextBoxes[1]基于一阶段目标检测器SSD[2]算法,调整目标框使之适合极端长宽比的文本行,CTPN[3]则是基于Faster RCNN[4]架构改进而来。但是文本检测与目标检测在目标信息以及任务本身上仍存在一些区别,如文本一般长宽比较大,往往呈“条状”,文本行之间可能比较密集,弯曲文本等,因此又衍生了很多专用于文本检测的算法。本项目基于PP-OCRv3算法进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 PP-OCRv3检测算法介绍
|
||||
PP-OCRv3检测模型是对PP-OCRv2中的CML(Collaborative Mutual Learning) 协同互学习文本检测蒸馏策略进行了升级。如下图所示,CML的核心思想结合了①传统的Teacher指导Student的标准蒸馏与 ②Students网络之间的DML互学习,可以让Students网络互学习的同时,Teacher网络予以指导。PP-OCRv3分别针对教师模型和学生模型进行进一步效果优化。其中,在对教师模型优化时,提出了大感受野的PAN结构LK-PAN和引入了DML(Deep Mutual Learning)蒸馏策略;在对学生模型优化时,提出了残差注意力机制的FPN结构RSE-FPN。
|
||||
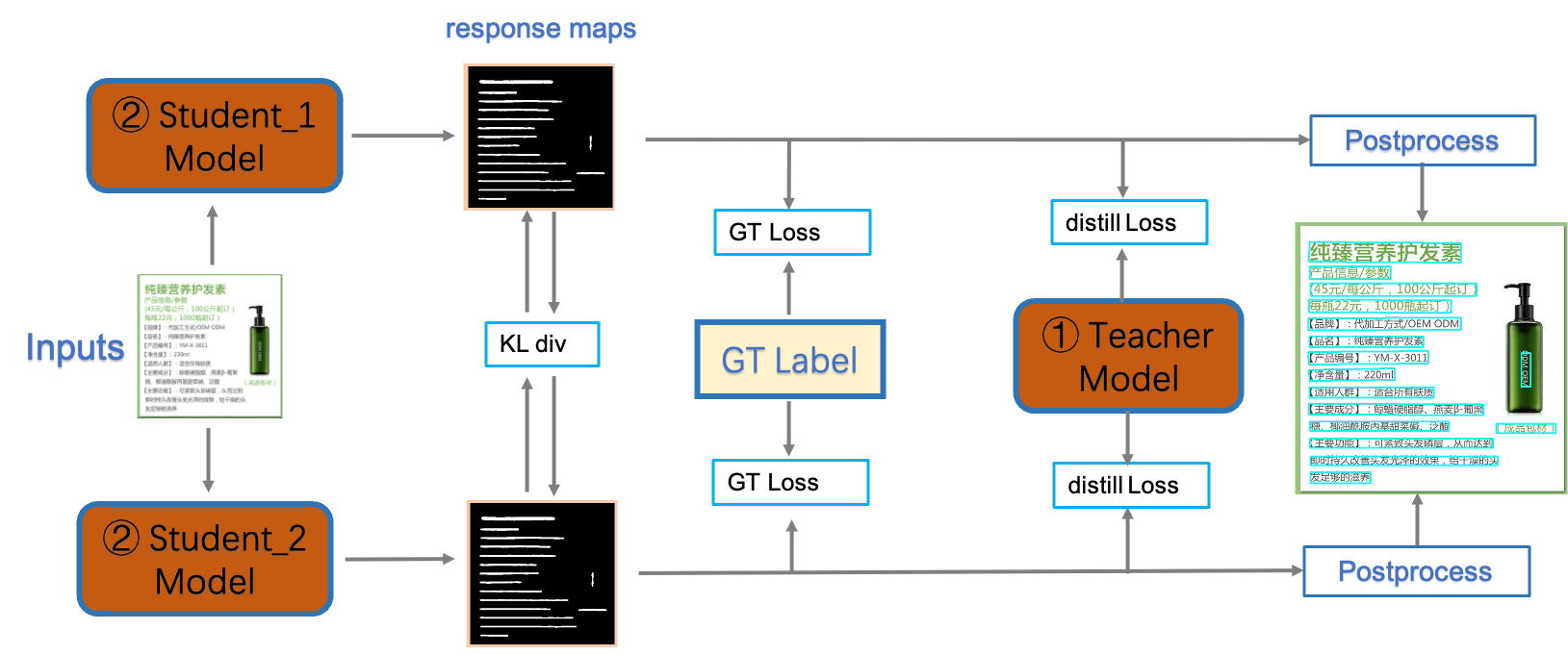
|
||||
|
||||
详细优化策略描述请参考[PP-OCRv3优化策略](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md#2)
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 数据准备
|
||||
[计量设备屏幕字符检测数据集](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/127845)数据来源于实际项目中各种计量设备的数显屏,以及在网上搜集的一些其他数显屏,包含训练集755张,测试集355张。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 在PaddleOCR下创建新的文件夹train_data
|
||||
mkdir train_data
|
||||
# 下载数据集并解压到指定路径下
|
||||
unzip icdar2015.zip -d train_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 随机查看文字检测数据集图片
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
train = './train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test'
|
||||
# 从指定目录中选取一张图片
|
||||
def get_one_image(train):
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
files = os.listdir(train)
|
||||
n = len(files)
|
||||
ind = np.random.randint(0,n)
|
||||
img_dir = os.path.join(train,files[ind])
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_dir)
|
||||
plt.imshow(image)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
image = image.resize([208, 208])
|
||||
|
||||
get_one_image(train)
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3 模型训练
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.1 预训练模型直接评估
|
||||
下载我们需要的PP-OCRv3检测预训练模型,更多选择请自行选择其他的[文字检测模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md#1-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E6%A3%80%E6%B5%8B%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#使用该指令下载需要的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrained_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压预训练模型文件
|
||||
tar -xf ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar -C pretrained_models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在训练之前,我们可以直接使用下面命令来评估预训练模型的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.50%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.2 预训练模型直接finetune
|
||||
##### 修改配置文件
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 开始训练
|
||||
使用我们上面修改的配置文件configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml,训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 开始训练模型
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.50%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.20%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.3 基于预训练模型Finetune_student模型
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.50%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.20%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.00%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.4 基于预训练模型Finetune_teacher模型
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要从提供的预训练模型best_accuracy.pdparams中提取teacher参数,组合成适合dml训练的初始化模型,提取代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd ./pretrained_models/
|
||||
# transform teacher params in best_accuracy.pdparams into teacher_dml.paramers
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
# load pretrained model
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
# keep teacher params
|
||||
t_params = {key[len("Teacher."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Teacher." in key}
|
||||
|
||||
# print(t_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
s_params = {"Student." + key: t_params[key] for key in t_params}
|
||||
s2_params = {"Student2." + key: t_params[key] for key in t_params}
|
||||
s_params = {**s_params, **s2_params}
|
||||
# print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml.pdparams")
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch:100
|
||||
save_epoch_step:10
|
||||
eval_batch_step:[0, 50]
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.00025
|
||||
num_workers: 0 # 如果单卡训练,建议将Train和Eval的loader部分的num_workers设置为0,否则会出现`/dev/shm insufficient`的报错
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_dml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_dml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.50%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.20%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.00%|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune教师模型 |84.80%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.5 采用CML蒸馏进一步提升student模型精度
|
||||
|
||||
需要从4.3.3和4.3.4训练得到的best_accuracy.pdparams中提取各自代表student和teacher的参数,组合成适合cml训练的初始化模型,提取代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# transform teacher params and student parameters into cml model
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
t_params = paddle.load("./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_teacher/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(t_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
s_params = paddle.load("./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_student/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
for key in all_params:
|
||||
# teacher is OK
|
||||
if "Teacher." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Teacher", "Student")
|
||||
#print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == t_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = t_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
if "Student." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Student.", "")
|
||||
#print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == s_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = s_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
if "Student2." in key:
|
||||
new_key = key.replace("Student2.", "")
|
||||
print("{} >> {}\n".format(key, new_key))
|
||||
assert all_params[key].shape == s_params[new_key].shape
|
||||
all_params[key] = s_params[new_key]
|
||||
|
||||
paddle.save(all_params, "./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_cml_student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/teacher_cml_student Global.save_model_dir=./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
评估训练好的模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估训练好的模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |47.50%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune |65.20%|
|
||||
| 2 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune学生模型 |80.00%|
|
||||
| 3 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型fintune教师模型 |84.80%|
|
||||
| 4 | 基于2和3训练好的模型fintune |82.70%|
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.3.6 模型导出推理
|
||||
训练完成后,可以将训练模型转换成inference模型。inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
##### 4.3.6.1 模型导出
|
||||
导出命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 转化为推理模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py \
|
||||
-c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml \
|
||||
-o Global.pretrained_model=./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_det_finetune/best_accuracy \
|
||||
-o Global.save_inference_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 4.3.6.2 模型推理
|
||||
导出模型后,可以使用如下命令进行推理预测:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 推理预测
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/1.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 文字识别
|
||||
文本识别的任务是识别出图像中的文字内容,一般输入来自于文本检测得到的文本框截取出的图像文字区域。文本识别一般可以根据待识别文本形状分为规则文本识别和不规则文本识别两大类。规则文本主要指印刷字体、扫描文本等,文本大致处在水平线位置;不规则文本往往不在水平位置,存在弯曲、遮挡、模糊等问题。不规则文本场景具有很大的挑战性,也是目前文本识别领域的主要研究方向。本项目基于PP-OCRv3算法进行优化。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1 PP-OCRv3识别算法介绍
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模块是基于文本识别算法[SVTR](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.00159)优化。SVTR不再采用RNN结构,通过引入Transformers结构更加有效地挖掘文本行图像的上下文信息,从而提升文本识别能力。如下图所示,PP-OCRv3采用了6个优化策略。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
优化策略汇总如下:
|
||||
* SVTR_LCNet:轻量级文本识别网络
|
||||
* GTC:Attention指导CTC训练策略
|
||||
* TextConAug:挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略
|
||||
* TextRotNet:自监督的预训练模型
|
||||
* UDML:联合互学习策略
|
||||
* UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案
|
||||
|
||||
详细优化策略描述请参考[PP-OCRv3优化策略](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md#3-%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96)
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2 数据准备
|
||||
[计量设备屏幕字符识别数据集](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/128714)数据来源于实际项目中各种计量设备的数显屏,以及在网上搜集的一些其他数显屏,包含训练集19912张,测试集4099张。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 解压下载的数据集到指定路径下
|
||||
unzip ic15_data.zip -d train_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 随机查看文字检测数据集图片
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
train = './train_data/ic15_data/train'
|
||||
# 从指定目录中选取一张图片
|
||||
def get_one_image(train):
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
files = os.listdir(train)
|
||||
n = len(files)
|
||||
ind = np.random.randint(0,n)
|
||||
img_dir = os.path.join(train,files[ind])
|
||||
image = Image.open(img_dir)
|
||||
plt.imshow(image)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
image = image.resize([208, 208])
|
||||
|
||||
get_one_image(train)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.3 模型训练
|
||||
#### 下载预训练模型
|
||||
下载我们需要的PP-OCRv3识别预训练模型,更多选择请自行选择其他的[文字识别模型](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/release/2.5/doc/doc_ch/models_list.md#2-%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E8%AF%86%E5%88%AB%E6%A8%A1%E5%9E%8B)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 使用该指令下载需要的预训练模型
|
||||
wget -P ./pretrained_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
# 解压预训练模型文件
|
||||
tar -xf ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar -C pretrained_models
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 修改配置文件
|
||||
我们使用configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml,主要修改训练轮数和学习率参相关参数,设置预训练模型路径,设置数据集路径。 另外,batch_size可根据自己机器显存大小进行调整。 具体修改如下几个地方:
|
||||
```
|
||||
epoch_num: 100 # 训练epoch数
|
||||
save_model_dir: ./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec
|
||||
save_epoch_step: 10
|
||||
eval_batch_step: [0, 100] # 评估间隔,每隔100step评估一次
|
||||
cal_metric_during_train: true
|
||||
pretrained_model: ./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy # 预训练模型路径
|
||||
character_dict_path: ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt
|
||||
use_space_char: true # 使用空格
|
||||
|
||||
lr:
|
||||
name: Cosine # 修改学习率衰减策略为Cosine
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.0002 # 修改fine-tune的学习率
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 2 # 修改warmup轮数
|
||||
|
||||
Train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data/ # 训练集图片路径
|
||||
ext_op_transform_idx: 1
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_train.txt # 训练集标签
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
drop_last: true
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
Eval:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
name: SimpleDataSet
|
||||
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data/ # 测试集图片路径
|
||||
label_file_list:
|
||||
- ./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_test.txt # 测试集标签
|
||||
ratio_list:
|
||||
- 1.0
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
shuffle: false
|
||||
drop_last: false
|
||||
batch_size_per_card: 64
|
||||
num_workers: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在训练之前,我们可以直接使用下面命令来评估预训练模型的效果:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./pretrained_models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |accuracy|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测 |70.40%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开始训练
|
||||
我们使用上面修改好的配置文件configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml,预训练模型,数据集路径,学习率,训练轮数等都已经设置完毕后,可以使用下面命令开始训练。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 开始训练识别模型
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
训练完成后,可以对训练模型中最好的进行测试,评估命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 评估finetune效果
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.checkpoints="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结果如下:
|
||||
| | 方案 |accuracy|
|
||||
|---|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| 0 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测 |70.40%|
|
||||
| 1 | PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型finetune |82.20%|
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
将下载或训练完成的模型放置在对应目录下即可完成模型推理。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.4 模型导出推理
|
||||
训练完成后,可以将训练模型转换成inference模型。inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
#### 模型导出
|
||||
导出命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 转化为推理模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml -o Global.pretrained_model="./output/ch_PP-OCR_v3_rec/best_accuracy" Global.save_inference_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 模型推理
|
||||
导出模型后,可以使用如下命令进行推理预测
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 推理预测
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="train_data/ic15_data/test/1_crop_0.jpg" --rec_model_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. 系统串联
|
||||
我们将上面训练好的检测和识别模型进行系统串联测试,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#串联测试
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py --image_dir="./train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/142.jpg" --det_model_dir="./inference/det_ppocrv3/Student" --rec_model_dir="./inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试结果保存在`./inference_results/`目录下,可以用下面代码进行可视化
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
# 显示结果
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
img_path= "./inference_results/142.jpg"
|
||||
img = Image.open(img_path)
|
||||
plt.figure("test_img", figsize=(30,30))
|
||||
plt.imshow(img)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.1 后处理
|
||||
如果需要获取key-value信息,可以基于启发式的规则,将识别结果与关键字库进行匹配;如果匹配上了,则取该字段为key, 后面一个字段为value。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def postprocess(rec_res):
|
||||
keys = ["型号", "厂家", "版本号", "检定校准分类", "计量器具编号", "烟尘流量",
|
||||
"累积体积", "烟气温度", "动压", "静压", "时间", "试验台编号", "预测流速",
|
||||
"全压", "烟温", "流速", "工况流量", "标杆流量", "烟尘直读嘴", "烟尘采样嘴",
|
||||
"大气压", "计前温度", "计前压力", "干球温度", "湿球温度", "流量", "含湿量"]
|
||||
key_value = []
|
||||
if len(rec_res) > 1:
|
||||
for i in range(len(rec_res) - 1):
|
||||
rec_str, _ = rec_res[i]
|
||||
for key in keys:
|
||||
if rec_str in key:
|
||||
key_value.append([rec_str, rec_res[i + 1][0]])
|
||||
break
|
||||
return key_value
|
||||
key_value = postprocess(filter_rec_res)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. PaddleServing部署
|
||||
首先需要安装PaddleServing部署相关的环境
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle-serving-server-gpu
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle_serving_client
|
||||
python -m pip install paddle-serving-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.1 转化检测模型
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cd deploy/pdserving/
|
||||
python -m paddle_serving_client.convert --dirname ../../inference/det_ppocrv3/Student/ \
|
||||
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
|
||||
--serving_server ./ppocr_det_v3_serving/ \
|
||||
--serving_client ./ppocr_det_v3_client/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.2 转化识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python -m paddle_serving_client.convert --dirname ../../inference/rec_ppocrv3/Student \
|
||||
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
|
||||
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
|
||||
--serving_server ./ppocr_rec_v3_serving/ \
|
||||
--serving_client ./ppocr_rec_v3_client/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.3 启动服务
|
||||
首先可以将后处理代码加入到web_service.py中,具体修改如下:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# 代码153行后面增加下面代码
|
||||
def _postprocess(rec_res):
|
||||
keys = ["型号", "厂家", "版本号", "检定校准分类", "计量器具编号", "烟尘流量",
|
||||
"累积体积", "烟气温度", "动压", "静压", "时间", "试验台编号", "预测流速",
|
||||
"全压", "烟温", "流速", "工况流量", "标杆流量", "烟尘直读嘴", "烟尘采样嘴",
|
||||
"大气压", "计前温度", "计前压力", "干球温度", "湿球温度", "流量", "含湿量"]
|
||||
key_value = []
|
||||
if len(rec_res) > 1:
|
||||
for i in range(len(rec_res) - 1):
|
||||
rec_str, _ = rec_res[i]
|
||||
for key in keys:
|
||||
if rec_str in key:
|
||||
key_value.append([rec_str, rec_res[i + 1][0]])
|
||||
break
|
||||
return key_value
|
||||
key_value = _postprocess(rec_list)
|
||||
res = {"result": str(key_value)}
|
||||
# res = {"result": str(result_list)}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动服务端
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python web_service.py 2>&1 >log.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.4 发送请求
|
||||
然后再开启一个新的终端,运行下面的客户端代码
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
python pipeline_http_client.py --image_dir ../../train_data/icdar2015/text_localization/test/142.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以获取到最终的key-value结果:
|
||||
```
|
||||
大气压, 100.07kPa
|
||||
干球温度, 0000℃
|
||||
计前温度, 0000℃
|
||||
湿球温度, 0000℃
|
||||
计前压力, -0000kPa
|
||||
流量, 00.0L/min
|
||||
静压, 00000kPa
|
||||
含湿量, 00.0 %
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,832 @@
|
|||
# 一种基于PaddleOCR的轻量级车牌识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
- [1. 项目介绍](#1-项目介绍)
|
||||
- [2. 环境搭建](#2-环境搭建)
|
||||
- [3. 数据集准备](#3-数据集准备)
|
||||
- [3.1 数据集标注规则](#31-数据集标注规则)
|
||||
- [3.2 制作符合PP-OCR训练格式的标注文件](#32-制作符合pp-ocr训练格式的标注文件)
|
||||
- [4. 实验](#4-实验)
|
||||
- [4.1 检测](#41-检测)
|
||||
- [4.1.1 预训练模型直接预测](#411-预训练模型直接预测)
|
||||
- [4.1.2 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune](#412-ccpd车牌数据集fine-tune)
|
||||
- [4.1.3 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune+量化训练](#413-ccpd车牌数据集fine-tune量化训练)
|
||||
- [4.1.4 模型导出](#414-模型导出)
|
||||
- [4.2 识别](#42-识别)
|
||||
- [4.2.1 预训练模型直接预测](#421-预训练模型直接预测)
|
||||
- [4.2.2 预训练模型直接预测+改动后处理](#422-预训练模型直接预测改动后处理)
|
||||
- [4.2.3 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune](#423-ccpd车牌数据集fine-tune)
|
||||
- [4.2.4 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune+量化训练](#424-ccpd车牌数据集fine-tune量化训练)
|
||||
- [4.2.5 模型导出](#425-模型导出)
|
||||
- [4.3 计算End2End指标](#43-计算End2End指标)
|
||||
- [4.4 部署](#44-部署)
|
||||
- [4.5 实验总结](#45-实验总结)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 项目介绍
|
||||
|
||||
车牌识别(Vehicle License Plate Recognition,VLPR) 是计算机视频图像识别技术在车辆牌照识别中的一种应用。车牌识别技术要求能够将运动中的汽车牌照从复杂背景中提取并识别出来,在高速公路车辆管理,停车场管理和城市交通中得到广泛应用。
|
||||
|
||||
本项目难点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 车牌在图像中的尺度差异大、在车辆上的悬挂位置不固定
|
||||
2. 车牌图像质量层次不齐: 角度倾斜、图片模糊、光照不足、过曝等问题严重
|
||||
3. 边缘和端测场景应用对模型大小有限制,推理速度有要求
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上问题, 本例选用 PP-OCRv3 这一开源超轻量OCR系统进行车牌识别系统的开发。基于PP-OCRv3模型,在CCPD数据集达到99%的检测和94%的识别精度,模型大小12.8M(2.5M+10.3M)。基于量化对模型体积进行进一步压缩到5.8M(1M+4.8M), 同时推理速度提升25%。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
aistudio项目链接: [基于PaddleOCR的轻量级车牌识别范例](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3919091?contributionType=1)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 环境搭建
|
||||
|
||||
本任务基于Aistudio完成, 具体环境如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统: Linux
|
||||
- PaddlePaddle: 2.3
|
||||
- paddleslim: 2.2.2
|
||||
- PaddleOCR: Release/2.5
|
||||
|
||||
下载 PaddleOCR代码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone -b dygraph https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装依赖库
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 数据集准备
|
||||
|
||||
所使用的数据集为 CCPD2020 新能源车牌数据集,该数据集为
|
||||
|
||||
该数据集分布如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|数据集类型|数量|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|训练集| 5769|
|
||||
|验证集| 1001|
|
||||
|测试集| 5006|
|
||||
|
||||
数据集图片示例如下:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
数据集可以从这里下载 https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/datasetdetail/101595
|
||||
|
||||
下载好数据集后对数据集进行解压
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
unzip -d /home/aistudio/data /home/aistudio/data/data101595/CCPD2020.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 数据集标注规则
|
||||
|
||||
CPPD数据集的图片文件名具有特殊规则,详细可查看:https://github.com/detectRecog/CCPD
|
||||
|
||||
具体规则如下:
|
||||
|
||||
例如: 025-95_113-154&383_386&473-386&473_177&454_154&383_363&402-0_0_22_27_27_33_16-37-15.jpg
|
||||
|
||||
每个名称可以分为七个字段,以-符号作为分割。这些字段解释如下。
|
||||
|
||||
- 025:车牌面积与整个图片区域的面积比。025 (25%)
|
||||
|
||||
- 95_113:水平倾斜程度和垂直倾斜度。水平 95度 垂直 113度
|
||||
|
||||
- 154&383_386&473:左上和右下顶点的坐标。左上(154,383) 右下(386,473)
|
||||
|
||||
- 386&473_177&454_154&383_363&402:整个图像中车牌的四个顶点的精确(x,y)坐标。这些坐标从右下角顶点开始。(386,473) (177,454) (154,383) (363,402)
|
||||
|
||||
- 0_0_22_27_27_33_16:CCPD中的每个图像只有一个车牌。每个车牌号码由一个汉字,一个字母和五个字母或数字组成。有效的中文车牌由七个字符组成:省(1个字符),字母(1个字符),字母+数字(5个字符)。“ 0_0_22_27_27_33_16”是每个字符的索引。这三个数组定义如下。每个数组的最后一个字符是字母O,而不是数字0。我们将O用作“无字符”的符号,因为中文车牌字符中没有O。因此以上车牌拼起来即为 皖AY339S
|
||||
|
||||
- 37:牌照区域的亮度。 37 (37%)
|
||||
|
||||
- 15:车牌区域的模糊度。15 (15%)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
provinces = ["皖", "沪", "津", "渝", "冀", "晋", "蒙", "辽", "吉", "黑", "苏", "浙", "京", "闽", "赣", "鲁", "豫", "鄂", "湘", "粤", "桂", "琼", "川", "贵", "云", "藏", "陕", "甘", "青", "宁", "新", "警", "学", "O"]
|
||||
alphabets = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W','X', 'Y', 'Z', 'O']
|
||||
ads = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X','Y', 'Z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'O']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 制作符合PP-OCR训练格式的标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
在开始训练之前,可使用如下代码制作符合PP-OCR训练格式的标注文件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import json
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
provinces = ["皖", "沪", "津", "渝", "冀", "晋", "蒙", "辽", "吉", "黑", "苏", "浙", "京", "闽", "赣", "鲁", "豫", "鄂", "湘", "粤", "桂", "琼", "川", "贵", "云", "藏", "陕", "甘", "青", "宁", "新", "警", "学", "O"]
|
||||
alphabets = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'O']
|
||||
ads = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'O']
|
||||
|
||||
def make_label(img_dir, save_gt_folder, phase):
|
||||
crop_img_save_dir = os.path.join(save_gt_folder, phase, 'crop_imgs')
|
||||
os.makedirs(crop_img_save_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
f_det = open(os.path.join(save_gt_folder, phase, 'det.txt'), 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
f_rec = open(os.path.join(save_gt_folder, phase, 'rec.txt'), 'w', encoding='utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
for filename in tqdm(os.listdir(os.path.join(img_dir, phase))):
|
||||
str_list = filename.split('-')
|
||||
if len(str_list) < 5:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
coord_list = str_list[3].split('_')
|
||||
txt_list = str_list[4].split('_')
|
||||
boxes = []
|
||||
for coord in coord_list:
|
||||
boxes.append([int(x) for x in coord.split("&")])
|
||||
boxes = [boxes[2], boxes[3], boxes[0], boxes[1]]
|
||||
lp_number = provinces[int(txt_list[0])] + alphabets[int(txt_list[1])] + ''.join([ads[int(x)] for x in txt_list[2:]])
|
||||
|
||||
# det
|
||||
det_info = [{'points':boxes, 'transcription':lp_number}]
|
||||
f_det.write('{}\t{}\n'.format(os.path.join(phase, filename), json.dumps(det_info, ensure_ascii=False)))
|
||||
|
||||
# rec
|
||||
boxes = np.float32(boxes)
|
||||
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(img_dir, phase, filename))
|
||||
# crop_img = img[int(boxes[:,1].min()):int(boxes[:,1].max()),int(boxes[:,0].min()):int(boxes[:,0].max())]
|
||||
crop_img = get_rotate_crop_image(img, boxes)
|
||||
crop_img_save_filename = '{}_{}.jpg'.format(i,'_'.join(txt_list))
|
||||
crop_img_save_path = os.path.join(crop_img_save_dir, crop_img_save_filename)
|
||||
cv2.imwrite(crop_img_save_path, crop_img)
|
||||
f_rec.write('{}/crop_imgs/{}\t{}\n'.format(phase, crop_img_save_filename, lp_number))
|
||||
i+=1
|
||||
f_det.close()
|
||||
f_rec.close()
|
||||
|
||||
def get_rotate_crop_image(img, points):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
img_height, img_width = img.shape[0:2]
|
||||
left = int(np.min(points[:, 0]))
|
||||
right = int(np.max(points[:, 0]))
|
||||
top = int(np.min(points[:, 1]))
|
||||
bottom = int(np.max(points[:, 1]))
|
||||
img_crop = img[top:bottom, left:right, :].copy()
|
||||
points[:, 0] = points[:, 0] - left
|
||||
points[:, 1] = points[:, 1] - top
|
||||
'''
|
||||
assert len(points) == 4, "shape of points must be 4*2"
|
||||
img_crop_width = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3])))
|
||||
img_crop_height = int(
|
||||
max(
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]),
|
||||
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2])))
|
||||
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
|
||||
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
|
||||
[0, img_crop_height]])
|
||||
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
|
||||
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
|
||||
img,
|
||||
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
|
||||
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
|
||||
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
|
||||
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
|
||||
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
|
||||
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)
|
||||
return dst_img
|
||||
|
||||
img_dir = '/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green'
|
||||
save_gt_folder = '/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR'
|
||||
# phase = 'train' # change to val and test to make val dataset and test dataset
|
||||
for phase in ['train','val','test']:
|
||||
make_label(img_dir, save_gt_folder, phase)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过上述命令可以完成了`训练集`,`验证集`和`测试集`的制作,制作完成的数据集信息如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 类型 | 数据集 | 图片地址 | 标签地址 | 图片数量 |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| 检测 | 训练集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/train | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/det.txt | 5769 |
|
||||
| 检测 | 验证集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/val | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/val/det.txt | 1001 |
|
||||
| 检测 | 测试集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt | 5006 |
|
||||
| 识别 | 训练集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/crop_imgs | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/rec.txt | 5769 |
|
||||
| 识别 | 验证集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/val/crop_imgs | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/val/rec.txt | 1001 |
|
||||
| 识别 | 测试集 | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/crop_imgs | /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt | 5006 |
|
||||
|
||||
在普遍的深度学习流程中,都是在训练集训练,在验证集选择最优模型后在测试集上进行测试。在本例中,我们省略中间步骤,直接在训练集训练,在测试集选择最优模型,因此我们只使用训练集和测试集。
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 实验
|
||||
|
||||
由于数据集比较少,为了模型更好和更快的收敛,这里选用 PaddleOCR 中的 PP-OCRv3 模型进行文本检测和识别,并且使用 PP-OCRv3 模型参数作为预训练模型。PP-OCRv3在PP-OCRv2的基础上,中文场景端到端Hmean指标相比于PP-OCRv2提升5%, 英文数字模型端到端效果提升11%。详细优化细节请参考[PP-OCRv3](../doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)技术报告。
|
||||
|
||||
由于车牌场景均为端侧设备部署,因此对速度和模型大小有比较高的要求,因此还需要采用量化训练的方式进行模型大小的压缩和模型推理速度的加速。模型量化可以在基本不损失模型的精度的情况下,将FP32精度的模型参数转换为Int8精度,减小模型参数大小并加速计算,使用量化后的模型在移动端等部署时更具备速度优势。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,本实验中对于车牌检测和识别有如下3种方案:
|
||||
|
||||
1. PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量预训练模型直接预测
|
||||
2. CCPD车牌数据集在PP-OCRv3模型上fine-tune
|
||||
3. CCPD车牌数据集在PP-OCRv3模型上fine-tune后量化
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 检测
|
||||
#### 4.1.1 预训练模型直接预测
|
||||
|
||||
从下表中下载PP-OCRv3文本检测预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
|模型名称|模型简介|配置文件|推理模型大小|下载地址|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ch_PP-OCRv3_det| 【最新】原始超轻量模型,支持中英文、多语种文本检测 |[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_cml.yml)| 3.8M |[推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar)|
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令下载预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir models
|
||||
cd models
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预训练模型下载完成后,我们使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml](../configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml) 配置文件进行后续实验,在开始评估之前需要对配置文件中部分字段进行设置,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 模型存储和训练相关:
|
||||
1. Global.pretrained_model: 指向PP-OCRv3文本检测预训练模型地址
|
||||
2. 数据集相关
|
||||
1. Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向测试集图片存放目录
|
||||
2. Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向测试集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
上述字段均为必须修改的字段,可以通过修改配置文件的方式改动,也可在不需要修改配置文件的情况下,改变训练的参数。这里使用不改变配置文件的方式 。使用如下命令进行PP-OCRv3文本检测预训练模型的评估
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
上述指令中,通过-c 选择训练使用配置文件,通过-o参数在不需要修改配置文件的情况下,改变训练的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 方案 |hmeans|
|
||||
|---------------------------|---|
|
||||
| PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测 |76.12%|
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.1.2 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
**训练**
|
||||
|
||||
为了进行fine-tune训练,我们需要在配置文件中设置需要使用的预训练模型地址,学习率和数据集等参数。 具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 模型存储和训练相关:
|
||||
1. Global.pretrained_model: 指向PP-OCRv3文本检测预训练模型地址
|
||||
2. Global.eval_batch_step: 模型多少step评估一次,这里设为从第0个step开始没隔772个step评估一次,772为一个epoch总的step数。
|
||||
2. 优化器相关:
|
||||
1. Optimizer.lr.name: 学习率衰减器设为常量 Const
|
||||
2. Optimizer.lr.learning_rate: 做 fine-tune 实验,学习率需要设置的比较小,此处学习率设为配置文件中的0.05倍
|
||||
3. Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch: warmup_epoch设为0
|
||||
3. 数据集相关:
|
||||
1. Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
2. Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
3. Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向测试集图片存放目录
|
||||
4. Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向测试集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下代码即可启动在CCPD车牌数据集上的fine-tune。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=output/CCPD/det \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step="[0, 772]" \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.name=Const \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate=0.0005 \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch=0 \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/det.txt] \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上述命令中,通过`-o`的方式修改了配置文件中的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**评估**
|
||||
|
||||
训练完成后使用如下命令进行评估
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型和CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune,指标分别如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|hmeans|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测|76.12%|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune|99.00%|
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到进行fine-tune能显著提升车牌检测的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.1.3 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune+量化训练
|
||||
|
||||
此处采用 PaddleOCR 中提供好的[量化教程](../deploy/slim/quantization/README.md)对模型进行量化训练。
|
||||
|
||||
量化训练可通过如下命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3.7 deploy/slim/quantization/quant.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=output/CCPD/det_quant \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step="[0, 772]" \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.name=Const \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate=0.0005 \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch=0 \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/det.txt] \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
量化后指标对比如下
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|hmeans| 模型大小 | 预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|---|---|------|------------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune|99.00%| 2.5M | 223ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune+量化|98.91%| 1.0M | 189ms |
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到通过量化训练在精度几乎无损的情况下,降低模型体积60%并且推理速度提升15%。
|
||||
|
||||
速度测试基于[PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)完成。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.1.4 模型导出
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令可以将训练好的模型进行导出
|
||||
|
||||
* 非量化模型
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/det/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
* 量化模型
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python deploy/slim/quantization/export_model.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det_quant/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/det/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 识别
|
||||
#### 4.2.1 预训练模型直接预测
|
||||
|
||||
从下表中下载PP-OCRv3文本识别预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
|模型名称|模型简介|配置文件|推理模型大小|下载地址|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|ch_PP-OCRv3_rec|【最新】原始超轻量模型,支持中英文、数字识别|[ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_distillation.yml)| 12.4M |[推理模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_infer.tar) / [训练模型](https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar) |
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令下载预训练模型
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir models
|
||||
cd models
|
||||
wget https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
tar -xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train.tar
|
||||
cd /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PaddleOCR提供的PP-OCRv3识别模型采用蒸馏训练策略,因此提供的预训练模型中会包含`Teacher`和`Student`模型的参数,详细信息可参考[knowledge_distillation.md](../doc/doc_ch/knowledge_distillation.md)。 因此,模型下载完成后需要使用如下代码提取`Student`模型的参数:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
# 加载预训练模型
|
||||
all_params = paddle.load("models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy.pdparams")
|
||||
# 查看权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(all_params.keys())
|
||||
# 学生模型的权重提取
|
||||
s_params = {key[len("Student."):]: all_params[key] for key in all_params if "Student." in key}
|
||||
# 查看学生模型权重参数的keys
|
||||
print(s_params.keys())
|
||||
# 保存
|
||||
paddle.save(s_params, "models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预训练模型下载完成后,我们使用[ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml](../configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml) 配置文件进行后续实验,在开始评估之前需要对配置文件中部分字段进行设置,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 模型存储和训练相关:
|
||||
1. Global.pretrained_model: 指向PP-OCRv3文本识别预训练模型地址
|
||||
2. 数据集相关
|
||||
1. Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向测试集图片存放目录
|
||||
2. Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向测试集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令进行PP-OCRv3文本识别预训练模型的评估
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如需获取已训练模型,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
评估部分日志如下:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:02] ppocr INFO: load pretrain successful from models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/best_accuracy
|
||||
eval model:: 100%|██████████████████████████████| 40/40 [00:15<00:00, 2.57it/s]
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: metric eval ***************
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: acc:0.0
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: norm_edit_dis:0.8656084923002452
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: Teacher_acc:0.000399520574511545
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: Teacher_norm_edit_dis:0.8657902943394548
|
||||
[2022/05/12 19:52:17] ppocr INFO: fps:1443.1801978719905
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
使用预训练模型进行评估,指标如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|acc|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测|0%|
|
||||
|
||||
从评估日志中可以看到,直接使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型进行评估,acc非常低,但是norm_edit_dis很高。因此,我们猜测是模型大部分文字识别是对的,只有少部分文字识别错误。使用如下命令进行infer查看模型的推理结果进行验证:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.infer_img=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/crop_imgs/0_0_0_3_32_30_31_30_30.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出部分日志如下:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[2022/05/01 08:51:57] ppocr INFO: train with paddle 2.2.2 and device CUDAPlace(0)
|
||||
W0501 08:51:57.127391 11326 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 11.0, Runtime API Version: 10.1
|
||||
W0501 08:51:57.132315 11326 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
|
||||
[2022/05/01 08:52:00] ppocr INFO: load pretrain successful from models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student
|
||||
[2022/05/01 08:52:00] ppocr INFO: infer_img: /home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/crop_imgs/0_0_3_32_30_31_30_30.jpg
|
||||
[2022/05/01 08:52:00] ppocr INFO: result: {"Student": {"label": "皖A·D86766", "score": 0.9552637934684753}, "Teacher": {"label": "皖A·D86766", "score": 0.9917094707489014}}
|
||||
[2022/05/01 08:52:00] ppocr INFO: success!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
从infer结果可以看到,车牌中的文字大部分都识别正确,只是多识别出了一个`·`。针对这种情况,有如下两种方案:
|
||||
1. 直接通过后处理去掉多识别的`·`。
|
||||
2. 进行 fine-tune。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.2 预训练模型直接预测+改动后处理
|
||||
|
||||
直接通过后处理去掉多识别的`·`,在后处理的改动比较简单,只需在 [ppocr/postprocess/rec_postprocess.py](../ppocr/postprocess/rec_postprocess.py) 文件的76行添加如下代码:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
text = text.replace('·','')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
改动前后指标对比:
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|acc|
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测|0.20%|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测+后处理去掉多识别的`·`|90.97%|
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,去掉多余的`·`能大幅提高精度。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.3 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
**训练**
|
||||
|
||||
为了进行fine-tune训练,我们需要在配置文件中设置需要使用的预训练模型地址,学习率和数据集等参数。 具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 模型存储和训练相关:
|
||||
1. Global.pretrained_model: 指向PP-OCRv3文本识别预训练模型地址
|
||||
2. Global.eval_batch_step: 模型多少step评估一次,这里设为从第0个step开始没隔45个step评估一次,45为一个epoch总的step数。
|
||||
2. 优化器相关
|
||||
1. Optimizer.lr.name: 学习率衰减器设为常量 Const
|
||||
2. Optimizer.lr.learning_rate: 做 fine-tune 实验,学习率需要设置的比较小,此处学习率设为配置文件中的0.05倍
|
||||
3. Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch: warmup_epoch设为0
|
||||
3. 数据集相关
|
||||
1. Train.dataset.data_dir:指向训练集图片存放目录
|
||||
2. Train.dataset.label_file_list:指向训练集标注文件
|
||||
3. Eval.dataset.data_dir:指向测试集图片存放目录
|
||||
4. Eval.dataset.label_file_list:指向测试集标注文件
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令启动 fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/train.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=output/CCPD/rec/ \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step="[0, 90]" \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.name=Const \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate=0.0005 \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch=0 \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/rec.txt] \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**评估**
|
||||
|
||||
训练完成后使用如下命令进行评估
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用预训练模型和CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune,指标分别如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|方案| acc |
|
||||
|---|--------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测| 0.00% |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测+后处理去掉多识别的`·`| 90.97% |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune| 94.54% |
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到进行fine-tune能显著提升车牌识别的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.4 CCPD车牌数据集fine-tune+量化训练
|
||||
|
||||
此处采用 PaddleOCR 中提供好的[量化教程](../deploy/slim/quantization/README.md)对模型进行量化训练。
|
||||
|
||||
量化训练可通过如下命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3.7 deploy/slim/quantization/quant.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_model_dir=output/CCPD/rec_quant/ \
|
||||
Global.eval_batch_step="[0, 90]" \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.name=Const \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.learning_rate=0.0005 \
|
||||
Optimizer.lr.warmup_epoch=0 \
|
||||
Train.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Train.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/train/rec.txt] \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
量化后指标对比如下
|
||||
|
||||
|方案| acc | 模型大小 | 预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|---|--------|-------|------------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune| 94.54% | 10.3M | 4.2ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune + 量化| 93.40% | 4.8M | 1.8ms |
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到量化后能降低模型体积53%并且推理速度提升57%,但是由于识别数据过少,量化带来了1%的精度下降。
|
||||
|
||||
速度测试基于[PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)完成。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.2.5 模型导出
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令可以将训练好的模型进行导出。
|
||||
|
||||
* 非量化模型
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/rec/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
* 量化模型
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python deploy/slim/quantization/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec_quant/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/rec_quant/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3 计算End2End指标
|
||||
|
||||
端到端指标可通过 [PaddleOCR内置脚本](../tools/end2end/readme.md) 进行计算,具体步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 导出模型
|
||||
|
||||
通过如下命令进行模型的导出。注意,量化模型导出时,需要配置eval数据集
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 检测模型
|
||||
|
||||
# 预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/infer
|
||||
|
||||
# 非量化模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/det/infer
|
||||
|
||||
# 量化模型
|
||||
python deploy/slim/quantization/export_model.py -c configs/det/ch_PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_student.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/det_quant/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/det_quant/infer \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt] \
|
||||
Eval.loader.num_workers=0
|
||||
|
||||
# 识别模型
|
||||
|
||||
# 预训练模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/student.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/infer
|
||||
|
||||
# 非量化模型
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/rec/infer
|
||||
|
||||
# 量化模型
|
||||
python deploy/slim/quantization/export_model.py -c configs/rec/PP-OCRv3/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec.yml -o \
|
||||
Global.pretrained_model=output/CCPD/rec_quant/best_accuracy.pdparams \
|
||||
Global.save_inference_dir=output/CCPD/rec_quant/infer \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.data_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR \
|
||||
Eval.dataset.label_file_list=[/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/rec.txt]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 用导出的模型对测试集进行预测
|
||||
|
||||
此处,分别使用PP-OCRv3预训练模型,fintune模型和量化模型对测试集的所有图像进行预测,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py --det_model_dir=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train/infer --rec_model_dir=models/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_train/infer --det_limit_side_len=736 --det_limit_type=min --image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test/ --draw_img_save_dir=infer/pretrain --use_dilation=true
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py --det_model_dir=output/CCPD/det/infer --rec_model_dir=output/CCPD/rec/infer --det_limit_side_len=736 --det_limit_type=min --image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test/ --draw_img_save_dir=infer/fine-tune --use_dilation=true
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune +量化,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune +量化 结果转换和评估
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_system.py --det_model_dir=output/CCPD/det_quant/infer --rec_model_dir=output/CCPD/rec_quant/infer --det_limit_side_len=736 --det_limit_type=min --image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test/ --draw_img_save_dir=infer/quant --use_dilation=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 转换label并计算指标
|
||||
|
||||
将gt和上一步保存的预测结果转换为端对端评测需要的数据格式,并根据转换后的数据进行端到端指标计算
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py --mode=gt --label_path=/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/PPOCR/test/det.txt --save_folder=end2end/gt
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 结果转换和评估
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py --mode=pred --label_path=infer/pretrain/system_results.txt --save_folder=end2end/pretrain
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py end2end/gt end2end/pretrain
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+后处理去掉多识别的`·` 结果转换和评估
|
||||
# 需手动修改后处理函数
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py --mode=pred --label_path=infer/post/system_results.txt --save_folder=end2end/post
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py end2end/gt end2end/post
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune 结果转换和评估
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py --mode=pred --label_path=infer/fine-tune/system_results.txt --save_folder=end2end/fine-tune
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py end2end/gt end2end/fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
# PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune +量化,PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune +量化 结果转换和评估
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py --mode=pred --label_path=infer/quant/system_results.txt --save_folder=end2end/quant
|
||||
python3 tools/end2end/eval_end2end.py end2end/gt end2end/quant
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
日志如下:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
The convert label saved in end2end/gt
|
||||
The convert label saved in end2end/pretrain
|
||||
start testing...
|
||||
hit, dt_count, gt_count 2 5988 5006
|
||||
character_acc: 70.42%
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_field: 2.37
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_img: 2.37
|
||||
precision: 0.03%
|
||||
recall: 0.04%
|
||||
fmeasure: 0.04%
|
||||
The convert label saved in end2end/post
|
||||
start testing...
|
||||
hit, dt_count, gt_count 4224 5988 5006
|
||||
character_acc: 81.59%
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_field: 1.47
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_img: 1.47
|
||||
precision: 70.54%
|
||||
recall: 84.38%
|
||||
fmeasure: 76.84%
|
||||
The convert label saved in end2end/fine-tune
|
||||
start testing...
|
||||
hit, dt_count, gt_count 4286 4898 5006
|
||||
character_acc: 94.16%
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_field: 0.47
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_img: 0.47
|
||||
precision: 87.51%
|
||||
recall: 85.62%
|
||||
fmeasure: 86.55%
|
||||
The convert label saved in end2end/quant
|
||||
start testing...
|
||||
hit, dt_count, gt_count 4349 4951 5006
|
||||
character_acc: 94.13%
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_field: 0.47
|
||||
avg_edit_dist_img: 0.47
|
||||
precision: 87.84%
|
||||
recall: 86.88%
|
||||
fmeasure: 87.36%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
各个方案端到端指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型| 指标 |
|
||||
|---|--------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型| 0.04% |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + 后处理去掉多识别的`·`| 78.27% |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune| 87.14% |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune+量化 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune+量化| 88.00% |
|
||||
|
||||
从结果中可以看到对预训练模型不做修改,只根据场景下的具体情况进行后处理的修改就能大幅提升端到端指标到78.27%,在CCPD数据集上进行 fine-tune 后指标进一步提升到87.14%, 在经过量化训练之后,由于检测模型的recall变高,指标进一步提升到88%。但是这个结果仍旧不符合检测模型+识别模型的真实性能(99%*94%=93%),因此我们需要对 base case 进行具体分析。
|
||||
|
||||
在之前的端到端预测结果中,可以看到很多不符合车牌标注的文字被识别出来, 因此可以进行简单的过滤来提升precision
|
||||
|
||||
为了快速评估,我们在 ` tools/end2end/convert_ppocr_label.py` 脚本的 58 行加入如下代码,对非8个字符的结果进行过滤
|
||||
```python
|
||||
if len(txt) != 8: # 车牌字符串长度为8
|
||||
continue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此外,通过可视化box可以发现有很多框都是竖直翻转之后的框,并且没有完全框住车牌边界,因此需要进行框的竖直翻转以及轻微扩大,示意图如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
修改前后个方案指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
各个方案端到端指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|模型|base|A:识别结果过滤|B:use_dilation|C:flip_box|best|
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型|0.04%|0.08%|0.02%|0.05%|0.00%(A)|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + 后处理去掉多识别的`·`|78.27%|90.84%|78.61%|79.43%|91.66%(A+B+C)|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune|87.14%|90.40%|87.66%|89.98%|92.50%(A+B+C)|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune+量化 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune+量化|88.00%|90.54%|88.50%|89.46%|92.02%(A+B+C)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
从结果中可以看到对预训练模型不做修改,只根据场景下的具体情况进行后处理的修改就能大幅提升端到端指标到91.66%,在CCPD数据集上进行 fine-tune 后指标进一步提升到92.5%, 在经过量化训练之后,指标变为92.02%。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.4 部署
|
||||
|
||||
- 基于 Paddle Inference 的python推理
|
||||
|
||||
检测模型和识别模型分别 fine-tune 并导出为inference模型之后,可以使用如下命令基于 Paddle Inference 进行端到端推理并对结果进行可视化。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/infer/predict_system.py \
|
||||
--det_model_dir=output/CCPD/det/infer/ \
|
||||
--rec_model_dir=output/CCPD/rec/infer/ \
|
||||
--image_dir="/home/aistudio/data/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test/04131106321839081-92_258-159&509_530&611-527&611_172&599_159&509_530&525-0_0_3_32_30_31_30_30-109-106.jpg" \
|
||||
--rec_image_shape=3,48,320
|
||||
```
|
||||
推理结果如下
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- 端侧部署
|
||||
|
||||
端侧部署我们采用基于 PaddleLite 的 cpp 推理。Paddle Lite是飞桨轻量化推理引擎,为手机、IOT端提供高效推理能力,并广泛整合跨平台硬件,为端侧部署及应用落地问题提供轻量化的部署方案。具体可参考 [PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.5 实验总结
|
||||
|
||||
我们分别使用PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量预训练模型在车牌数据集上进行了直接评估和 fine-tune 和 fine-tune +量化3种方案的实验,并基于[PaddleOCR lite教程](../deploy/lite/readme_ch.md)进行了速度测试,指标对比如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 检测
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|hmeans| 模型大小 | 预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|---|---|------|------------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型直接预测|76.12%|2.5M| 233ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune|99.00%| 2.5M | 233ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 fine-tune + 量化|98.91%| 1.0M | 189ms |fine-tune
|
||||
|
||||
- 识别
|
||||
|
||||
|方案| acc | 模型大小 | 预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|---|--------|-------|------------|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测| 0.00% |10.3M| 4.2ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型直接预测+后处理去掉多识别的`·`| 90.97% |10.3M| 4.2ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune| 94.54% | 10.3M | 4.2ms |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 fine-tune + 量化| 93.40% | 4.8M | 1.8ms |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 端到端指标如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|方案|fmeasure|模型大小|预测速度(lite) |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型|0.08%|12.8M|298ms|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型 + 后处理去掉多识别的`·`|91.66%|12.8M|298ms|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune|92.50%|12.8M|298ms|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量检测预训练模型+fine-tune+量化 <br> PP-OCRv3中英文超轻量识别预训练模型+fine-tune+量化|92.02%|5.80M|224ms|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**结论**
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的检测模型在未经过fine-tune的情况下,在车牌数据集上也有一定的精度,经过 fine-tune 后能够极大的提升检测效果,精度达到99%。在使用量化训练后检测模型的精度几乎无损,并且模型大小压缩60%。
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3的识别模型在未经过fine-tune的情况下,在车牌数据集上精度为0,但是经过分析可以知道,模型大部分字符都预测正确,但是会多预测一个特殊字符,去掉这个特殊字符后,精度达到90%。PP-OCRv3识别模型在经过 fine-tune 后识别精度进一步提升,达到94.4%。在使用量化训练后识别模型大小压缩53%,但是由于数据量多少,带来了1%的精度损失。
|
||||
|
||||
从端到端结果中可以看到对预训练模型不做修改,只根据场景下的具体情况进行后处理的修改就能大幅提升端到端指标到91.66%,在CCPD数据集上进行 fine-tune 后指标进一步提升到92.5%, 在经过量化训练之后,指标轻微下降到92.02%但模型大小降低54%。
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
|||
# 高精度中文场景文本识别模型SVTR
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 简介
|
||||
|
||||
PP-OCRv3是百度开源的超轻量级场景文本检测识别模型库,其中超轻量的场景中文识别模型SVTR_LCNet使用了SVTR算法结构。为了保证速度,SVTR_LCNet将SVTR模型的Local Blocks替换为LCNet,使用两层Global Blocks。在中文场景中,PP-OCRv3识别主要使用如下优化策略([详细技术报告](../doc/doc_ch/PP-OCRv3_introduction.md)):
|
||||
- GTC:Attention指导CTC训练策略;
|
||||
- TextConAug:挖掘文字上下文信息的数据增广策略;
|
||||
- TextRotNet:自监督的预训练模型;
|
||||
- UDML:联合互学习策略;
|
||||
- UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案。
|
||||
|
||||
其中 *UIM:无标注数据挖掘方案* 使用了高精度的SVTR中文模型进行无标注文件的刷库,该模型在PP-OCRv3识别的数据集上训练,精度对比如下表。
|
||||
|
||||
|中文识别算法|模型|UIM|精度|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |--- |
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3|SVTR_LCNet| w/o |78.40%|
|
||||
|PP-OCRv3|SVTR_LCNet| w |79.40%|
|
||||
|SVTR|SVTR-Tiny|-|82.50%|
|
||||
|
||||
aistudio项目链接: [高精度中文场景文本识别模型SVTR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4263032)
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. SVTR中文模型使用
|
||||
|
||||
### 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本任务基于Aistudio完成, 具体环境如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统: Linux
|
||||
- PaddlePaddle: 2.3
|
||||
- PaddleOCR: dygraph
|
||||
|
||||
下载 PaddleOCR代码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone -b dygraph https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装依赖库
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 快速使用
|
||||
|
||||
获取SVTR中文模型文件,请扫码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取全部OCR垂类模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/dd721099bd50478f9d5fb13d8dd00fad69c22d6848244fd3a1d3980d7fefc63e" width = "150" height = "150" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 解压模型文件
|
||||
tar xf svtr_ch_high_accuracy.tar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
预测中文文本,以下图为例:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
预测命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# CPU预测
|
||||
python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg Global.use_gpu=False
|
||||
|
||||
# GPU预测
|
||||
#python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.infer_img=./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg Global.use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到最后打印结果为
|
||||
- result: 韩国小馆 0.9853458404541016
|
||||
|
||||
0.9853458404541016为预测置信度。
|
||||
|
||||
### 推理模型导出与预测
|
||||
|
||||
inference 模型(paddle.jit.save保存的模型) 一般是模型训练,把模型结构和模型参数保存在文件中的固化模型,多用于预测部署场景。 训练过程中保存的模型是checkpoints模型,保存的只有模型的参数,多用于恢复训练等。 与checkpoints模型相比,inference 模型会额外保存模型的结构信息,在预测部署、加速推理上性能优越,灵活方便,适合于实际系统集成。
|
||||
|
||||
运行识别模型转inference模型命令,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rec/rec_svtrnet_ch.yml -o Global.pretrained_model=./svtr_ch_high_accuracy/best_accuracy Global.save_inference_dir=./inference/svtr_ch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
转换成功后,在目录下有三个文件:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
inference/svtr_ch/
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams # 识别inference模型的参数文件
|
||||
├── inference.pdiparams.info # 识别inference模型的参数信息,可忽略
|
||||
└── inference.pdmodel # 识别inference模型的program文件
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
inference模型预测,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# CPU预测
|
||||
python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg" --rec_algorithm='SVTR' --rec_model_dir=./inference/svtr_ch/ --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' --rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt --use_gpu=False
|
||||
|
||||
# GPU预测
|
||||
#python3 tools/infer/predict_rec.py --image_dir="./doc/imgs_words/ch/word_1.jpg" --rec_algorithm='SVTR' --rec_model_dir=./inference/svtr_ch/ --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' --rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt --use_gpu=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用SVTR算法时,需要指定--rec_algorithm='SVTR'
|
||||
- 如果使用自定义字典训练的模型,需要将--rec_char_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt修改为自定义的字典
|
||||
- --rec_image_shape='3, 32, 320' 该参数不能去掉
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
*.html linguist-language=python
|
||||
*.ipynb linguist-language=python
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
|||
.DS_Store
|
||||
*.pth
|
||||
*.pyc
|
||||
*.pyo
|
||||
*.log
|
||||
*.tmp
|
||||
*.pkl
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
.idea/
|
||||
output/
|
||||
test/*.jpg
|
||||
datasets/
|
||||
index/
|
||||
train_log/
|
||||
log/
|
||||
profiling_log/
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
|||
Apache License
|
||||
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
||||
|
||||
1. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
||||
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
||||
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
||||
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
||||
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
||||
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
||||
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
||||
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
||||
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
||||
|
||||
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
||||
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
||||
source, and configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
||||
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
||||
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
||||
and conversions to other media types.
|
||||
|
||||
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
||||
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
||||
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
||||
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
||||
|
||||
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
||||
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
||||
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
||||
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
||||
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
||||
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
||||
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
||||
|
||||
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
||||
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
||||
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
||||
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
||||
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
||||
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
||||
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
||||
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
||||
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
||||
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
||||
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
||||
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
||||
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
||||
|
||||
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
||||
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
||||
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
||||
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
||||
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
||||
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
||||
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
||||
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
||||
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
||||
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
||||
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
||||
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
||||
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
||||
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
||||
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
||||
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
||||
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
||||
meet the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
||||
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
||||
|
||||
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
||||
stating that You changed the files; and
|
||||
|
||||
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
||||
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
||||
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
||||
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
||||
the Derivative Works; and
|
||||
|
||||
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
||||
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
||||
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
||||
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
||||
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
||||
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
||||
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
||||
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
||||
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
||||
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
||||
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
||||
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
||||
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
||||
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
||||
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
||||
as modifying the License.
|
||||
|
||||
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
||||
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
||||
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
||||
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
||||
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
||||
the conditions stated in this License.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
||||
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
||||
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
||||
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
||||
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
||||
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
||||
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
||||
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
||||
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
||||
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
||||
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
||||
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
||||
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
||||
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
||||
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
||||
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
||||
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
||||
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
||||
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
||||
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
||||
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
||||
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
||||
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
||||
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
||||
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
||||
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
||||
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
||||
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
||||
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
||||
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
||||
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
||||
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
||||
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
||||
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
||||
|
||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
||||
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
|
||||
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
||||
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
||||
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
||||
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
||||
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
||||
identification within third-party archives.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
|||
# Real-time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization
|
||||
|
||||
**note**: some code is inherited from [WenmuZhou/DBNet.pytorch](https://github.com/WenmuZhou/DBNet.pytorch)
|
||||
|
||||
[中文解读](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94677957)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## update
|
||||
2020-06-07: 添加灰度图训练,训练灰度图时需要在配置里移除`dataset.args.transforms.Normalize`
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Using Conda
|
||||
```
|
||||
conda env create -f environment.yml
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/WenmuZhou/DBNet.paddle.git
|
||||
cd DBNet.paddle/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
## Install Manually
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda create -n dbnet python=3.6
|
||||
conda activate dbnet
|
||||
|
||||
conda install ipython pip
|
||||
|
||||
# python dependencies
|
||||
pip install -r requirement.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# clone repo
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/WenmuZhou/DBNet.paddle.git
|
||||
cd DBNet.paddle/
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
* paddlepaddle 2.4+
|
||||
|
||||
## Download
|
||||
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Preparation
|
||||
|
||||
Training data: prepare a text `train.txt` in the following format, use '\t' as a separator
|
||||
```
|
||||
./datasets/train/img/001.jpg ./datasets/train/gt/001.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Validation data: prepare a text `test.txt` in the following format, use '\t' as a separator
|
||||
```
|
||||
./datasets/test/img/001.jpg ./datasets/test/gt/001.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Store images in the `img` folder
|
||||
- Store groundtruth in the `gt` folder
|
||||
|
||||
The groundtruth can be `.txt` files, with the following format:
|
||||
```
|
||||
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, annotation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
1. config the `dataset['train']['dataset'['data_path']'`,`dataset['validate']['dataset'['data_path']`in [config/icdar2015_resnet18_fpn_DBhead_polyLR.yaml](cconfig/icdar2015_resnet18_fpn_DBhead_polyLR.yaml)
|
||||
* . single gpu train
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash singlel_gpu_train.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
* . Multi-gpu training
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash multi_gpu_train.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Test
|
||||
|
||||
[eval.py](tools/eval.py) is used to test model on test dataset
|
||||
|
||||
1. config `model_path` in [eval.sh](eval.sh)
|
||||
2. use following script to test
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash eval.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Predict
|
||||
[predict.py](tools/predict.py) Can be used to inference on all images in a folder
|
||||
1. config `model_path`,`input_folder`,`output_folder` in [predict.sh](predict.sh)
|
||||
2. use following script to predict
|
||||
```
|
||||
bash predict.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can change the `model_path` in the `predict.sh` file to your model location.
|
||||
|
||||
tips: if result is not good, you can change `thre` in [predict.sh](predict.sh)
|
||||
|
||||
## Export Model
|
||||
|
||||
[export_model.py](tools/export_model.py) Can be used to inference on all images in a folder
|
||||
|
||||
use following script to export inference model
|
||||
```
|
||||
python tools/export_model.py --config_file config/icdar2015_resnet50_FPN_DBhead_polyLR.yaml -o trainer.resume_checkpoint=model_best.pth trainer.output_dir=output/infer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Paddle Inference infer
|
||||
|
||||
[infer.py](tools/infer.py) Can be used to inference on all images in a folder
|
||||
|
||||
use following script to export inference model
|
||||
```
|
||||
python tools/infer.py --model-dir=output/infer/ --img-path imgs/paper/db.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<h2 id="Performance">Performance</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
### [ICDAR 2015](http://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=4)
|
||||
only train on ICDAR2015 dataset
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | image size (short size) |learning rate | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F-measure (%) | FPS |
|
||||
|:--------------------------:|:-------:|:--------:|:--------:|:------------:|:---------------:|:-----:|
|
||||
| ImageNet-resnet50-FPN-DBHead(torch) |736 |1e-3|90.19 | 78.14 | 83.88 | 27 |
|
||||
| ImageNet-resnet50-FPN-DBHead(paddle) |736 |1e-3| 89.47 | 79.03 | 83.92 | 27 |
|
||||
| ImageNet-resnet50-FPN-DBHead(paddle_amp) |736 |1e-3| 88.62 | 79.95 | 84.06 | 27 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### examples
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### reference
|
||||
1. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08947.pdf
|
||||
2. https://github.com/WenmuZhou/DBNet.pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
**If this repository helps you,please star it. Thanks.**
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
from .base_trainer import BaseTrainer
|
||||
from .base_dataset import BaseDataSet
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
|||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
# @Time : 2019/12/4 13:12
|
||||
# @Author : zhoujun
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
from paddle.io import Dataset
|
||||
from data_loader.modules import *
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseDataSet(Dataset):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
data_path: str,
|
||||
img_mode,
|
||||
pre_processes,
|
||||
filter_keys,
|
||||
ignore_tags,
|
||||
transform=None,
|
||||
target_transform=None):
|
||||
assert img_mode in ['RGB', 'BRG', 'GRAY']
|
||||
self.ignore_tags = ignore_tags
|
||||
self.data_list = self.load_data(data_path)
|
||||
item_keys = [
|
||||
'img_path', 'img_name', 'text_polys', 'texts', 'ignore_tags'
|
||||
]
|
||||
for item in item_keys:
|
||||
assert item in self.data_list[
|
||||
0], 'data_list from load_data must contains {}'.format(
|
||||
item_keys)
|
||||
self.img_mode = img_mode
|
||||
self.filter_keys = filter_keys
|
||||
self.transform = transform
|
||||
self.target_transform = target_transform
|
||||
self._init_pre_processes(pre_processes)
|
||||
|
||||
def _init_pre_processes(self, pre_processes):
|
||||
self.aug = []
|
||||
if pre_processes is not None:
|
||||
for aug in pre_processes:
|
||||
if 'args' not in aug:
|
||||
args = {}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
args = aug['args']
|
||||
if isinstance(args, dict):
|
||||
cls = eval(aug['type'])(**args)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cls = eval(aug['type'])(args)
|
||||
self.aug.append(cls)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_data(self, data_path: str) -> list:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
把数据加载为一个list:
|
||||
:params data_path: 存储数据的文件夹或者文件
|
||||
return a dict ,包含了,'img_path','img_name','text_polys','texts','ignore_tags'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def apply_pre_processes(self, data):
|
||||
for aug in self.aug:
|
||||
data = aug(data)
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, index):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = copy.deepcopy(self.data_list[index])
|
||||
im = cv2.imread(data['img_path'], 1
|
||||
if self.img_mode != 'GRAY' else 0)
|
||||
if self.img_mode == 'RGB':
|
||||
im = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
|
||||
data['img'] = im
|
||||
data['shape'] = [im.shape[0], im.shape[1]]
|
||||
data = self.apply_pre_processes(data)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.transform:
|
||||
data['img'] = self.transform(data['img'])
|
||||
data['text_polys'] = data['text_polys'].tolist()
|
||||
if len(self.filter_keys):
|
||||
data_dict = {}
|
||||
for k, v in data.items():
|
||||
if k not in self.filter_keys:
|
||||
data_dict[k] = v
|
||||
return data_dict
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return data
|
||||
except:
|
||||
return self.__getitem__(np.random.randint(self.__len__()))
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.data_list)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,250 @@
|
|||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
# @Time : 2019/8/23 21:50
|
||||
# @Author : zhoujun
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import pathlib
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
from pprint import pformat
|
||||
|
||||
import anyconfig
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from paddle.jit import to_static
|
||||
from paddle.static import InputSpec
|
||||
|
||||
from utils import setup_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseTrainer:
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
config,
|
||||
model,
|
||||
criterion,
|
||||
train_loader,
|
||||
validate_loader,
|
||||
metric_cls,
|
||||
post_process=None):
|
||||
config['trainer']['output_dir'] = os.path.join(
|
||||
str(pathlib.Path(os.path.abspath(__name__)).parent),
|
||||
config['trainer']['output_dir'])
|
||||
config['name'] = config['name'] + '_' + model.name
|
||||
self.save_dir = config['trainer']['output_dir']
|
||||
self.checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(self.save_dir, 'checkpoint')
|
||||
|
||||
os.makedirs(self.checkpoint_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
self.global_step = 0
|
||||
self.start_epoch = 0
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.criterion = criterion
|
||||
# logger and tensorboard
|
||||
self.visualdl_enable = self.config['trainer'].get('visual_dl', False)
|
||||
self.epochs = self.config['trainer']['epochs']
|
||||
self.log_iter = self.config['trainer']['log_iter']
|
||||
if paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
anyconfig.dump(config, os.path.join(self.save_dir, 'config.yaml'))
|
||||
self.logger = setup_logger(os.path.join(self.save_dir, 'train.log'))
|
||||
self.logger_info(pformat(self.config))
|
||||
|
||||
self.model = self.apply_to_static(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# device
|
||||
if paddle.device.cuda.device_count(
|
||||
) > 0 and paddle.device.is_compiled_with_cuda():
|
||||
self.with_cuda = True
|
||||
random.seed(self.config['trainer']['seed'])
|
||||
np.random.seed(self.config['trainer']['seed'])
|
||||
paddle.seed(self.config['trainer']['seed'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.with_cuda = False
|
||||
self.logger_info('train with and paddle {}'.format(paddle.__version__))
|
||||
# metrics
|
||||
self.metrics = {
|
||||
'recall': 0,
|
||||
'precision': 0,
|
||||
'hmean': 0,
|
||||
'train_loss': float('inf'),
|
||||
'best_model_epoch': 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
self.train_loader = train_loader
|
||||
if validate_loader is not None:
|
||||
assert post_process is not None and metric_cls is not None
|
||||
self.validate_loader = validate_loader
|
||||
self.post_process = post_process
|
||||
self.metric_cls = metric_cls
|
||||
self.train_loader_len = len(train_loader)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.validate_loader is not None:
|
||||
self.logger_info(
|
||||
'train dataset has {} samples,{} in dataloader, validate dataset has {} samples,{} in dataloader'.
|
||||
format(
|
||||
len(self.train_loader.dataset), self.train_loader_len,
|
||||
len(self.validate_loader.dataset),
|
||||
len(self.validate_loader)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.logger_info(
|
||||
'train dataset has {} samples,{} in dataloader'.format(
|
||||
len(self.train_loader.dataset), self.train_loader_len))
|
||||
|
||||
self._initialize_scheduler()
|
||||
|
||||
self._initialize_optimizer()
|
||||
|
||||
# resume or finetune
|
||||
if self.config['trainer']['resume_checkpoint'] != '':
|
||||
self._load_checkpoint(
|
||||
self.config['trainer']['resume_checkpoint'], resume=True)
|
||||
elif self.config['trainer']['finetune_checkpoint'] != '':
|
||||
self._load_checkpoint(
|
||||
self.config['trainer']['finetune_checkpoint'], resume=False)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.visualdl_enable and paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
from visualdl import LogWriter
|
||||
self.writer = LogWriter(self.save_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# 混合精度训练
|
||||
self.amp = self.config.get('amp', None)
|
||||
if self.amp == 'None':
|
||||
self.amp = None
|
||||
if self.amp:
|
||||
self.amp['scaler'] = paddle.amp.GradScaler(
|
||||
init_loss_scaling=self.amp.get("scale_loss", 1024),
|
||||
use_dynamic_loss_scaling=self.amp.get(
|
||||
'use_dynamic_loss_scaling', True))
|
||||
self.model, self.optimizer = paddle.amp.decorate(
|
||||
models=self.model,
|
||||
optimizers=self.optimizer,
|
||||
level=self.amp.get('amp_level', 'O2'))
|
||||
|
||||
# 分布式训练
|
||||
if paddle.device.cuda.device_count() > 1:
|
||||
self.model = paddle.DataParallel(self.model)
|
||||
# make inverse Normalize
|
||||
self.UN_Normalize = False
|
||||
for t in self.config['dataset']['train']['dataset']['args'][
|
||||
'transforms']:
|
||||
if t['type'] == 'Normalize':
|
||||
self.normalize_mean = t['args']['mean']
|
||||
self.normalize_std = t['args']['std']
|
||||
self.UN_Normalize = True
|
||||
|
||||
def apply_to_static(self, model):
|
||||
support_to_static = self.config['trainer'].get('to_static', False)
|
||||
if support_to_static:
|
||||
specs = None
|
||||
print('static')
|
||||
specs = [InputSpec([None, 3, -1, -1])]
|
||||
model = to_static(model, input_spec=specs)
|
||||
self.logger_info(
|
||||
"Successfully to apply @to_static with specs: {}".format(specs))
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def train(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Full training logic
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for epoch in range(self.start_epoch + 1, self.epochs + 1):
|
||||
self.epoch_result = self._train_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
self._on_epoch_finish()
|
||||
if paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0 and self.visualdl_enable:
|
||||
self.writer.close()
|
||||
self._on_train_finish()
|
||||
|
||||
def _train_epoch(self, epoch):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Training logic for an epoch
|
||||
|
||||
:param epoch: Current epoch number
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def _eval(self, epoch):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
eval logic for an epoch
|
||||
|
||||
:param epoch: Current epoch number
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def _on_epoch_finish(self):
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def _on_train_finish(self):
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def _save_checkpoint(self, epoch, file_name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Saving checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
:param epoch: current epoch number
|
||||
:param log: logging information of the epoch
|
||||
:param save_best: if True, rename the saved checkpoint to 'model_best.pth.tar'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
state_dict = self.model.state_dict()
|
||||
state = {
|
||||
'epoch': epoch,
|
||||
'global_step': self.global_step,
|
||||
'state_dict': state_dict,
|
||||
'optimizer': self.optimizer.state_dict(),
|
||||
'config': self.config,
|
||||
'metrics': self.metrics
|
||||
}
|
||||
filename = os.path.join(self.checkpoint_dir, file_name)
|
||||
paddle.save(state, filename)
|
||||
|
||||
def _load_checkpoint(self, checkpoint_path, resume):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Resume from saved checkpoints
|
||||
:param checkpoint_path: Checkpoint path to be resumed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger_info("Loading checkpoint: {} ...".format(checkpoint_path))
|
||||
checkpoint = paddle.load(checkpoint_path)
|
||||
self.model.set_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
|
||||
if resume:
|
||||
self.global_step = checkpoint['global_step']
|
||||
self.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
|
||||
self.config['lr_scheduler']['args']['last_epoch'] = self.start_epoch
|
||||
# self.scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['scheduler'])
|
||||
self.optimizer.set_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
|
||||
if 'metrics' in checkpoint:
|
||||
self.metrics = checkpoint['metrics']
|
||||
self.logger_info("resume from checkpoint {} (epoch {})".format(
|
||||
checkpoint_path, self.start_epoch))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.logger_info("finetune from checkpoint {}".format(
|
||||
checkpoint_path))
|
||||
|
||||
def _initialize(self, name, module, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
module_name = self.config[name]['type']
|
||||
module_args = self.config[name].get('args', {})
|
||||
assert all([k not in module_args for k in kwargs
|
||||
]), 'Overwriting kwargs given in config file is not allowed'
|
||||
module_args.update(kwargs)
|
||||
return getattr(module, module_name)(*args, **module_args)
|
||||
|
||||
def _initialize_scheduler(self):
|
||||
self.lr_scheduler = self._initialize('lr_scheduler',
|
||||
paddle.optimizer.lr)
|
||||
|
||||
def _initialize_optimizer(self):
|
||||
self.optimizer = self._initialize(
|
||||
'optimizer',
|
||||
paddle.optimizer,
|
||||
parameters=self.model.parameters(),
|
||||
learning_rate=self.lr_scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
def inverse_normalize(self, batch_img):
|
||||
if self.UN_Normalize:
|
||||
batch_img[:, 0, :, :] = batch_img[:, 0, :, :] * self.normalize_std[
|
||||
0] + self.normalize_mean[0]
|
||||
batch_img[:, 1, :, :] = batch_img[:, 1, :, :] * self.normalize_std[
|
||||
1] + self.normalize_mean[1]
|
||||
batch_img[:, 2, :, :] = batch_img[:, 2, :, :] * self.normalize_std[
|
||||
2] + self.normalize_mean[2]
|
||||
|
||||
def logger_info(self, s):
|
||||
if paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
self.logger.info(s)
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
type: SynthTextDataset # 数据集类型
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path: ''# SynthTextDataset 根目录
|
||||
pre_processes: # 数据的预处理过程,包含augment和标签制作
|
||||
- type: IaaAugment # 使用imgaug进行变换
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- {'type':Fliplr, 'args':{'p':0.5}}
|
||||
- {'type': Affine, 'args':{'rotate':[-10,10]}}
|
||||
- {'type':Resize,'args':{'size':[0.5,3]}}
|
||||
- type: EastRandomCropData
|
||||
args:
|
||||
size: [640,640]
|
||||
max_tries: 50
|
||||
keep_ratio: true
|
||||
- type: MakeBorderMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
- type: MakeShrinkMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
min_text_size: 8
|
||||
transforms: # 对图片进行的变换方式
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
filter_keys: ['img_path','img_name','text_polys','texts','ignore_tags','shape'] # 返回数据之前,从数据字典里删除的key
|
||||
ignore_tags: ['*', '###']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 0
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/SynthText.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 10
|
||||
show_images_iter: 50
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path: ./datasets/SynthText
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 2
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
type: ICDAR2015Dataset # 数据集类型
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path: # 一个存放 img_path \t gt_path的文件
|
||||
- ''
|
||||
pre_processes: # 数据的预处理过程,包含augment和标签制作
|
||||
- type: IaaAugment # 使用imgaug进行变换
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- {'type':Fliplr, 'args':{'p':0.5}}
|
||||
- {'type': Affine, 'args':{'rotate':[-10,10]}}
|
||||
- {'type':Resize,'args':{'size':[0.5,3]}}
|
||||
- type: EastRandomCropData
|
||||
args:
|
||||
size: [640,640]
|
||||
max_tries: 50
|
||||
keep_ratio: true
|
||||
- type: MakeBorderMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
thresh_min: 0.3
|
||||
thresh_max: 0.7
|
||||
- type: MakeShrinkMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
min_text_size: 8
|
||||
transforms: # 对图片进行的变换方式
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
filter_keys: [img_path,img_name,text_polys,texts,ignore_tags,shape] # 返回数据之前,从数据字典里删除的key
|
||||
ignore_tags: ['*', '###']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 0
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
type: ICDAR2015Dataset
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ''
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
filter_keys: []
|
||||
ignore_tags: ['*', '###']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 0
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/icdar2015.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: deformable_resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 10
|
||||
show_images_iter: 50
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.txt
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.txt
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/icdar2015.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 10
|
||||
show_images_iter: 50
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.txt
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.txt
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/icdar2015.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: StepLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
step_size: 10
|
||||
gama: 0.8
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 500
|
||||
log_iter: 10
|
||||
show_images_iter: 50
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.txt
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.txt
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/icdar2015.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnet50
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: Polynomial
|
||||
args:
|
||||
learning_rate: 0.001
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 10
|
||||
show_images_iter: 50
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output/fp16_o2
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.txt
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 16
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.txt
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
type: DetDataset # 数据集类型
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path: # 一个存放 img_path \t gt_path的文件
|
||||
- ''
|
||||
pre_processes: # 数据的预处理过程,包含augment和标签制作
|
||||
- type: IaaAugment # 使用imgaug进行变换
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- {'type':Fliplr, 'args':{'p':0.5}}
|
||||
- {'type': Affine, 'args':{'rotate':[-10,10]}}
|
||||
- {'type':Resize,'args':{'size':[0.5,3]}}
|
||||
- type: EastRandomCropData
|
||||
args:
|
||||
size: [640,640]
|
||||
max_tries: 50
|
||||
keep_ratio: true
|
||||
- type: MakeBorderMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
thresh_min: 0.3
|
||||
thresh_max: 0.7
|
||||
- type: MakeShrinkMap
|
||||
args:
|
||||
shrink_ratio: 0.4
|
||||
min_text_size: 8
|
||||
transforms: # 对图片进行的变换方式
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
filter_keys: [img_path,img_name,text_polys,texts,ignore_tags,shape] # 返回数据之前,从数据字典里删除的key
|
||||
ignore_tags: ['*', '###']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 0
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
type: DetDataset
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ''
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
transforms:
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false # 是否加载字符级标注
|
||||
expand_one_char: false # 是否对只有一个字符的框进行宽度扩充,扩充后w = w+h
|
||||
filter_keys: []
|
||||
ignore_tags: ['*', '###']
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 0
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/open_dataset.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: deformable_resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 1
|
||||
show_images_iter: 1
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.json
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 2
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.json
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/open_dataset.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnest50
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 1
|
||||
show_images_iter: 1
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.json
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 2
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.json
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
|||
name: DBNet
|
||||
base: ['config/open_dataset.yaml']
|
||||
arch:
|
||||
type: Model
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
type: resnet18
|
||||
pretrained: true
|
||||
neck:
|
||||
type: FPN
|
||||
inner_channels: 256
|
||||
head:
|
||||
type: DBHead
|
||||
out_channels: 2
|
||||
k: 50
|
||||
post_processing:
|
||||
type: SegDetectorRepresenter
|
||||
args:
|
||||
thresh: 0.3
|
||||
box_thresh: 0.7
|
||||
max_candidates: 1000
|
||||
unclip_ratio: 1.5 # from paper
|
||||
metric:
|
||||
type: QuadMetric
|
||||
args:
|
||||
is_output_polygon: false
|
||||
loss:
|
||||
type: DBLoss
|
||||
alpha: 1
|
||||
beta: 10
|
||||
ohem_ratio: 3
|
||||
optimizer:
|
||||
type: Adam
|
||||
args:
|
||||
lr: 0.001
|
||||
weight_decay: 0
|
||||
amsgrad: true
|
||||
lr_scheduler:
|
||||
type: WarmupPolyLR
|
||||
args:
|
||||
warmup_epoch: 3
|
||||
trainer:
|
||||
seed: 2
|
||||
epochs: 1200
|
||||
log_iter: 1
|
||||
show_images_iter: 1
|
||||
resume_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
finetune_checkpoint: ''
|
||||
output_dir: output
|
||||
visual_dl: false
|
||||
amp:
|
||||
scale_loss: 1024
|
||||
amp_level: O2
|
||||
custom_white_list: []
|
||||
custom_black_list: ['exp', 'sigmoid', 'concat']
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
train:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/train.json
|
||||
transforms: # 对图片进行的变换方式
|
||||
- type: ToTensor
|
||||
args: {}
|
||||
- type: Normalize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
|
||||
std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 2
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ''
|
||||
validate:
|
||||
dataset:
|
||||
args:
|
||||
data_path:
|
||||
- ./datasets/test.json
|
||||
pre_processes:
|
||||
- type: ResizeShortSize
|
||||
args:
|
||||
short_size: 736
|
||||
resize_text_polys: false
|
||||
img_mode: RGB
|
||||
load_char_annotation: false
|
||||
expand_one_char: false
|
||||
loader:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
shuffle: true
|
||||
num_workers: 6
|
||||
collate_fn: ICDARCollectFN
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
|||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
# @Time : 2019/8/23 21:52
|
||||
# @Author : zhoujun
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import paddle
|
||||
from paddle.io import DataLoader, DistributedBatchSampler, BatchSampler
|
||||
|
||||
from paddle.vision import transforms
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_dataset(data_path, module_name, transform, dataset_args):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
获取训练dataset
|
||||
:param data_path: dataset文件列表,每个文件内以如下格式存储 ‘path/to/img\tlabel’
|
||||
:param module_name: 所使用的自定义dataset名称,目前只支持data_loaders.ImageDataset
|
||||
:param transform: 该数据集使用的transforms
|
||||
:param dataset_args: module_name的参数
|
||||
:return: 如果data_path列表不为空,返回对于的ConcatDataset对象,否则None
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from . import dataset
|
||||
s_dataset = getattr(dataset, module_name)(transform=transform,
|
||||
data_path=data_path,
|
||||
**dataset_args)
|
||||
return s_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_transforms(transforms_config):
|
||||
tr_list = []
|
||||
for item in transforms_config:
|
||||
if 'args' not in item:
|
||||
args = {}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
args = item['args']
|
||||
cls = getattr(transforms, item['type'])(**args)
|
||||
tr_list.append(cls)
|
||||
tr_list = transforms.Compose(tr_list)
|
||||
return tr_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ICDARCollectFN:
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, batch):
|
||||
data_dict = {}
|
||||
to_tensor_keys = []
|
||||
for sample in batch:
|
||||
for k, v in sample.items():
|
||||
if k not in data_dict:
|
||||
data_dict[k] = []
|
||||
if isinstance(v, (np.ndarray, paddle.Tensor, PIL.Image.Image)):
|
||||
if k not in to_tensor_keys:
|
||||
to_tensor_keys.append(k)
|
||||
data_dict[k].append(v)
|
||||
for k in to_tensor_keys:
|
||||
data_dict[k] = paddle.stack(data_dict[k], 0)
|
||||
return data_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_dataloader(module_config, distributed=False):
|
||||
if module_config is None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
config = copy.deepcopy(module_config)
|
||||
dataset_args = config['dataset']['args']
|
||||
if 'transforms' in dataset_args:
|
||||
img_transfroms = get_transforms(dataset_args.pop('transforms'))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img_transfroms = None
|
||||
# 创建数据集
|
||||
dataset_name = config['dataset']['type']
|
||||
data_path = dataset_args.pop('data_path')
|
||||
if data_path == None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
data_path = [x for x in data_path if x is not None]
|
||||
if len(data_path) == 0:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
if 'collate_fn' not in config['loader'] or config['loader'][
|
||||
'collate_fn'] is None or len(config['loader']['collate_fn']) == 0:
|
||||
config['loader']['collate_fn'] = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
config['loader']['collate_fn'] = eval(config['loader']['collate_fn'])()
|
||||
|
||||
_dataset = get_dataset(
|
||||
data_path=data_path,
|
||||
module_name=dataset_name,
|
||||
transform=img_transfroms,
|
||||
dataset_args=dataset_args)
|
||||
sampler = None
|
||||
if distributed:
|
||||
# 3)使用DistributedSampler
|
||||
batch_sampler = DistributedBatchSampler(
|
||||
dataset=_dataset,
|
||||
batch_size=config['loader'].pop('batch_size'),
|
||||
shuffle=config['loader'].pop('shuffle'))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
batch_sampler = BatchSampler(
|
||||
dataset=_dataset,
|
||||
batch_size=config['loader'].pop('batch_size'),
|
||||
shuffle=config['loader'].pop('shuffle'))
|
||||
loader = DataLoader(
|
||||
dataset=_dataset, batch_sampler=batch_sampler, **config['loader'])
|
||||
return loader
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
|||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
# @Time : 2019/8/23 21:54
|
||||
# @Author : zhoujun
|
||||
import pathlib
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import scipy.io as sio
|
||||
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
from base import BaseDataSet
|
||||
from utils import order_points_clockwise, get_datalist, load, expand_polygon
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ICDAR2015Dataset(BaseDataSet):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
data_path: str,
|
||||
img_mode,
|
||||
pre_processes,
|
||||
filter_keys,
|
||||
ignore_tags,
|
||||
transform=None,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(data_path, img_mode, pre_processes, filter_keys,
|
||||
ignore_tags, transform)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_data(self, data_path: str) -> list:
|
||||
data_list = get_datalist(data_path)
|
||||
t_data_list = []
|
||||
for img_path, label_path in data_list:
|
||||
data = self._get_annotation(label_path)
|
||||
if len(data['text_polys']) > 0:
|
||||
item = {
|
||||
'img_path': img_path,
|
||||
'img_name': pathlib.Path(img_path).stem
|
||||
}
|
||||
item.update(data)
|
||||
t_data_list.append(item)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('there is no suit bbox in {}'.format(label_path))
|
||||
return t_data_list
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_annotation(self, label_path: str) -> dict:
|
||||
boxes = []
|
||||
texts = []
|
||||
ignores = []
|
||||
with open(label_path, encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as f:
|
||||
for line in f.readlines():
|
||||
params = line.strip().strip('\ufeff').strip(
|
||||
'\xef\xbb\xbf').split(',')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
box = order_points_clockwise(
|
||||
np.array(list(map(float, params[:8]))).reshape(-1, 2))
|
||||
if cv2.contourArea(box) > 0:
|
||||
boxes.append(box)
|
||||
label = params[8]
|
||||
texts.append(label)
|
||||
ignores.append(label in self.ignore_tags)
|
||||
except:
|
||||
print('load label failed on {}'.format(label_path))
|
||||
data = {
|
||||
'text_polys': np.array(boxes),
|
||||
'texts': texts,
|
||||
'ignore_tags': ignores,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DetDataset(BaseDataSet):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
data_path: str,
|
||||
img_mode,
|
||||
pre_processes,
|
||||
filter_keys,
|
||||
ignore_tags,
|
||||
transform=None,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
self.load_char_annotation = kwargs['load_char_annotation']
|
||||
self.expand_one_char = kwargs['expand_one_char']
|
||||
super().__init__(data_path, img_mode, pre_processes, filter_keys,
|
||||
ignore_tags, transform)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_data(self, data_path: str) -> list:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
从json文件中读取出 文本行的坐标和gt,字符的坐标和gt
|
||||
:param data_path:
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
data_list = []
|
||||
for path in data_path:
|
||||
content = load(path)
|
||||
for gt in tqdm(
|
||||
content['data_list'], desc='read file {}'.format(path)):
|
||||
img_path = os.path.join(content['data_root'], gt['img_name'])
|
||||
polygons = []
|
||||
texts = []
|
||||
illegibility_list = []
|
||||
language_list = []
|
||||
for annotation in gt['annotations']:
|
||||
if len(annotation['polygon']) == 0 or len(annotation[
|
||||
'text']) == 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if len(annotation['text']) > 1 and self.expand_one_char:
|
||||
annotation['polygon'] = expand_polygon(annotation[
|
||||
'polygon'])
|
||||
polygons.append(annotation['polygon'])
|
||||
texts.append(annotation['text'])
|
||||
illegibility_list.append(annotation['illegibility'])
|
||||
language_list.append(annotation['language'])
|
||||
if self.load_char_annotation:
|
||||
for char_annotation in annotation['chars']:
|
||||
if len(char_annotation['polygon']) == 0 or len(
|
||||
char_annotation['char']) == 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
polygons.append(char_annotation['polygon'])
|
||||
texts.append(char_annotation['char'])
|
||||
illegibility_list.append(char_annotation[
|
||||
'illegibility'])
|
||||
language_list.append(char_annotation['language'])
|
||||
data_list.append({
|
||||
'img_path': img_path,
|
||||
'img_name': gt['img_name'],
|
||||
'text_polys': np.array(polygons),
|
||||
'texts': texts,
|
||||
'ignore_tags': illegibility_list
|
||||
})
|
||||
return data_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SynthTextDataset(BaseDataSet):
|
||||
def __init__(self,
|
||||
data_path: str,
|
||||
img_mode,
|
||||
pre_processes,
|
||||
filter_keys,
|
||||
transform=None,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
self.transform = transform
|
||||
self.dataRoot = pathlib.Path(data_path)
|
||||
if not self.dataRoot.exists():
|
||||
raise FileNotFoundError('Dataset folder is not exist.')
|
||||
|
||||
self.targetFilePath = self.dataRoot / 'gt.mat'
|
||||
if not self.targetFilePath.exists():
|
||||
raise FileExistsError('Target file is not exist.')
|
||||
targets = {}
|
||||
sio.loadmat(
|
||||
self.targetFilePath,
|
||||
targets,
|
||||
squeeze_me=True,
|
||||
struct_as_record=False,
|
||||
variable_names=['imnames', 'wordBB', 'txt'])
|
||||
|
||||
self.imageNames = targets['imnames']
|
||||
self.wordBBoxes = targets['wordBB']
|
||||
self.transcripts = targets['txt']
|
||||
super().__init__(data_path, img_mode, pre_processes, filter_keys,
|
||||
transform)
|
||||
|
||||
def load_data(self, data_path: str) -> list:
|
||||
t_data_list = []
|
||||
for imageName, wordBBoxes, texts in zip(
|
||||
self.imageNames, self.wordBBoxes, self.transcripts):
|
||||
item = {}
|
||||
wordBBoxes = np.expand_dims(
|
||||
wordBBoxes, axis=2) if (wordBBoxes.ndim == 2) else wordBBoxes
|
||||
_, _, numOfWords = wordBBoxes.shape
|
||||
text_polys = wordBBoxes.reshape(
|
||||
[8, numOfWords], order='F').T # num_words * 8
|
||||
text_polys = text_polys.reshape(numOfWords, 4,
|
||||
2) # num_of_words * 4 * 2
|
||||
transcripts = [word for line in texts for word in line.split()]
|
||||
if numOfWords != len(transcripts):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
item['img_path'] = str(self.dataRoot / imageName)
|
||||
item['img_name'] = (self.dataRoot / imageName).stem
|
||||
item['text_polys'] = text_polys
|
||||
item['texts'] = transcripts
|
||||
item['ignore_tags'] = [x in self.ignore_tags for x in transcripts]
|
||||
t_data_list.append(item)
|
||||
return t_data_list
|
||||